


Biofeedback Therapy Training Guide
Biofeedback is a scientifically based method that uses monitoring instruments to measure and provide feedback information about physiological parameters of the body that are out of conscious control: muscle tension, heart rate, breath, sweat responses, skin temperature, or brain activity. Terms associated with therapeutic biofeedback or biofeedback therapy training are also viewed as a mind-body therapy method used in complementary and alternative medicine. Biofeedback is essential to understanding the relationship between physical state and thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Upon measurement parameters, biofeedback training has various modalities and spheres of use.
Table of Contents
Toggle- Biofeedback Therapy Training Guide
- Types of biofeedback therapy training modalities
- Electroencephalographic biofeedback (EEG BFB) or Neurofeedback
- Electromyographic biofeedback (EMG BFB)
- Breathing biofeedback
- Heart rate variability biofeedback (HRV BFB)
- Temperature or thermal biofeedback (Thermal BFB)
- Galvanic or electrodermal skin response (GSR BFB)
- Goals of Biofeedback Therapy Training
- The various sphere of use of biofeedback
- Applications of Biofeedback in Professional and Therapeutic Settings
- Stress-Related Conditions Biofeedback and Relaxation Techniques
- Relaxation Training Biofeedback
- Biofeedback Therapy Training in the Treatment of Pain
- Biofeedback therapy training in medicine
- Biofeedback therapy training in the treatment of essential hypertension
- Biofeedback therapy training for the treatment of Morbus Raynaud
- Biofeedback therapy training for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders
- Biofeedback therapy training for Paresis and Paralysis
- Neurofeedback therapy training in the treatment of ADHD
- Neurofeedback Applications for Insomnia and Broader Benefits
- FAQ: Biofeedback Therapy Training Guide
- BIOFEEDBACK HOME USE DEVICE
- Types of biofeedback therapy training modalities
Biofeedback therapy training aims to help individuals become more aware of their physical reactions to stress. This stress can be physical, emotional, or psychological. Moreover, biofeedback seeks to improve their ability to control these physiological responses. Through this process, individuals develop self-regulation skills, which can enhance their health and well-being.
Currently, scientists do not fully understand how biofeedback works. However, most patients who benefit from biofeedback learn to relax and modify their behavior. In fact, many scientists believe that relaxation is a crucial part of biofeedback therapy, especially for disorders caused or worsened by stress. Their reasoning stems from what we know about how stress affects the body. To summarize, stressful events trigger strong emotions, which lead to specific physical responses. The sympathetic nervous system, which prepares the body to handle emergencies through “fight or flight,” controls many of these reactions.
Patients may find it hard to accept that mental or psychological factors can cause diseases. Biofeedback facilitates the realization of “invisible influences” of the mind activated by thoughts, feelings or fears, especially for “skeptical patients”. This happens via objectively visible parameters onscreen. Thus, patients’ models of diseases open up to psychological causes.
Types of biofeedback therapy training modalities
Different physiological parameters can be measured depending on the specific health problems and goals. Feedback is then provided to help individuals learn to self-regulate these parameters. Additionally, there are several types of biofeedback, each based on the specific parameters being measured and the feedback given.
Electroencephalographic biofeedback (EEG BFB) or Neurofeedback
Sensors attached to the scalp monitor brain wave activity in different brain areas. Sensors can treat conditions that impact brain wave patterns, whether proven or suspected. For example, doctors often use them to address seizure disorders, epilepsy, ADHD, learning disabilities, migraines, tension headaches, traumatic brain injuries, and sleep disorders. Additionally, these sensors help individuals perform highly in various areas of human activity.
On the Therapeutic Neurofeedback page of this website, you can find detailed information about Neurofeedback. This includes its indications for use, the methodology, and how to use the device at home. Additionally, by following the Articles page, you can stay updated on new applications of Neurofeedback, its use for various conditions, and its effectiveness.
