Tinnitus is not just an annoying ringing or buzzing in the ears — for many people, it reflects deeper issues involving stress, brain activity, and nervous system imbalances. This is precisely where biofeedback for tinnitus becomes a valuable tool. Unlike conventional therapies, biofeedback for tinnitus focuses on helping individuals regain control over the body’s stress response, muscle tension, and autonomic nervous system. Moreover, neurofeedback tinnitus techniques directly target irregular brainwave patterns often associated with tinnitus perception. Through biofeedback tinnitus training, individuals learn to influence physiological processes, including heart rate variability, breathing, and muscle relaxation.
Additionally, tinnitus biofeedback training often improves resilience to stress, which is known to worsen tinnitus symptoms. In this article, you will discover how these methods work, what benefits they offer, and how to start your own training. If you would like to know more about what tinnitus is, its causes, and symptoms, please read our previous article, CBT for Tinnitus.
Table of Contents
Toggle- Introduction — How Biofeedback and Neurofeedback Relate to Tinnitus
- What is Biofeedback and Neurofeedback from a Tinnitus Perspective?
- Mechanisms of Biofeedback for Tinnitus
- Tinnitus Biofeedback Training Techniques
- Benefits of Biofeedback for Tinnitus
- Evidence-Based Review
- How to Start Tinnitus Biofeedback Training
- Who Should Consider Biofeedback for Tinnitus?
- FAQ – Biofeedback for Tinnitus
- 10. Conclusion: Biofeedback for Tinnitus – A Complementary Solution
- FAQ – Biofeedback for Tinnitus: Does It Work?
Introduction — How Biofeedback and Neurofeedback Relate to Tinnitus
Understanding Tinnitus as a Stress and Autonomic Nervous System Disorder
If you are struggling with tinnitus, you may have noticed that it feels worse when you are anxious, stressed, or tense. This is not a coincidence. Numerous scientific studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between tinnitus and the body’s response to stress, as well as the functioning of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) — the system responsible for regulating vital functions such as heart rate and breathing. When the ANS is out of balance, tinnitus often becomes louder, more disturbing, and harder to ignore.
This is where biofeedback for tinnitus can offer hope. Biofeedback does not simply try to mask or block the sound. Instead, it helps you recognize and regulate the hidden processes within your body that may be contributing to or exacerbating your tinnitus. People with tinnitus often experience what’s called “autonomic dysregulation,” meaning their stress response is too easily triggered, and their nervous system struggles to return to a calm state.
By learning to rebalance your body’s reactions through biofeedback tinnitus techniques, you may reduce not only the stress associated with tinnitus but also the intensity of the sound itself. Understanding this connection is the first step toward taking back control.
The Role of Brainwaves, Muscle Tension, and Heart Rate in Tinnitus Perception
You may also wonder: Why does tinnitus sometimes get louder when I’m tense, tired, or trying to relax?
The answer lies in how your brain and body work together. Research indicates that irregular brainwave patterns, particularly in areas related to hearing and attention, are frequently associated with tinnitus. This is where neurofeedback tinnitus training can help.
Neurofeedback tinnitus methods aim to guide your brain back into healthier brainwave patterns gently. These techniques don’t just tell your brain what to do. They train it through feedback. This helps the brain learn to reduce the abnormal patterns often associated with tinnitus. This is not about forcing change but about allowing your brain to adjust itself.

Additionally, many people with tinnitus unknowingly hold chronic muscle tension, especially in the neck, shoulders, or jaw. This tension can make tinnitus worse or even trigger it. Tinnitus biofeedback training helps you become aware of these tensions and teaches you how to release them. Another critical factor is your heart rate variability (HRV), which reflects how well your nervous system adapts to stress. Reduced HRV is a common finding among individuals with tinnitus and stress-related conditions. Luckily, biofeedback for tinnitus can directly improve HRV, helping your body return to a calmer, more balanced state.
What is Biofeedback and Neurofeedback from a Tinnitus Perspective?
The Basics of Biofeedback and Neurofeedback

If you are dealing with tinnitus, you may feel like your body and mind are working against you. The ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound is often constant and uncontrollable. However, methods like biofeedback for tinnitus and the neurofeedback tinnitus technique are designed to help you regain control. They work by targeting the root of the problem — your body’s and brain’s stress response and regulation systems.
