In today’s fast-paced and often stress-inducing world, anxiety has become a prevalent concern affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Whether triggered by work pressures, personal challenges, or societal expectations, anxiety can significantly impact one’s quality of life, emotional well-being, and overall health. Fortunately, advancements in technology have paved the way for innovative solutions to help individuals better manage and alleviate symptoms of anxiety. In the realm of anxiety management, biofeedback devices stand out as promising tools, offering real-time insights into physiological responses and empowering individuals to regulate their anxiety levels effectively. In today’s fast-paced world, where stressors abound and mental well-being is paramount, the emergence of biofeedback devices for anxiety marks a significant stride towards personalized, tech-enabled solutions.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Anxiety
Anxiety is a complex and multifaceted emotion that manifests differently from person to person. While it’s normal to experience occasional feelings of worry or nervousness, anxiety becomes problematic when it interferes with daily functioning and quality of life. Understanding the nature of anxiety is essential for effectively managing it, and biofeedback devices for anxiety can play a significant role in this process.
Anxiety is characterized by feelings of unease, worry, or fear about future events, situations, or outcomes. It can manifest physically, emotionally, and cognitively, leading to symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and irritability. To delve deeper into the causes, types, and symptoms of anxiety, we invite you to explore our article titled “Neurofeedback for Anxiety.”
By gaining a deeper understanding of anxiety and its underlying mechanisms, individuals can empower themselves to explore effective strategies for managing and alleviating its impact on their lives. Biofeedback devices provide valuable tools for monitoring and regulating physiological indicators of anxiety, facilitating a proactive approach to self-care and emotional well-being.
Role of Biofeedback in Anxiety Management
Biofeedback is a therapeutic technique that enables individuals to gain awareness and control over their physiological responses through real-time monitoring of bodily functions. In the context of anxiety management, biofeedback offers a valuable tool for identifying and regulating the physical manifestations of stress and anxiety. Understanding the role of biofeedback in anxiety management can provide insights into its effectiveness as a complementary therapy.
Principles of Biofeedback
Biofeedback relies on the principle of operant conditioning, where individuals learn to modify their physiological responses through feedback provided by monitoring devices. By observing real-time data on parameters such as heart rate, respiration, skin conductivity, skin temperature, muscle tension, and brain activity individuals can learn to recognize patterns and make conscious adjustments to achieve desired physiological states.
How Biofeedback Works for Anxiety
Anxiety often involves heightened physiological arousal, including increased heart rate, shallow breathing, cold hands, muscle tension and rumination. Biofeedback devices provide objective feedback on these physiological markers, allowing individuals to identify signs of anxiety and implement relaxation techniques to counteract them. Through repeated practice and reinforcement, individuals can learn to regulate their physiological responses, reducing the intensity and frequency of anxiety symptoms over time.
Different Modalities of Biofeedback Devices for Anxiety Management
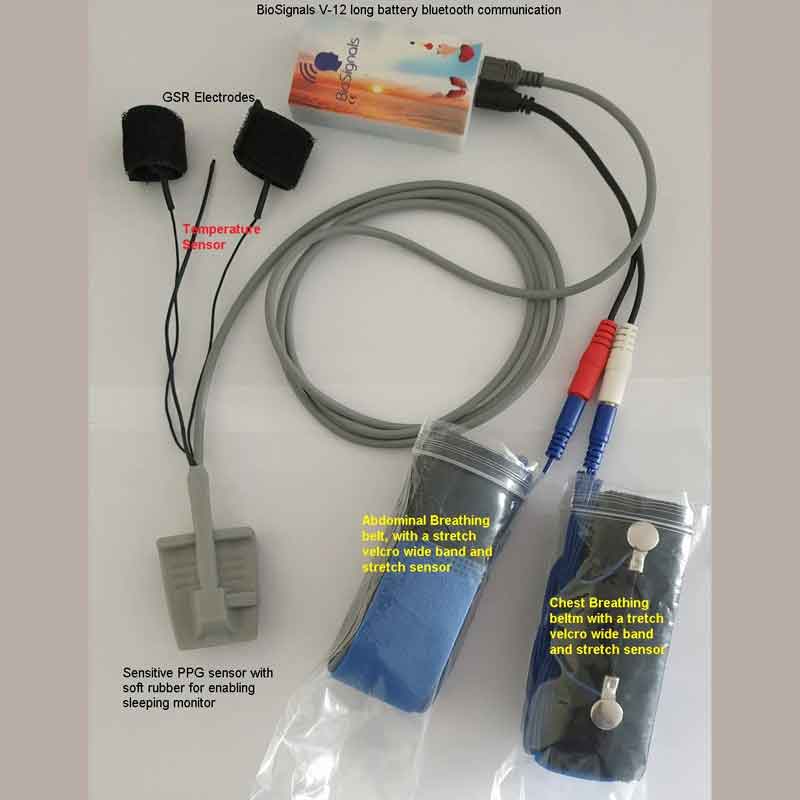
Within the realm of anxiety management, a diverse array of biofeedback devices has emerged, each offering unique modalities to assist individuals in monitoring and regulating their physiological responses. Biofeedback devices for anxiety encompass various technologies, including heart rate variability (HRV) monitors, electrodermal activity (EDA) sensors, respiration rate monitors, muscle tension sensors, temperature monitors, and EEG neurofeedback devices. Each of these biofeedback devices for anxiety serves a specific purpose in aiding individuals with anxiety by providing real-time feedback on physiological parameters associated with stress and relaxation. By harnessing these biofeedback modalities, individuals gain greater awareness of their bodily responses to anxiety triggers and develop effective strategies for self-regulation and stress reduction.
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Biofeedback Devices for Anxiety
HRV Biofeedback focuses on optimizing the variability in the intervals between heartbeats, promoting a state of physiological coherence associated with relaxation and emotional balance.
HRV biofeedback devices for anxiety is a technique that involves training individuals to regulate their heart rate variability, which is the variation in time intervals between successive heartbeats. HRV biofeedback devices for anxiety works by providing individuals with real-time feedback on their heart rate patterns, typically through visual or auditory cues, allowing them to learn to modulate their physiological responses and achieve a state of coherence between heart rate variability and respiration.
Here’s how HRV biofeedback works in anxiety, including the initial changes in anxiety and the effects after a biofeedback session.