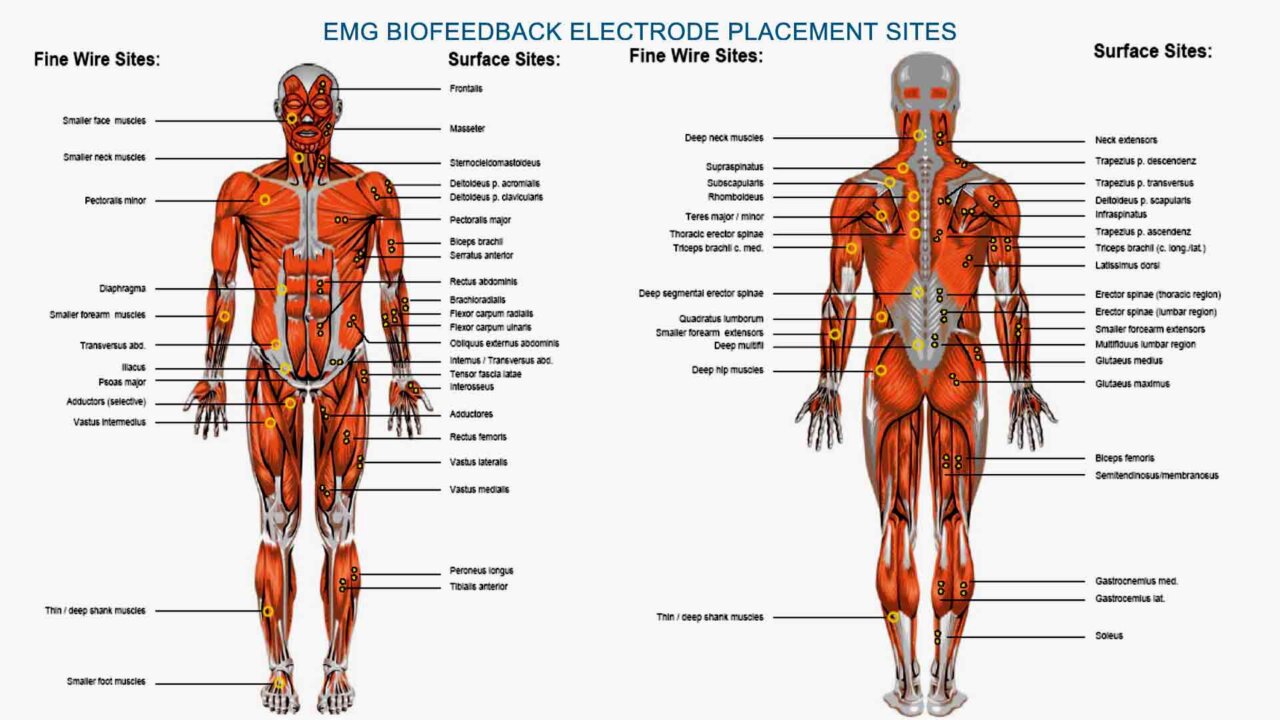
Electromyographic biofeedback (EMG BFB)
Practitioners place sensors or electrodes on the skin over specific body parts when performing electromyographic biofeedback training. These sensors monitor muscle electrical activity, particularly muscle tension. This method is the most commonly used biofeedback for treating neurologic and neuromuscular disorders. For example, practitioners often use it for conditions like stroke, cerebral palsy, traumatic brain injury, and multiple sclerosis. EMG biofeedback can also treat tension headaches, enuresis, and encopresis. Practitioners place sensors on the jaw muscles to address temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ) or bruxism. For chronic pain, muscle tension is monitored on specific body parts in different areas. Additionally, this method can treat conditions in children, such as clubfoot, poor posture, tics, and others.
This website’s EMG BFB page provides more detailed information regarding EMG Biofeedback, its indications for use and methodology, and its home use device. You can also stay informed regarding new applications of EMG BFB, its use in different conditions, methodology, and effectiveness by following the Article page of this website.
Breathing biofeedback
During respiratory biofeedback training, practitioners place bands around the abdomen and chest. These bands monitor the breathing pattern and respiration rate while teaching conscious abdominal (diaphragmatic) breathing. This quick-to-learn technique allows patients to respond to stress and strain actively. Additionally, practitioners can use breath control training to treat panic attacks, asthma, and various stress-related conditions, including professional performance anxiety.
The Breathing Biofeedback page of this website provides more detailed information about breathing biofeedback, its indications for use, methodology, and a personal home-use device. You can also follow the Articles page to stay informed about new applications, their use in different conditions, methodology, and effectiveness.