In simple terms, biofeedback tinnitus training helps you “see” what your body is doing unconsciously. For example, with biofeedback, you may learn to monitor and regulate:
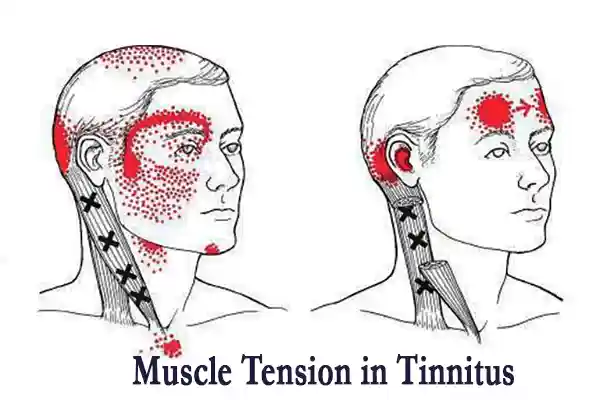
- Muscle tension (especially in the neck, jaw, and shoulders)
- Breathing patterns
- Skin conductance (stress response)
- Body temperature (often linked to vascular tension)
When you have tinnitus, these factors often show signs of dysregulation. For example, your HRV may be too low, indicating that your nervous system is constantly in a state of alertness. Alternatively, you may experience chronic muscle tension, which can exacerbate or even trigger tinnitus symptoms. With biofeedback for tinnitus, you are guided through gentle exercises to regulate these body functions. Over time, your nervous system learns to calm down, resulting in reduced tinnitus intensity, improved sleep, and less emotional distress.
Neurofeedback tinnitus takes this concept a step further by focusing directly on your brainwave patterns. Many tinnitus sufferers exhibit irregular activity in brain regions related to hearing, attention, and emotional regulation. Neurofeedback helps you re-train these brainwaves, encouraging healthier and more stable activity. For many, this leads to less intrusive tinnitus sounds, a reduced sense of alarm when tinnitus is present, and greater mental resilience.
Why These Methods Are Used for Tinnitus Management
One of the most challenging parts of living with tinnitus is that it’s rarely just the sound. Tinnitus is often accompanied by:
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Muscle tension
- Feeling overwhelmed or hopeless
- Heightened stress response
Each of these symptoms can create a vicious cycle where tinnitus worsens, making you feel even more anxious and distressed. Here is how biofeedback tinnitus and neurofeedback tinnitus can help interrupt this cycle:
Anxiety & Stress Reduction
Anxiety often fuels tinnitus. Through biofeedback for tinnitus, you learn to calm your body’s stress response, lower your heart rate, and activate your parasympathetic nervous system — the system responsible for rest and recovery. When anxiety decreases, tinnitus usually becomes less intrusive and distressing.


Muscle Tension Release
For many people, chronic muscle tension in the neck, jaw (TMJ), or shoulders is directly linked to tinnitus. Using muscle-based tinnitus biofeedback training, you will be able to spot unconscious muscle tension patterns and learn to release them. This alone often brings noticeable relief.
Improved Sleep
People with tinnitus often suffer from insomnia due to the constant presence of the sound. HRV biofeedback and neurofeedback can help you regulate your body’s relaxation response, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.

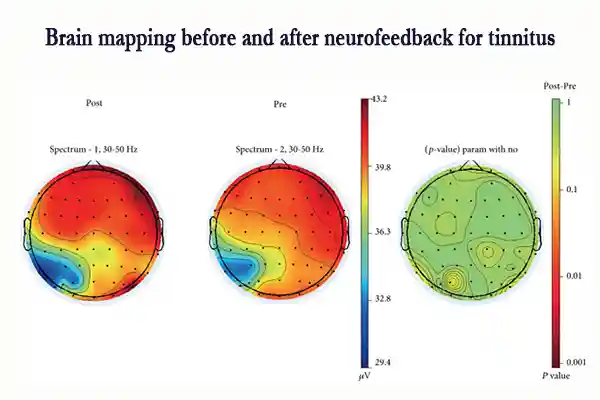
Brainwave Regulation
With neurofeedback tinnitus training, you work directly on normalizing irregular brainwave patterns. Many people with tinnitus show hyperactivity in auditory or attention-related brain areas. Neurofeedback trains the brain to reduce this hyperactivity, helping to lower the perceived loudness and emotional impact of tinnitus.
Cognitive and Emotional Resilience
Tinnitus often creates a feeling of helplessness. Both biofeedback tinnitus and neurofeedback tinnitus training build up your ability to cope emotionally and cognitively with the condition. Many users report that even if the sound is still present, it becomes less bothersome and no longer dominates their lives.
Better Adaptation to Everyday Stress
Stress can worsen tinnitus, but with tinnitus biofeedback training, you can improve your overall ability to adapt to life’s daily challenges. This leads to fewer flare-ups, less emotional reactivity to tinnitus, and greater peace of mind.
In short, biofeedback for tinnitus and neurofeedback tinnitus offers you something that typical treatments often cannot — active participation in your own healing. By learning to directly influence the biological and neurological patterns associated with your tinnitus, you don’t just mask the symptom; you work towards addressing its root causes.
In the following sections of this guide, you will learn about the most effective types of biofeedback tinnitus methods, how to choose the right one for your situation, and how you can start your own home-based training.
Mechanisms of Biofeedback for Tinnitus
How Biofeedback Influences the Body’s Response to Tinnitus
If you are reading this, you probably feel that tinnitus is not just about the sound itself — it’s about how your whole body reacts to it. The key idea behind biofeedback for tinnitus is that by regulating your body’s response, you can reduce both the intensity of tinnitus and how much it bothers you.