1. Initial Changes in Anxiety:
• When individuals experience anxiety, the body’s autonomic nervous system becomes activated, leading to physiological changes such as increased heart rate, shallow breathing, and heightened sympathetic arousal.
• These physiological responses are often accompanied by decreased heart rate variability, reflecting a more rigid and less adaptive autonomic nervous system functioning.
• Individuals may experience symptoms such as palpitations, chest tightness, sweating, and feelings of nervousness or dread.
2. During HRV Biofeedback Session:
• During an HRV biofeedback session, individuals are typically instructed to focus on their breathing while monitoring their heart rate variability through biofeedback equipment.
• Visual or auditory cues provide real-time feedback on changes in heart rate variability, helping individuals establish a coherent pattern between heart rate variability and respiration.
• Through paced breathing exercises and relaxation techniques, individuals learn to synchronize their breathing with changes in heart rate variability, promoting a shift towards parasympathetic dominance and reducing sympathetic arousal.
• As individuals practice HRV biofeedback, they may experience a sense of relaxation, calmness, and increased awareness of their physiological responses.
Video – HRV Biofeedback: Breathing and HRV synchronization
3. After HRV Biofeedback Session:
• After completing an HRV biofeedback session, individuals may experience immediate reductions in anxiety symptoms, such as decreased heart rate, reduced muscle tension, and improved mood.
• With continued practice over multiple sessions, individuals may notice longer-lasting effects, including improvements in overall stress resilience, emotional regulation, and coping with anxiety triggers.
• Over time, HRV biofeedback training can lead to enduring changes in autonomic nervous system functioning, enhancing flexibility and adaptability in response to stressors.
• Individuals may also develop greater self-awareness and self-regulation skills, empowering them to manage anxiety more effectively in daily life.
In summary, the HRV biofeedback device for anxiety trains individuals to regulate their heart rate variability, promoting coherence between heart rate variability and respiration. Through repeated practice, HRV biofeedback can lead to immediate and long-term reductions in anxiety symptoms and improvements in overall stress resilience and emotional well-being.
Breathing Biofeedback Devices for Anxiety Management
Breathing Biofeedback involves paced breathing exercises to promote relaxation and reduce respiratory rate, leading to decreased sympathetic nervous system activity and increased parasympathetic activation.
Breathing (respiration) biofeedback devices for anxiety is a technique that focuses on training individuals to control their breathing patterns to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and alleviate symptoms of anxiety. Here’s how breathing biofeedback works in anxiety, including the initial changes in anxiety and the effects after a biofeedback session.
1. Initial Changes in Anxiety:
• Anxiety often leads to physiological changes in the body, including increased respiratory rate, shallow breathing, and chest tightness.
• Individuals may experience symptoms such as hyperventilation, where they breathe rapidly and shallowly, leading to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels in the blood and an imbalance in the body’s oxygen-carbon dioxide ratio.
• These changes in breathing patterns can further exacerbate feelings of anxiety, leading to a cycle of increased stress and physiological arousal.
2. During Breathing Biofeedback Session:
• During a breathing biofeedback session, individuals are typically connected to biofeedback equipment that monitors their respiration rate and depth.
• Visual or auditory cues provide real-time feedback on changes in breathing patterns, allowing individuals to observe their respiration rate and adjust it accordingly.
• Individuals are guided to engage in paced breathing exercises, where they synchronize their breathing with the cues provided by the biofeedback device.
• By practicing slow, deep diaphragmatic breathing (link to video: Diaphragmatic Breathing: How to Perform), individuals learn to regulate their respiratory rate, increase carbon dioxide levels in the blood, and promote relaxation.
Video – Exercise your proper breathing 4/6 with video-guide
3. After Breathing Biofeedback Session:
• After completing a breathing biofeedback session, individuals may experience immediate reductions in anxiety symptoms, such as decreased heart rate, muscle tension, and feelings of stress.
• By engaging in slow, deep diaphragmatic breathing, individuals activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation and counters the sympathetic arousal associated with anxiety.
• With continued practice over multiple sessions, individuals may notice longer-lasting effects, including improvements in overall respiratory function, stress resilience, and emotional well-being.
• Breathing biofeedback training can also help individuals develop greater awareness of their breathing patterns and the ability to self-regulate their responses to stressors in daily life.
In summary, respiratory biofeedback devices for anxiety work by training individuals to control breathing patterns, promote relaxation, and reduce symptoms of anxiety. Through repeated practice, breathing biofeedback can lead to immediate and long-term improvements in respiratory function, stress resilience, and emotional well-being, empowering individuals to manage anxiety more effectively in daily life.
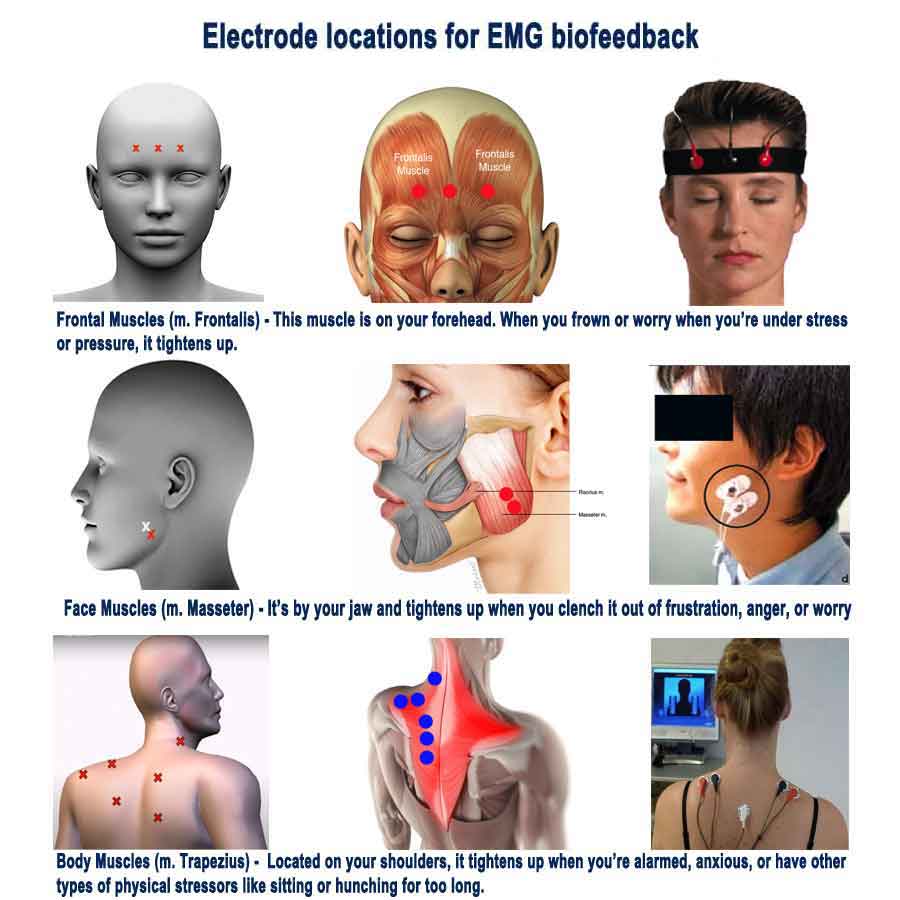
EMG Biofeedback Devices for Anxiety Management
EMG Biofeedback utilizes surface electromyography (sEMG) to measure muscle tension levels. By becoming aware of and reducing excessive muscle tension, individuals can alleviate physical symptoms of anxiety, such as headaches and muscle stiffness.