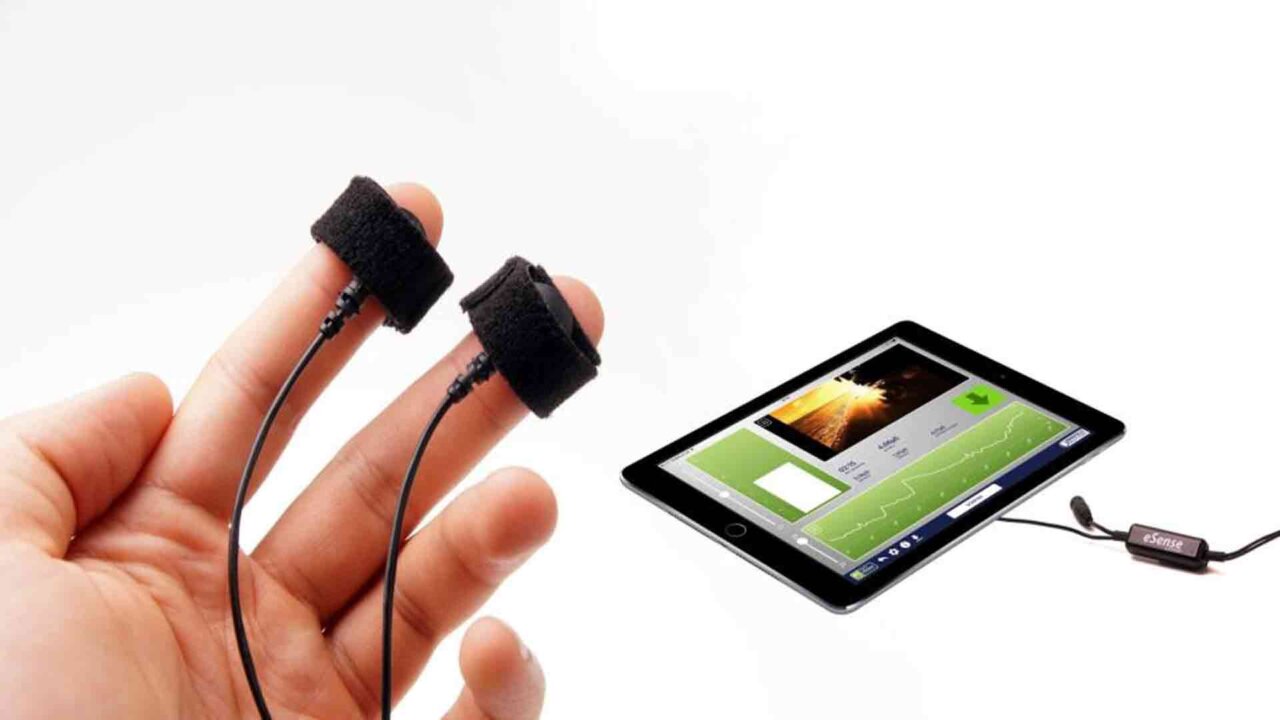
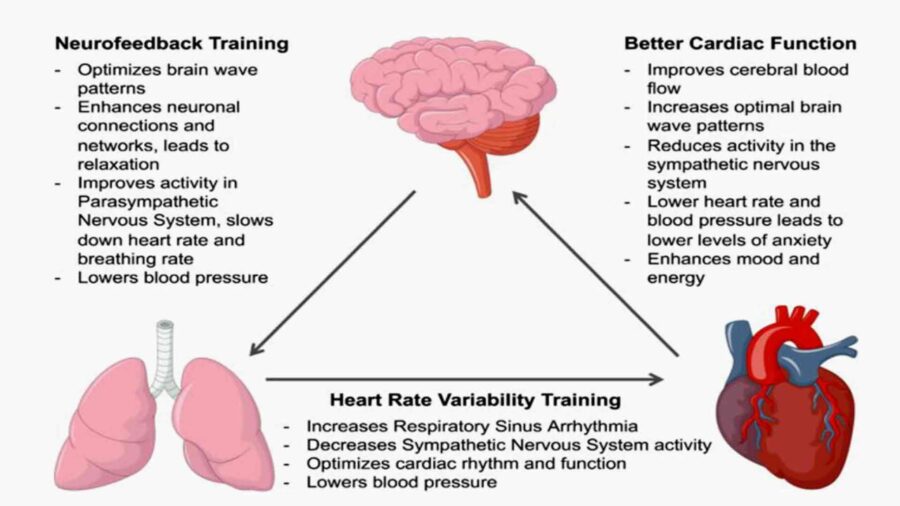
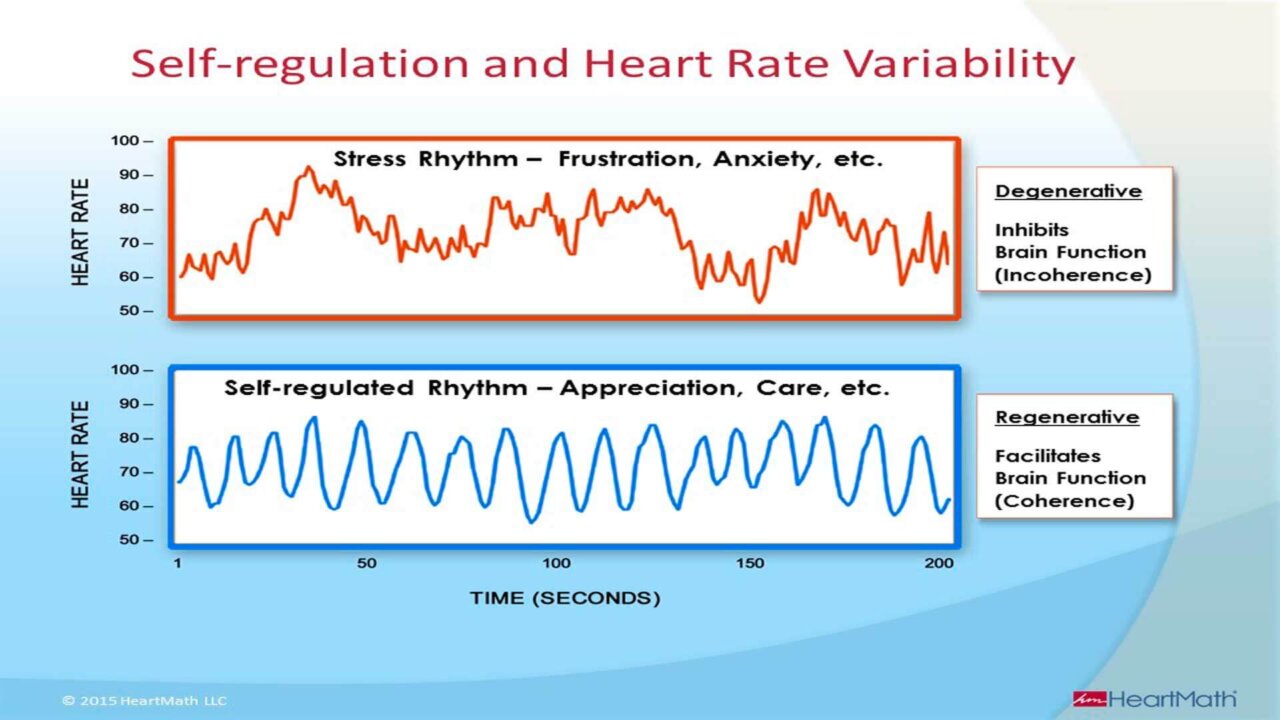
Heart rate variability biofeedback (HRV BFB)
Understanding HRV Biofeedback and Its Mechanisms
During HRV biofeedback therapy training, the practitioner places a pulse sensor or electrode on the fingertip. This sensor monitors the pulse rate. Emotional arousal, such as anger or fear, causes the heart rate to increase. Conversely, decreases in heart rate indicate relaxation.
The magnitude and complexity of heart rate variability (HRV) indicate the efficiency of autonomic regulation in response to internal and environmental demands. In addition, HRV reflects the combined actions of several systems working together. Notably, low HRV directly increases health risks, contributing to mortality and sudden death from myocardial infarction. It also plays a significant role in conditions like hypertension, fibromyalgia, depressive symptoms, anxiety disorders, generalized anxiety disorder, PTSD, panic disorders, insomnia, and more.
HRV BFB was conceived as an intervention targeting the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). The HRV BFB training influences the organism through three possible mechanisms:
1. affecting cardiovascular homeostatic reflexes to increase flexibility and recovery from fight/flight adaptive situations;
2. the vagal afferent pathways that are stimulated by slow diaphragmatic breathing and may explain some of the central effects;
3. The third pathway involves the cholinergic or parasympathetic systems regulating the inflammatory response.