EMG (Electromyography) biofeedback devices for anxiety management is a technique that focuses on training individuals to recognize and regulate muscle tension levels in their body. Here’s how EMG biofeedback works in anxiety, including the initial changes in anxiety and the effects after a biofeedback session.
1. Initial Changes in Anxiety:
• Anxiety often manifests in the body as increased muscle tension, particularly in areas such as the neck, shoulders, jaw, and back.
• Individuals may experience symptoms such as muscle tightness, clenched jaw, stiff neck, or tension headaches as a result of heightened stress and anxiety.
• Chronic muscle tension can contribute to feelings of discomfort, fatigue, and physical stress, exacerbating the overall experience of anxiety.
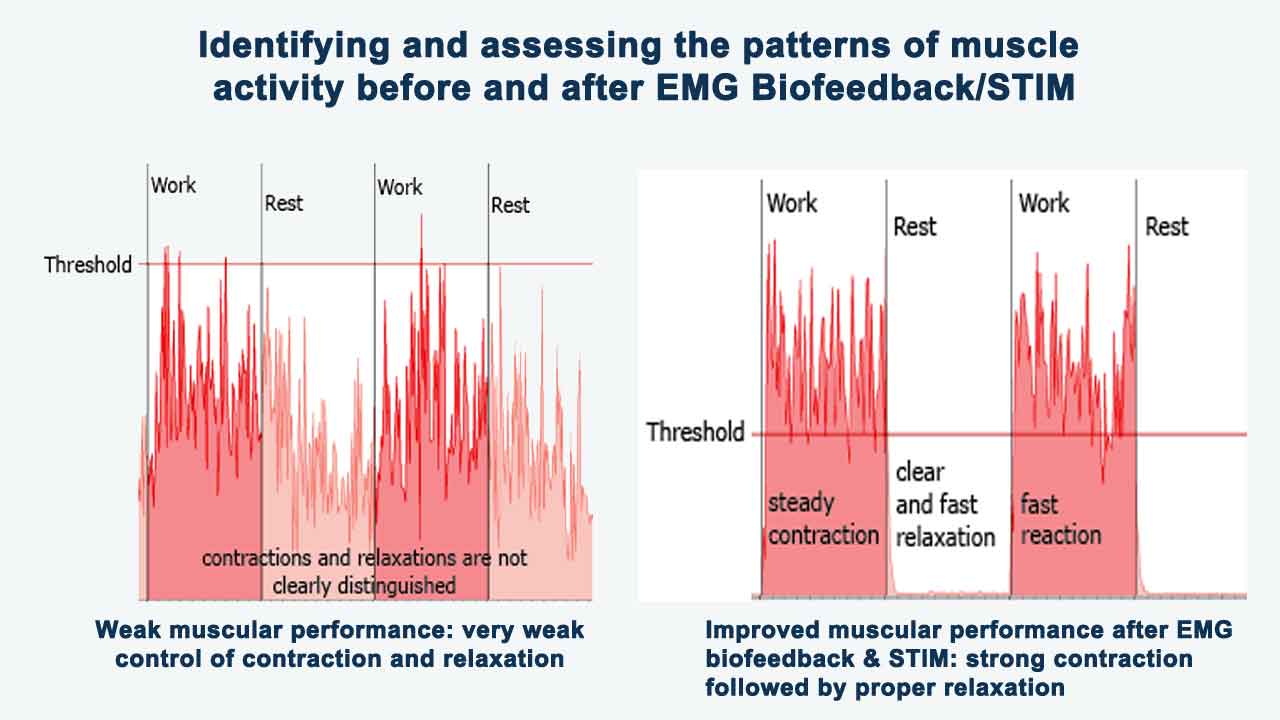
2. During EMG Biofeedback Session:
• During an EMG biofeedback session, individuals are connected to biofeedback equipment that measures their muscle activity, typically using surface electrodes placed on target muscle groups.
• Visual or auditory cues provide real-time feedback on changes in muscle tension levels, allowing individuals to observe their muscle activity and learn to control it.
• Individuals are guided through relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery while monitoring their muscle tension on the biofeedback display.
• By consciously relaxing tense muscles and reducing muscle activity, individuals learn to modulate their physiological responses and promote relaxation.
3. After EMG Biofeedback Session:
• After completing an EMG biofeedback session, individuals may experience immediate reductions in muscle tension and feelings of physical relaxation.
• By learning to release tension in specific muscle groups, individuals can alleviate physical symptoms associated with anxiety, such as muscle tightness or stiffness.
• With continued practice over multiple sessions, individuals may notice longer-lasting effects, including improvements in overall muscle awareness, stress resilience, and emotional well-being.
• EMG biofeedback training can also help individuals develop greater mindfulness of their muscle tension patterns and the ability to intervene proactively to prevent tension buildup in response to stressors.
In summary, EMG biofeedback devices for anxiety work by training individuals to recognize and regulate muscle tension levels, promoting relaxation and reducing physical symptoms of anxiety. Through repeated practice, EMG biofeedback can lead to immediate and long-term improvements in muscle relaxation, stress resilience, and emotional well-being, empowering individuals to manage anxiety-related muscle tension more effectively in daily life.