Applications and Efficacy of HRV Biofeedback
HRV biofeedback applications: Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD), Cardiovascular disease, Hypertension, Fibromyalgia. Major depressive disorder, Anxiety & PTSD, Abdominal pain, and many others.
Heart Rate Variability biofeedback has shown efficacy in various conditions. For instance, in cardiovascular diseases, it leads to modestly lower blood pressure and improvements in heart failure symptoms. Patients often walk farther in a 6-minute walk test and report decreased emotional distress.
In fibromyalgia, patients experience improved daily functioning, along with a decrease in pain and depressive symptoms. Similarly, in depressive disorders, HRV biofeedback results in a reduction in heart rate, an increase in HRV, and reduced anxiety and depression.
Additionally, in anxiety disorders, patients report reduced anxiety and anger symptoms, as well as improved sleep quality. For those with repetitive abdominal pain, HRV biofeedback helps decrease both the intensity and frequency of pain, with effects mediated by changes in vagal tone.
Overall, HRV biofeedback treatment is a cost-effective and relatively brief option. Typically, it involves 6 to 10 sessions and serves as an alternative or supplement to standard medical or psychiatric treatment.
The HRV Biofeedback page of this website provides more detailed information about the HRV BFB, its indications for use and methodology, and personal home use devices. You can also follow the Articles page to stay informed about new applications of HRV BFB, its use in different conditions, methodology, and effectiveness.