Electrodermal Skin Activity (EDA) Biofeedback Devices
Electrodermal Skin Activity (EDA) or Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) biofeedback is a technique that focuses on training individuals to recognize and regulate changes in skin conductance, which reflects changes in sympathetic nervous system activity and arousal levels. By learning to modulate skin conductance, individuals can reduce physiological arousal and anxiety.
Here’s how EDA biofeedback works in anxiety, including the initial changes in anxiety and the effects after a biofeedback session.
1. Initial Changes in Anxiety:
• Anxiety often leads to activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which can result in changes in skin conductance.
• Skin conductance reflects the activity of sweat glands in the skin, which are controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. When individuals experience stress or anxiety, sweat gland activity increases, leading to an increase in skin conductance.
• These changes in skin conductance can manifest as sweating, clamminess, or changes in skin temperature, which are physiological responses to sympathetic arousal.
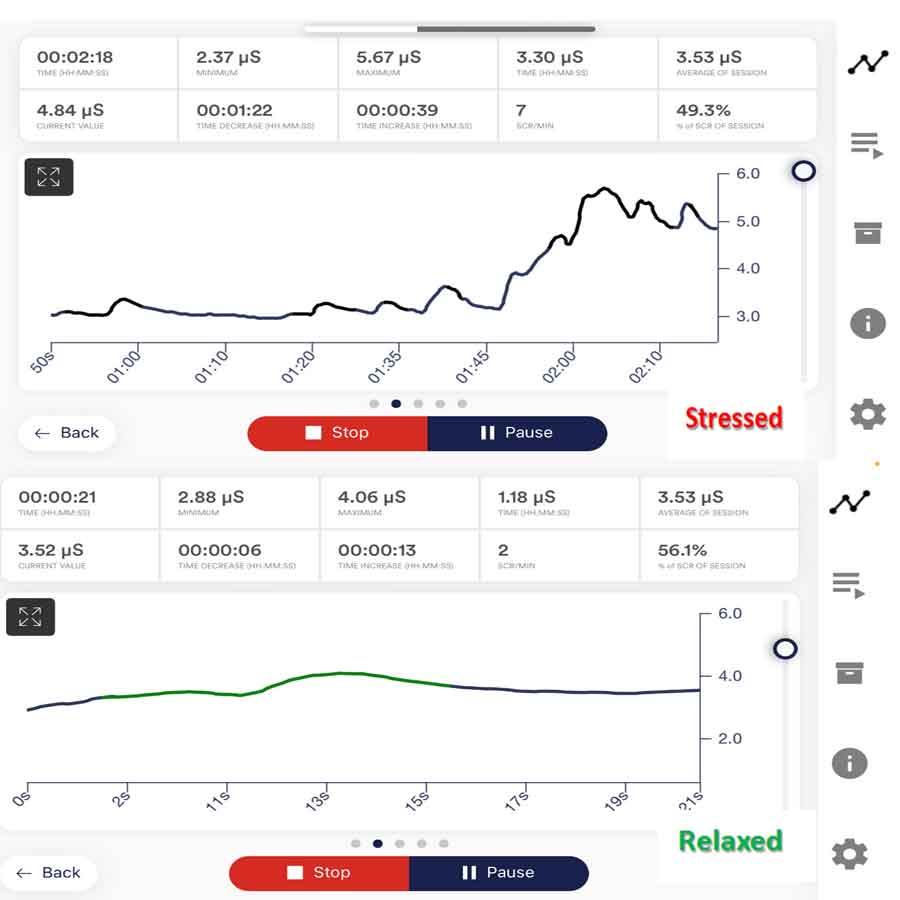
2. During EDA Biofeedback Session:
• During an EDA biofeedback session, individuals are connected to biofeedback equipment that measures their skin conductance level, typically using electrodes placed on the fingers or palm of the hand.
• Visual or auditory cues provide real-time feedback on changes in skin conductance, allowing individuals to observe their physiological responses and learn to modulate them.
• Individuals are guided through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, visualization, or mindfulness exercises, while monitoring their skin conductance on the biofeedback display.
• By consciously inducing a state of relaxation and reducing sympathetic arousal, individuals learn to lower their skin conductance levels and promote a sense of calmness.
3. After EDA Biofeedback Session:
• After completing an EDA biofeedback session, individuals may experience immediate reductions in skin conductance and feelings of physical relaxation.
• By learning to regulate sympathetic nervous system activity, individuals can alleviate physiological symptoms associated with anxiety, such as sweating or clamminess.
• With continued practice over multiple sessions, individuals may notice longer-lasting effects, including improvements in overall stress resilience, emotional well-being, and the ability to manage anxiety-related physiological responses.
• EDA biofeedback training can also help individuals develop greater awareness of their physiological arousal patterns and the ability to intervene proactively to reduce stress and anxiety in daily life.
In summary, EDA biofeedback devices for anxiety work by training individuals to recognize and regulate changes in skin conductance, reflecting sympathetic nervous system activity. Through repeated practice, EDA biofeedback can lead to immediate and long-term improvements in physiological relaxation, stress resilience, and emotional well-being, empowering individuals to manage anxiety-related physiological responses more effectively in daily life.
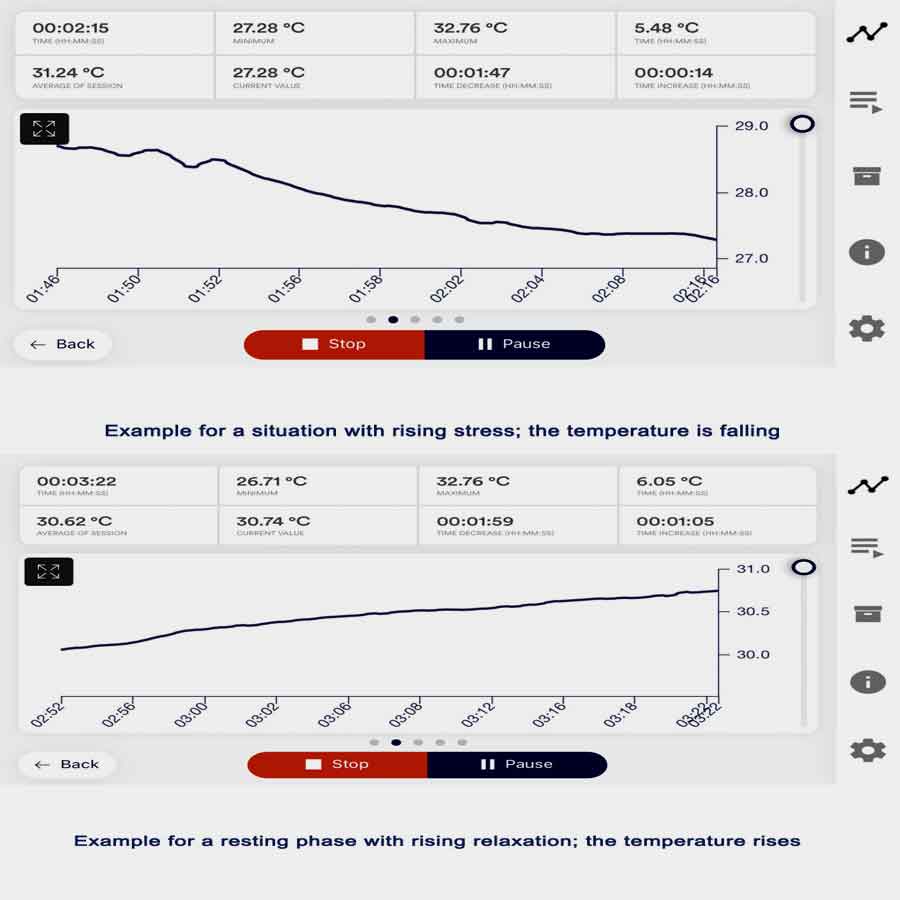
Temperature Biofeedback Devices for Anxiety Management
Temperature biofeedback is a technique that involves training individuals to regulate their skin temperature, typically in the hands or fingers, to promote relaxation and reduce symptoms of anxiety. Here’s how temperature biofeedback devices for anxiety management work in anxiety, including the initial changes in anxiety and the effects after a biofeedback session.
1. Initial Changes in Anxiety:
• Anxiety often leads to physiological changes in the body, including alterations in peripheral blood flow and skin temperature.
• When individuals experience stress or anxiety, the sympathetic nervous system becomes activated, leading to vasoconstriction in peripheral blood vessels, including those in the hands.
• This vasoconstriction reduces blood flow to the hands and can lead to a decrease in skin temperature, resulting in sensations of coldness or clamminess in the hands.
• These changes in skin temperature are often accompanied by feelings of tension, discomfort, or physiological arousal associated with anxiety.
2. During Temperature Biofeedback Session:
• During a temperature biofeedback session, individuals are connected to biofeedback equipment that measures their skin temperature, typically using thermistors or infrared sensors placed on the fingers or hands.
• Visual or auditory cues provide real-time feedback on changes in skin temperature, allowing individuals to observe their physiological responses and learn to modulate them.
• Individuals are guided through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery while monitoring their skin temperature on the biofeedback display.
• By consciously inducing a state of relaxation and promoting peripheral vasodilation, individuals learn to increase blood flow to the hands and raise skin temperature, promoting a sense of warmth and relaxation.
3. After Temperature Biofeedback Session:
• After completing a temperature biofeedback session, individuals may experience immediate reductions in skin temperature and feelings of physical relaxation.
• By learning to regulate peripheral blood flow and skin temperature, individuals can alleviate physiological symptoms associated with anxiety, such as cold hands or clamminess.
• With continued practice over multiple sessions, individuals may notice longer-lasting effects, including improvements in overall stress resilience, emotional well-being, and the ability to manage anxiety-related physiological responses.
• Temperature biofeedback training can also help individuals develop greater awareness of their physiological arousal patterns and the ability to intervene proactively to reduce stress and anxiety in daily life.
In summary, temperature biofeedback devices for anxiety work by training individuals to regulate their skin temperature to promote relaxation and reduce symptoms of anxiety. Through repeated practice, temperature biofeedback can lead to immediate and long-term improvements in physiological relaxation, stress resilience, and emotional well-being, empowering individuals to manage anxiety-related physiological responses more effectively in daily life.
EEG Biofeedback Devices for Anxiety Management
EEG (Electroencephalography) biofeedback, also known as neurofeedback or EEG neurofeedback, is a technique that focuses on training individuals to regulate their brainwave activity to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and alleviate symptoms of anxiety. For further information on the EEG Biofeedback (Neurofeedback) technique (including neurofeedback protocols) in anxiety management, please refer to the article titled “Neurofeedback for Anxiety Disorders.”
Here’s how EEG biofeedback devices for anxiety management work, including the initial changes in anxiety and the effects after a biofeedback session.
1. Initial Changes in Anxiety:
• Anxiety often involves dysregulation of brainwave activity, including increased activity in regions of the brain associated with heightened arousal and emotional reactivity.
• Individuals experiencing anxiety may exhibit patterns of excessive beta wave activity, which is associated with alertness, rumination, and stress.
• Other individuals may show imbalances in alpha, theta, or delta wave activity, which can contribute to difficulties in attention, relaxation, and emotional regulation.
• These patterns of brainwave activity can exacerbate feelings of anxiety, leading to a cycle of heightened stress and physiological arousal.
2. During EEG Biofeedback Session:
• During an EEG biofeedback session, individuals are connected to biofeedback equipment that measures their brainwave activity, typically using electrodes placed on the scalp (Video – Practical guides for measurement for EEG 10-20 system electrode placement for Neurofeedback).
• Visual or auditory cues provide real-time feedback on changes in brainwave activity, allowing individuals to observe their brainwave patterns and learn to modulate them.
• Individuals are guided through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, mindfulness, or visualization exercises while monitoring their brainwave activity on the biofeedback display.
• By consciously inducing a state of relaxation and promoting desirable patterns of brainwave activity, individuals learn to regulate their neural responses and reduce stress and anxiety.
3. After EEG Biofeedback Session:
• After completing an EEG biofeedback session, individuals may experience immediate reductions in symptoms of anxiety, such as decreased rumination, improved mood, and increased feelings of calmness.
• By learning to modulate their brainwave activity, individuals can alleviate physiological and cognitive symptoms associated with anxiety, promoting a sense of emotional well-being and relaxation.
• With continued practice over multiple sessions, individuals may notice longer-lasting effects, including improvements in overall brainwave regulation, stress resilience, and emotional self-regulation.
• EEG biofeedback training can also help individuals develop greater self-awareness of their cognitive and emotional states and the ability to intervene proactively to reduce stress and anxiety in daily life.