Temperature or thermal biofeedback (Thermal BFB)
How Thermal Biofeedback Works
Thermal biofeedback therapy training works by attaching a temperature sensor or thermistor to a patient, usually the finger or hands. Sensors monitor body temperature and changes in blood flow. Temperature readout is then shown on a digital screen to the patient, who can see body temperature by the minute. How tense a person is can be measured by a drop in temperature in their hands. This is because, during stress, the body will divert blood from the body’s surface area to the muscles and organs, allowing us to better respond to a nearby threat. This is also referred to as the “fight or flight” response. When our surface temperature is high, it typically means we are relaxed or sleepy.
Benefits and Applications of Thermal Biofeedback
Temperature biofeedback may help treat migraine headaches, Raynaud’s disorder, and anxiety disorders. Studies have shown that thermal biofeedback can effectively treat migraines. Moreover, its success increases when combined with traditional migraine medications. When used consistently and under proper conditions, thermal biofeedback can remedy the effects of stress and tension in the body. Besides helping to alleviate various medical issues, thermal biofeedback can also improve one’s mental state and overall mood. By improving one’s mood, one can perform at higher levels of concentration and, subsequently, higher levels of success. This can be applied to job performance, athletics, or day-to-day activities. Overall, thermal biofeedback is an effective and inexpensive therapy for one to use, as a person can use it simply and in their own homes. With just a little guidance and thorough practice, anyone can use the technique to improve their physical state and well-being.
On this website, the Thermal Biofeedback page, you can find more detailed information regarding the Thermal BFB, its indications for use and methodology, and its use as a personal home device. You can also stay informed regarding new applications of the Thermal BFB, its use in different conditions, methodology, and effectiveness by following the Articles page of this website.
Galvanic or electrodermal skin response (GSR BFB)
During electrodermal skin activity biofeedback training, practitioners place sensors on the fingers. These sensors monitor perspiration, which reflects individuals’ emotional states. Furthermore, practitioners can use GSR to treat anxiety, fears or phobias, stress, and sleep problems.
On this website’s Electrodermal Activity BFB page, you can find more detailed information about the GSR BFB, indications for use and methodology, and a personal home use device.
Follow the Articles page of this website to stay informed about new applications of GSR BFB, its use in different conditions, methodology, and effectiveness.
Goals of Biofeedback Therapy Training
1. Education about connections between patient symptoms and physiology,
2. Skills training in changing biofeedback signals corresponding to physiologic processes,
3. Development of awareness of internal states linked to arousal and relaxation,
4. Application of skills training to carry over in recognizing and modifying internal states without the aid of instrumentation,
5. Development of a sense of self-efficacy and empowerment.
Therapeutic biofeedback helps restore balance and well-being, key elements of lasting personal success.
The various sphere of use of biofeedback
Applications of Biofeedback in Professional and Therapeutic Settings
Coaches and educators can use biofeedback therapy training to help people function better and achieve high professional performance. Additionally, therapists can use it to treat various pathological states and disorders. Research has demonstrated that biofeedback can effectively address many diseases and painful conditions.
Biofeedback has been integrated into comprehensive treatment approaches for several conditions. For example, it is used for
- chronic pain,
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS),
- temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ),
- Raynaud’s syndrome,
- epilepsy,
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD),
- anxiety,
- migraine headaches,
- depression,
- traumatic brain injury,
- and sleep disorders.
There is also some support for using biofeedback to treat diabetes, provided that self-monitoring of blood glucose levels is maintained and conducted under regular physician consultation and supervision.
Stress-Related Conditions Biofeedback and Relaxation Techniques
Biofeedback therapy training is valuable for helping individuals with urinary incontinence regain bladder control. In this case, sensors are placed in the vaginal or anal canal to assist individuals in learning when their muscles are properly contracted. A recent study found that this type of biofeedback treatment was safe, effective, and well-received by women patients aged 55 and older.
Moreover, biofeedback can treat stress-related conditions, including certain types of headaches, high blood pressure, bruxism (teeth grinding), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), eating disorders, substance abuse, and some anxiety disorders. In treating these stress-related conditions, biofeedback is often combined with relaxation training.
Sometimes, biofeedback is used to help individuals learn how to achieve more profound relaxation. This is particularly useful in childbirth education programs or general stress management, referred to as biofeedback-assisted relaxation training. Significantly, biofeedback can enhance relaxation techniques, even for those who can already achieve relaxation through other strategies, such as meditation. It offers unique advantages by allowing clinicians to track where individuals tense up and to help them understand the thoughts and feelings associated with that tension.
To stay informed about new applications of various types of biofeedback, its use in different conditions and disorders, methodology, and effectiveness, follow the Articles page of this website.