In summary, EEG biofeedback device for anxiety management work by training individuals to regulate their brainwave activity to promote relaxation and reduce symptoms of anxiety. Through repeated practice, EEG biofeedback can lead to immediate and long-term improvements in brainwave regulation, stress resilience, and emotional well-being, empowering individuals to manage anxiety-related symptoms more effectively in daily life.
Integrative Biofeedback Systems for Anxiety Management
• Some biofeedback devices integrate multiple sensors and modalities to provide comprehensive feedback on various physiological parameters simultaneously.
• These integrative systems may combine measurements of heart rate, respiration, skin conductance, temperature, and muscle tension to offer a holistic assessment of the individual’s physiological state.
• Integrative biofeedback systems can be particularly useful for addressing complex patterns of physiological arousal and tailoring interventions to individual needs.
By exploring the different types of biofeedback devices available, individuals can identify the most suitable tools for monitoring and regulating their physiological responses to anxiety. Whether focusing on heart rate variability, electrodermal activity, respiration, muscle tension, or brainwave activity, biofeedback devices offer versatile options for promoting self-awareness, relaxation, and emotional well-being.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Biofeedback Device
Selecting the right biofeedback device is crucial for effectively managing anxiety and achieving desired outcomes. Several key factors should be considered when choosing a biofeedback device to ensure compatibility with individual needs, preferences, and goals.
Accuracy and Reliability
• Accuracy: Choose biofeedback devices that provide precise and reliable measurements of physiological parameters, as inaccurate data may compromise the effectiveness of biofeedback interventions.
• Reliability: Look for devices that have been validated through scientific research and testing to ensure consistent performance and reproducible results.
Ease of Use
• User-Friendly Interface: Opt for biofeedback devices with intuitive interfaces and clear instructions for operation, making it easy for individuals to navigate and utilize the device effectively.
• Setup and Calibration: Consider the ease of setup and calibration procedures, as cumbersome or complex processes may deter users from using the device regularly.
Compatibility and Connectivity
• Device Compatibility: Ensure that the biofeedback device is compatible with the platforms and devices you intend to use, such as smartphones, tablets, or computers.
• Connectivity Options: Look for biofeedback devices that offer multiple connectivity options, such as Bluetooth, USB, or wireless connectivity, to facilitate data transfer and integration with other devices and software.
Feedback Mechanisms
• Visual Feedback: Evaluate the type and quality of visual feedback provided by the biofeedback device, such as graphs, charts, or animations, to ensure clarity and effectiveness in conveying physiological information.
• Auditory Feedback: Consider whether the device offers auditory cues or sound effects to complement visual feedback, as auditory stimuli can enhance engagement and attention during biofeedback training sessions.
Customization and Personalization
• Customization Options: Choose biofeedback devices that allow for customization of settings, parameters, and feedback thresholds to accommodate individual preferences and adapt to evolving needs.
• Personalized Feedback: Look for biofeedback devices that offer personalized feedback based on individual baseline measurements and progress, as personalized interventions are often more effective and motivating.
Cost Considerations
• Initial Investment: Assess the upfront cost of purchasing the biofeedback device, including any additional accessories or software required for operation.
• Long-Term Value: Consider the long-term value proposition of the biofeedback device, taking into account factors such as durability, warranty coverage, and potential for future upgrades or expansions.
• Cost-Benefit Analysis: Evaluate the potential benefits of using the biofeedback device in relation to its cost, weighing the investment against the expected outcomes and improvements in anxiety management and overall well-being.
By carefully considering these factors when choosing a biofeedback device, individuals can select the most suitable tool for their needs and maximize the effectiveness of their anxiety management efforts. Whether prioritizing accuracy, ease of use, connectivity, feedback mechanisms, customization, or cost-effectiveness, the right biofeedback device can empower individuals to gain greater self-awareness, regulate their physiological responses, and achieve meaningful progress in anxiety reduction and emotional resilience.
When selecting a biofeedback modality for anxiety management, it’s essential to consider the individual’s specific symptoms and underlying physiological responses. Different biofeedback modalities target distinct aspects of the body’s stress response system, making them more suitable for addressing specific symptoms associated with anxiety. For example, if an individual experiences prominent symptoms of rumination, characterized by persistent and intrusive thoughts, EEG biofeedback may be particularly beneficial. By training individuals to regulate their brainwave activity, EEG biofeedback helps reduce excessive beta wave activity associated with rumination and promotes a state of calmness and cognitive clarity. On the other hand, if an individual presents with symptoms of tachycardia or elevated heart rate, indicative of heightened sympathetic arousal, HRV (Heart Rate Variability) biofeedback may be more effective. By teaching individuals to modulate their heart rate variability, HRV biofeedback promotes relaxation, reduces physiological arousal, and helps restore balance to the autonomic nervous system. Similarly, individuals experiencing symptoms such as muscle tension, sweating, or clamminess may benefit from EMG (Electromyography) or temperature biofeedback, which focuses on regulating muscle tension or peripheral blood flow, respectively. By tailoring the choice of biofeedback modality to the individual’s specific symptoms and physiological responses, clinicians can maximize the effectiveness of biofeedback training in anxiety management and help individuals achieve meaningful improvements in their overall well-being.
How to Use Biofeedback Devices for Anxiety Relief
Biofeedback devices offer individuals a powerful tool for managing anxiety by providing real-time feedback on physiological responses and facilitating self-regulation techniques. Implementing biofeedback effectively involves understanding how to use these devices in a structured and purposeful manner to achieve anxiety relief.
Setting Realistic Goals
• Start by setting specific, measurable, and achievable goals for using biofeedback to manage anxiety. Identify areas of concern or specific symptoms you want to address, such as reducing heart rate, decreasing muscle tension, or promoting relaxation.
• Break down larger goals into smaller, manageable steps to track progress and maintain motivation. Celebrate achievements along the way to reinforce positive behaviors and outcomes.
Establishing Baselines
• Before beginning biofeedback training, establish baseline measurements of relevant physiological parameters, such as heart rate, respiration rate, skin conductivity, and muscle tension. These baseline measurements serve as a reference point for monitoring progress and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions.
• Conduct baseline assessments in a relaxed and calm state to obtain accurate baseline readings. Record baseline measurements regularly to track changes over time and adjust biofeedback strategies accordingly.
Practicing Regularly
• Consistent practice is essential for maximizing the benefits of biofeedback training for anxiety relief. Incorporate biofeedback sessions into your daily routine and allocate dedicated time for practice.
• Start with shorter practice sessions and gradually increase the duration and frequency as you become more comfortable with the techniques. Aim for regular practice sessions lasting at least 10-20 minutes to experience meaningful benefits.
• Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques during biofeedback sessions to enhance the effectiveness of the training. Focus on deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Integrating Biofeedback with Other Anxiety Management Techniques
• Combine biofeedback training with other evidence-based anxiety management techniques for a comprehensive approach to anxiety relief. Incorporate cognitive-behavioral strategies, mindfulness meditation, physical exercise, and stress management techniques to complement biofeedback interventions.
• Identify triggers and situations that provoke anxiety and develop coping strategies to manage them effectively. Use biofeedback as a tool to reinforce adaptive coping responses and reduce physiological arousal during anxiety-provoking situations.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Strategies
• Regularly monitor your progress by comparing current physiological measurements to baseline values and tracking changes over time. Pay attention to improvements in anxiety symptoms, stress levels, and overall well-being.
• Adjust biofeedback strategies and techniques based on your responses and preferences. Experiment with different biofeedback modalities, feedback mechanisms, and relaxation techniques to find what works best for you.
• Seek feedback from healthcare professionals or biofeedback practitioners to optimize your biofeedback training program and address any challenges or concerns.
By following these guidelines for using biofeedback devices for anxiety relief, individuals can harness the power of biofeedback to cultivate greater self-awareness, relaxation, and emotional resilience. With regular practice and commitment, biofeedback can serve as an effective tool for managing anxiety and improving overall quality of life.
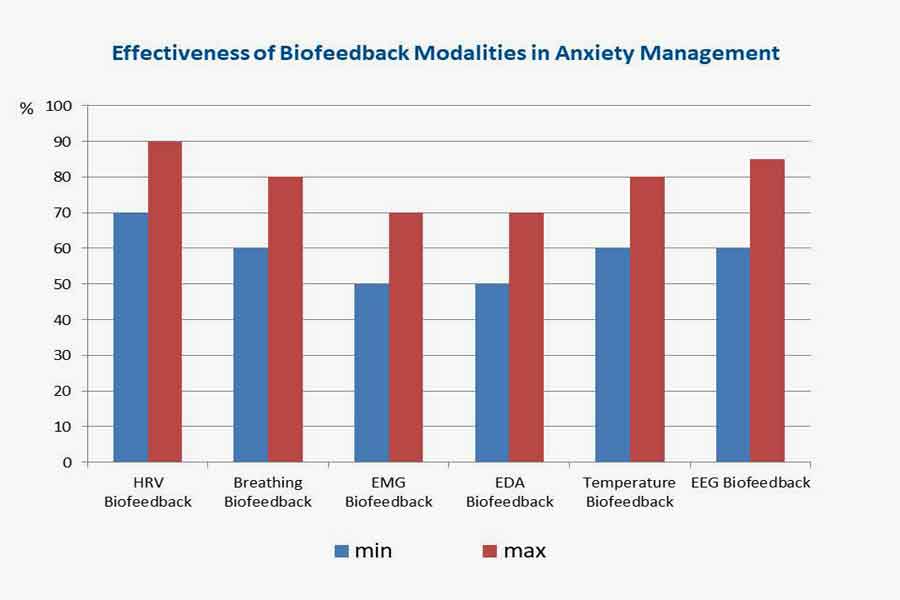
Effectiveness of Biofeedback Modalities in Anxiety Management
Biofeedback modalities offer promising avenues for anxiety management, with various techniques showing effectiveness in empirical studies. Here, we examine the efficacy of different biofeedback modalities based on research data, highlighting the percentage of effectiveness for each modality.
1. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Biofeedback:
Research indicates that HRV biofeedback is highly effective in anxiety management, with studies reporting success rates ranging from 70% to 90%. HRV biofeedback helps individuals regulate autonomic nervous system activity, promoting relaxation and emotional balance. By training individuals to achieve coherence between heart rate variability and respiration, HRV biofeedback can reduce anxiety symptoms and improve overall well-being.
2. Respiration Biofeedback:
Respiration biofeedback has demonstrated moderate to high effectiveness, with success rates ranging from 60% to 80%. Through paced breathing exercises and respiratory rate monitoring, respiration biofeedback helps individuals regulate their breathing patterns, promote relaxation, and reduce symptoms of anxiety. By synchronizing breathing with heart rate variability, respiration biofeedback facilitates the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to increased calmness and emotional well-being.
3. Muscle Tension Biofeedback:
Muscle tension biofeedback is considered moderately effective, with success rates typically ranging from 50% to 70%. By measuring muscle tension levels and providing feedback on electromyographic (EMG) activity, muscle tension biofeedback assists individuals in identifying and reducing excessive muscle tension associated with stress and anxiety. Through progressive muscle relaxation techniques and awareness training, muscle tension biofeedback promotes relaxation and physical comfort, contributing to anxiety reduction.
4. Electrodermal Activity (EDA) Biofeedback:
Studies have shown EDA biofeedback to be moderately effective, with success rates typically ranging from 50% to 70%. EDA biofeedback assists individuals in recognizing physiological signs of anxiety and implementing relaxation techniques to reduce stress and tension. By monitoring changes in skin conductance, EDA biofeedback provides valuable feedback on sympathetic nervous system arousal, helping individuals learn to modulate their stress responses effectively.
5. Temperature Biofeedback
Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of hand warming biofeedback in anxiety management, with success rates ranging from 60% to 80%. By increasing peripheral blood flow and promoting vasodilation, hand-warming biofeedback induces a relaxation response and reduces physiological arousal associated with anxiety. Research suggests that regular practice of hand-warming biofeedback can lead to improvements in anxiety symptoms, stress levels, and overall emotional well-being.
6. EEG Biofeedback:
EEG neurofeedback has shown moderate to high effectiveness in anxiety management, with success rates ranging from 60% to 85%. By monitoring and modulating brainwave activity, EEG neurofeedback helps individuals regulate their brain states and cognitive processes associated with anxiety. Through operant conditioning and reinforcement of desired brainwave patterns, EEG neurofeedback promotes emotional regulation, cognitive flexibility, and resilience to stressors.
Overall, biofeedback modalities offer effective strategies for anxiety management, with each modality demonstrating varying degrees of success in empirical research. By understanding the effectiveness of different biofeedback techniques, individuals can choose the most suitable approach for their needs and preferences, facilitating personalized and targeted interventions for anxiety reduction.