Relaxation Training Biofeedback
Biofeedback therapy training for Relaxation Training helps to consciously integrate regeneration phases into daily routines. The learned techniques can reduce many psychosomatic symptoms and prevent the negative consequences of chronic stress. Relaxation may be achieved through biofeedback training sessions using physiological parameters such as breathing, heart rate, brainwave, skin temperature, or muscle tension. Misguided effort, pressure to succeed, and fear of losing control inhibit relaxation. Biofeedback allows clients to see their SUCCESS immediately onscreen by applying relaxation techniques. These have a positive and relaxing effect on the body – even without conscious perception. An expectation regarding self-efficacy also increases.
Before starting a relaxation treatment, it is helpful to answer some questions first:
- Which body system reacts most strongly to mental stress?
- Which body system shows a delayed recovery after the stressor?
- Which content triggers the most vigorous physiological response?
The physical reaction to stressors and the ability to relax after the stressor is objectively measured and tested, as are the psycho-physiological effects of specific contents (ideas, people, situations, images). Biofeedback can also detect which relaxation technique is most appropriate for a patient.
Biofeedback therapy training in the treatment of Anxiety and Panic Disorders
Anxiety significantly hinders the daily lives of individuals who suffer from this condition. Moreover, it can lead to considerable psychological strain. Using biofeedback as a therapeutic intervention for anxiety disorders serves as a complementary therapy. This approach supports patients’ self-competence and positively influences their treatment progress.
Biofeedback therapy training helps patients become more aware of how their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors interact. This is why it’s frequently used with other therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or mindfulness meditation training, to reduce a patient’s stress response.
Biofeedback therapy is a training process, not a treatment, such as medications. Biofeedback teaches patients to pay more attention to how stress impacts the body. For example, anxiety causes someone’s heart rate to speed up (used HRV BFB), muscles to tense (EMG biofeedback of m.frontalis), and the mind to worry (EEG biofeedback can be used). This, in turn, makes sleep and relaxation difficult. Through purposefully tracking symptoms and learning over and over again to reduce those using Biofeedback as a guide, relaxation becomes better enforced.
Biofeedback therapy training in the treatment of Sleep Disorders
Stressful life events often accompany chronic sleeping disorders, increased general anxiety, depression, as well as anxiety relating to the disorder itself.
A standard treatment method for insomnia involves the prescription of drugs. While offering satisfactory effects, on the one hand, these drugs are accompanied by considerable drawbacks (deterioration of diurnal affectivity, addiction, or increase in dose due to tolerance).
While sleeping pills should be prescribed only in addition to therapy, especially during a crisis, behavior-oriented therapies, such as Biofeedback, offer long-lasting effectiveness and lack possible side effects. Thus, Biofeedback is regarded as a first-line treatment.
Biofeedback Therapy Training in the Treatment of Pain
Chronic stress and tension often result in a vicious circle of tension and pain, which leads to chronic pain disorders. Many patients are unaware that these tensions exist, but have become used to them.
Finding non-pharmacological techniques for controlling both short-term (acute) and chronic pain is now becoming more critical than ever, especially when taking into consideration the fact that so much attention has been given to the potential for addiction to pain-killing drugs.
EEG biofeedback therapy training is being used in many treatment settings as an alternative method for pain reduction. It’s being used for managing strokes, post-traumatic events, headaches, injuries, chronic muscle tension, diabetic neuropathic pain, and cancer recovery. Some evidence shows that it takes 40 to 60 training sessions to achieve the most benefits. Some studies show this amount can result in up to 70 percent less pain, depending on the condition. Research studies suggest that it’s helpful in both children and adults. One of the most valuable effects of Biofeedback is showing individuals the status quo and making them aware of the cause of their pain. Biofeedback helps patients learn conscious relaxation to break the vicious cycle.
The following pain disorders are treated with Biofeedback:
Biofeedback therapy training for headache and back pain
Throughout their lives, 70% of the population suffers from tension headaches and 15% from migraines. The German Headache and Migraine Society mentions Biofeedback as the most effective non-drug method for treating this condition.
Because it can lower someone’s stress response, clinical studies have shown that Biofeedback is effective in reducing the frequency and severity of tension and migraine headaches.
Multiple studies have shown a statistically significant decrease in the frequency and severity of headaches in the first 12 months. This benefit continued for 36 months. Studies have also documented that biofeedback training allowed many patients to decrease their dependence on pain medications and lower medical care costs.
More than 80% of individuals suffer from chronic back pain. Therapy trials showed that Biofeedback had the most significant and stable therapeutic results in treating chronic back pain.
Through breath or EMG Biofeedback therapy training, the patients learn to consciously relax a different muscle group, leading to lower pain. Improved body awareness is also helpful in stressful situations.
Biofeedback therapy training for Bruxism
Training and consolidation of general relaxation skills precede EMG biofeedback, which will subsequently be collected from the masseter muscle, the m. temporalis, and the m. frontalis to train the discriminative perception of the muscles. This skill can be used to maintain a relaxed state of the affected muscles independently and to ensure lasting freedom from symptoms.
Via Biofeedback of the m. frontalis, general relaxation is trained. After consolidating this skill, precise training will focus on discriminative muscle perception through different stress levels of the EMG signal. An increase in training, especially for Bruxism alongside dental damage, is achieved via massaged practice to build up a conditioned, reactive inhibition following additional training of relaxation and contraction of the m. masseter.
Biofeedback therapy training in the treatment of Spasmodic torticollis
EMG feedback therapy training is given bilaterally on the m. sternocleidomastoids to train both the reduction of tension and balancing of both sternocleidomastoid muscles, following the increasing level of difficulty of the exercises and the advancement of therapy.
After general relaxation training (EMG biofeedback of m. frontalis or sternocleidomastoids), the exercises progress to bilateral Biofeedback of the m. sternocleidomastoids. Suppose patients achieve the goals of this phase of therapy (conscious reduction of tension of the affected muscle, balancing out both sternocleidomastoid muscles, contraction or relaxation of the non-affected sternocleidomastoid muscle). These skills can be trained under gradually increasing difficulty (lying, standing, sitting, moving, during a conversation, etc.). It is also recommended that patients practice at home with EMG home use devices (relaxation practices, movement exercises of the neck). Therapy should be concluded with booster sessions after six or 12 months.
Biofeedback therapy training in medicine
Biofeedback can be used to treat many medical and psychological indications. From adjuvant support to exposure therapy for anxiety and phobias, muscle-building exercises after strokes, and the widely documented effects on incontinence, Biofeedback is a helpful therapy or support for many diseases.
Biofeedback therapy training in the treatment of essential hypertension
Essential hypertension covers all diseases regulating blood pressure, leading to chronically increased blood pressure without organic causes. Hypertension is considered a significant risk factor for cardiac infarction and stroke. Along with high cholesterol levels and smoking, it constitutes the major risk factors for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Practicing general relaxation techniques with Breathing biofeedback and HRV biofeedback in patients led to conscious variation in vascular resistance and an increase in heart rate variability (RSA), which results in ongoing relief of the cardiovascular system, reduces blood pressure, and subsequently facilitates medical treatment, increasing general well-being.
A 2011 study published in the Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine suggests that in patients with heart failure, biofeedback-assisted stress management (BFASM) may actually cause cellular and molecular remodeling of the failing heart, change abnormal heart rate variability, and positively impact side effects due to suffering from a severe chronic disease.
Biofeedback therapy training for the treatment of Morbus Raynaud
Understanding Raynaud’s Disease and Its Challenges
Raynaud’s disease is a circulatory syndrome, not a skin disorder. It manifests as numbness, pain, and coldness in the fingers and toes. It can sometimes spread to the entire hand, foot, or face. The disease stems from peripheral blood supply dysfunctions, causing significant ischemia due to blood vessel constriction and reduced blood flow. Small vessels that generally supply oxygen and warm blood to the skin spasm, restricting blood flow to the extremities. As a result, the affected areas turn white or blue, becoming cold and numb. Stress and freezing temperatures often trigger these vasospasms, making winter particularly difficult for those with Raynaud’s. According to a Danish study, 22% of women aged 21-50 suffer from this condition.
Sufferers face two main challenges: first, they need to reduce the stress that causes vasoconstriction; second, they must reverse the constriction once it occurs.
Thermal Biofeedback Therapy for Raynaud’s Disease
Thermal biofeedback therapy is an ideal treatment option for Raynaud, especially for those reluctant to pursue traditional medical treatment or medications. To begin therapy, readings should always be taken in a neutral-temperature room, ensuring the person is neither too hot nor cold. Next, hand-warming exercises are performed during the relaxation phases. Then, cold stimuli, such as room temperature or objects, are introduced to continue training.
After proper guidance from a specialist, individuals can perform thermal biofeedback at home. Consistency is key, and training effects are more enduring with regular home practice using a thermal biofeedback device. Anyone can learn to control body temperature with the right equipment, patience, and imagination. For instance, using mental imagery to visualize cold or warm environments can aid in temperature regulation. Children tend to excel in thermal biofeedback because they are naturally more imaginative than adults.
Research by the Association for Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback shows thermal biofeedback is highly effective in treating primary Raynaud’s disease. In fact, 80 to 90 percent of patients report improved circulation and reduced symptoms, such as numbness, throbbing, and swelling. Patients typically learn to control their blood vessels’ constriction and dilation during approximately 20 training sessions.