Comparing the effectiveness of biofeedback modalities with other treatment methods
Comparing the effectiveness of biofeedback modalities with other treatment methods for managing anxiety requires consideration of empirical research findings across different interventions. Here’s a comparison of the effectiveness of biofeedback modalities with medication and other treatment methods based on available research data:
1. Medication:
• Effectiveness: Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), benzodiazepines, and beta-blockers are commonly prescribed for anxiety management. Research suggests that medication can be effective for reducing anxiety symptoms in many individuals, with success rates ranging from 50% to 70%.
• However, medication may be associated with side effects, potential dependency, and limited long-term efficacy. Additionally, not all individuals respond positively to medication, and some may require dosage adjustments or alternative treatments due to treatment resistance or intolerance.
2. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
• Effectiveness: CBT is a widely studied and empirically supported psychotherapy approach for anxiety disorders. Research indicates that CBT is highly effective, with success rates ranging from 60% to 80%.
• CBT focuses on identifying and challenging maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors associated with anxiety, teaching coping skills, and promoting behavioral changes. CBT typically involves a structured treatment protocol delivered by trained therapists over a specified number of sessions.
3. Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR):
• Effectiveness: MBSR is a mindfulness-based intervention that incorporates meditation, yoga, and mindfulness practices to reduce stress and anxiety. Research suggests that MBSR can be effective, with success rates ranging from 50% to 70%.
• MBSR emphasizes present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance of thoughts and emotions, helping individuals develop resilience to stressors and cultivate greater emotional well-being. MBSR programs typically involve group-based training sessions and home practice.
4. Relaxation Techniques:
• Effectiveness: Relaxation techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, and guided imagery are commonly used for anxiety management. Research indicates that relaxation techniques can be moderately effective, with success rates ranging from 50% to 70%.
• These techniques promote relaxation, reduce physiological arousal, and alleviate symptoms of anxiety by eliciting the relaxation response and activating the parasympathetic nervous system. Regular practice is often necessary to achieve and maintain benefits.
5. Combined Approaches:
• Effectiveness: Combined approaches, such as medication plus psychotherapy or biofeedback plus mindfulness, are often utilized for comprehensive anxiety management. Research suggests that combining treatments can enhance effectiveness, with success rates ranging from 70% to 90%.
• Combined approaches capitalize on the synergistic effects of different interventions, addressing multiple facets of anxiety through complementary mechanisms. Personalized treatment plans may incorporate a combination of pharmacological, psychological, and behavioral strategies tailored to individual needs and preferences.
In summary, biofeedback modalities offer effective strategies for anxiety management, with success rates comparable to other treatment methods such as medication, cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness-based interventions, and relaxation techniques. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors such as symptom severity, treatment preferences, and response to previous interventions, highlighting the importance of personalized and evidence-based care in anxiety management.
List of references
1. Alneyadi, M., Drissi, N., Almeqbaali, M., & Ouhbi, S.Biofeedback-Based Connected Mental Health Interventions for Anxiety: Systematic Literature Review. JMIR MHealth and UHealth, 2021; 9(4). https://doi.org/10.2196/26038
2. Bandelow, B., Michaelis, S., & Wedekind, D. Treatment of anxiety disorders. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience. 2017; 19(2), 93–107.
3. Banerjee S, Argáez C. Neurofeedback and Biofeedback for Mood and Anxiety Disorders: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2017 Nov 13. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531603/
4. Chittaro, L., & Vianello, A. Evaluation of a mobile mindfulness app distributed through on-line stores: A 4-week study. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies. 2014; 72(4), 337–348. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhcs.2013.11.007
5. Dadashi M, Birashk B, Taremian F, Asgarnejad AA, Momtazi S. Effects of increase in amplitude of occipital alpha & theta brain waves on global functioning level of patients with GAD. Basic J Neurosci [Internet]. 2015 Jan [cited 2017 Oct 17];6(1):14-20. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4741268/pdf/BCN-6-14.pdf
6. Giggins, O. M., Persson, U. M., & Caulfield, B. Biofeedback in rehabilitation. Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation. 2013; 10(1), 60. doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-10-60
7. Lehrer, P. M., & Gevirtz, R. Heart rate variability biofeedback: How and why does it work? Frontiers in Psychology. 2014; 5, 756. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756
8. Moravec, C. S. Neurofeedback therapy for anxiety and anxiety disorders. In M. A. Teixeira (Ed.), Anxiety and Related Disorders. 2019; (pp. 177–191). IntechOpen. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.81768
9. Peira, N., Fredrikson, M., & Pourtois, G. (). Controlling the emotional heart: Heart rate biofeedback improves cardiac control during emotional reactions. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 2019; 146; 114–122. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2019.10.006
10. Rice KM, Blanchard EB, Purcell M. Biofeedback treatments of generalized anxiety disorder: preliminary results. Biofeedback Self Regul. 1993; 18(2):93-105.
11. Rosenbaum, D., Moss, D., Lowry, M., & Pedlow, T. Biofeedback for psychiatric disorders: A systematic review. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 2019; 44(4), 219–232. doi: 10.1007/s10484-019-09442-w
12. Sharma, M., & Rush, S. E. Mindfulness-based stress reduction as a stress management intervention for healthy individuals: A systematic review. Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine, 2014; 19(4), 271–286. doi: 10.1177/2156587214543143
13. Siniatchkin, M., Kropp, P., Gerber, W. D., & Stephani, U. Heart rate variability biofeedback in patients with epilepsy: A pilot study. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 2000; 25(4), 217–227. doi: 10.1023/a:1009563423080
14. Tan, G., Shaffer, F., Lyle, R., & Teo, I. Evidence-based use of heart rate variability biofeedback in clinical practice: A guide to effective use. Biofeedback. 2019; 47(1), 17–28. doi: 10.5298/1081-5937-47.1.03
15. Trudeau, D. L. EEG biofeedback for addictive disorders: A review of the efficacy and mechanisms for a novel treatment. Journal of Neurotherapy. 2005; 9(2), 5–16. doi: 10.1300/j184v09n02_02
16. van Dixhoorn, J., & White, A. Relaxation therapy for rehabilitation and prevention in ischaemic heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation. 2005; 12(3), 193–202. doi: 10.1097/01.hjr.0000176532.15823.68









Add a Comment