Biofeedback therapy training for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders
- Biofeedback for the treatment of Constipation
Biofeedback therapy is considered a well-established treatment modality for patients with several forms of chronic constipation (including dyssynergic defecation and fecal incontinence). Randomized controlled trials have found that 70 to 80 % of all patients undergoing specialized biofeedback training in treatment centers experience symptom improvements.
EMG biofeedback is used to help teach patients suffering from recurrent constipation to better sense and control muscles in their digestive system related to bowel movements. For example, biofeedback maneuvers correct impaired rectal sensation and a poor ability to squeeze muscles in the abdomen.
- Biofeedback for the treatment of incontinence
Biofeedback is a successful and effective treatment method for urinary and fecal incontinence. The muscle tone of the pelvic floor can be measured using vaginal and rectal electrodes and is shown to patients onscreen. The training focuses on systematic sequences of muscle contraction and relaxation. This non-invasive and non-medicinal biofeedback therapy offers essential advantages, including high success rates, no side effects, and the empowerment of patients through active participation in their treatment.
Biofeedback therapy training for Paresis and Paralysis
The purpose of training for patients with paresis or paralysis is efficient and extensive rehabilitation of as many impaired functions as possible due to damage to the central nervous system, spinal cord, or nerve damage in the periphery. It was possible to prove the efficiency of Biofeedback under many specific applications. Particularly, motivation increases as patients visualize residual activity in the EMG, and systematic training accelerates the treatment process.
Neurofeedback therapy training in the treatment of ADHD
EEG Biofeedback or Neurofeedback is a scientifically recognized method used to treat disorders linked to decreased cognitive performance, such as ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder). It helps improve mental performance, especially in children with ADHD, who often display reduced attention spans or increased motor activity. These issues can lead to difficulties in school, resulting in poor academic performance, even among brilliant children. Neurofeedback offers long-lasting therapeutic effects, as supported by various studies.
This non-invasive method uses EEG feedback to restructure the brain networks of children with ADHD, leading to symptom improvement. By training specific frequency bands, which differ between children with ADHD and healthy controls, neurofeedback helps them achieve better focus. During treatment, the system provides real-time feedback to the child, allowing them to practice and consolidate a focused yet relaxed state of mind. Children can memorize and retrieve this mental state with frequent training and home-use devices.
Neurofeedback Applications for Insomnia and Broader Benefits
EEG biofeedback offers a valuable tool for controlling hyperarousal symptoms, which often impact individuals with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), including insomnia. In 2011, researchers at the Department of Psychophysiology at Helfgott Research Institute in Oregon conducted a study that highlighted the effectiveness of two neurofeedback treatments: the sensorimotor protocol and sequential quantitative EEG, for treating insomnia. Participants completed 20 sessions of neurofeedback training lasting 15 minutes each and reported significant symptom reductions, such as daytime sleepiness and hyperarousal. They also showed improved scores on several insomnia measurement scales, including the Insomnia Severity Index and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Inventory.
On this website’s neurofeedback page, you can find more information about neurofeedback’s effectiveness in treating different conditions, its indications, and personal home-use devices. Additionally, the Articles page offers updates on new neurofeedback applications, methods, and their effectiveness in various conditions.
Learning biofeedback takes time, and results vary based on factors such as the severity of the condition, medications, and individual motivation levels. Biofeedback can help control symptoms or reduce medication needs. Eventually, anyone can practice these techniques at home using personal devices. Biofeedback is safe, and no adverse side effects have been reported.
FAQ: Biofeedback Therapy Training Guide
Biofeedback therapy training is a non-invasive technique that teaches individuals to control physiological functions (e.g., heart rate, muscle tension) using real-time feedback from sensors. It’s used for stress management, pain relief, and improving mental and physical health.
Biofeedback therapy uses sensors attached to the body to monitor signals like heart rate variability (HRV), muscle activity (EMG), or brainwaves (neurofeedback). The data is displayed on a screen, helping users learn self-regulation through visual or auditory cues (biofeedback loop).
Most people see improvements within 4–6 sessions, but chronic conditions may require 10–20 sessions. Consistency and practice (e.g., home training with devices like HeartMath) enhance outcomes.
Yes, biofeedback therapy is safe and drug-free. It has no side effects, making it suitable for children, adults, and seniors. Always consult a healthcare provider for severe conditions.
Absolutely! Devices like the Mendi or Neurosky headband, HeartMath, or EMG biofeedback device allow home-based training. Pair them with guided apps for optimal results.
You can find more about home-use biofeedback devices here.