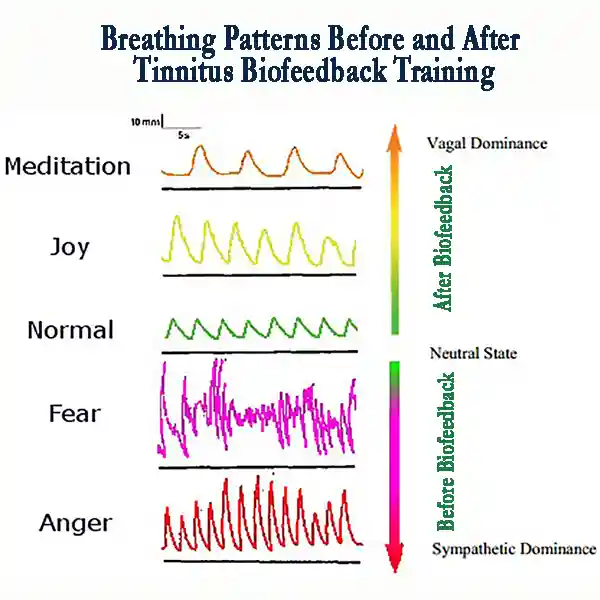
People with tinnitus often have an overactive stress system. The ringing may feel louder when you’re anxious, tense, or under pressure. Biofeedback tinnitus training works by providing you with real-time information about your body’s stress-related signals, such as heart rate variability, muscle tension, breathing patterns, or skin conductance. These are processes that most people are unaware of, yet they have a direct influence on tinnitus intensity.
By using tinnitus biofeedback training, you learn to adjust these functions consciously:
- Lower muscle tension in your neck, shoulders, and jaw
- Slow down and regulate your breathing
- Increase your heart rate variability (HRV)
- Calm down your stress-response system
As you practice, your body begins to remember how to maintain a more balanced state, even when tinnitus is present. Over time, this leads to:
- Reduced tinnitus intensity
- Fewer spikes triggered by stress
- Improved sense of control
You will no longer feel like tinnitus is an unstoppable force — you will have tools to influence how your body responds to it.
Stress Regulation, Autonomic Balance, and Tinnitus
Tinnitus is closely linked to dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Your ANS has two main branches:
- The sympathetic branch (fight-or-flight mode)
- The parasympathetic branch (rest-and-repair mode)
Tinnitus sufferers often exhibit signs of sympathetic dominance, indicating that their body is constantly in a state of fight-or-flight mode. This is why tinnitus often feels worse when you’re stressed, tired, or overwhelmed. Biofeedback for tinnitus aims to restore balance to your autonomic nervous system (ANS) by strengthening parasympathetic activity and calming sympathetic overactivation.
For example:
- HRV biofeedback helps you increase your heart rate variability, which is a marker of resilience and relaxation.
- Respiration biofeedback teaches you to breathe in a way that activates the vagus nerve, calming your nervous system.
- Muscle biofeedback helps reduce tension that contributes to tinnitus or worsens its perception.
As you train, you will notice that you are less reactive to tinnitus. Even if the sound is still present, it no longer bothers you as much. You may sleep better, concentrate more easily, and enjoy daily activities again.
Neurofeedback for Tinnitus: Modulating Brain Activity Patterns
Understanding Tinnitus and Brain Activity
While biofeedback helps regulate the body, neurofeedback tinnitus training targets the brain directly. Neuroimaging studies have revealed that individuals with tinnitus often exhibit abnormal brain activity, particularly in the auditory cortex and related brain regions.
These abnormalities include:
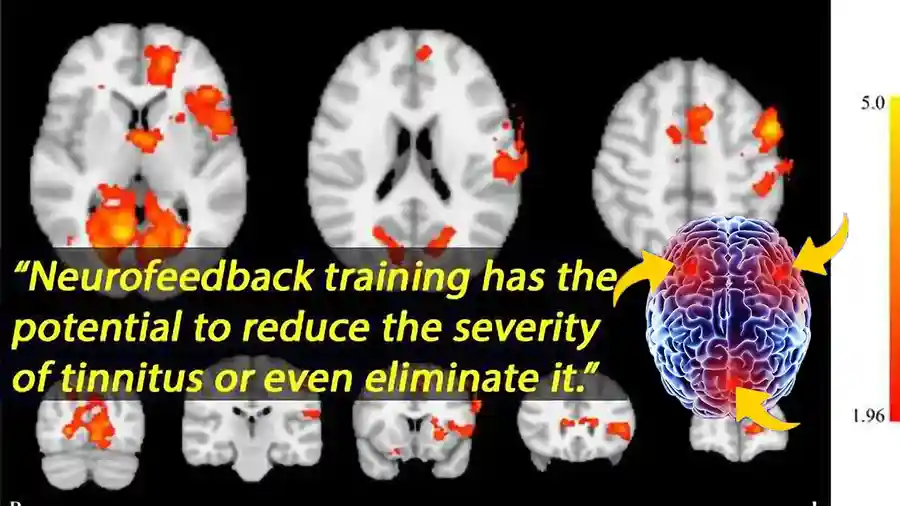
- Excessive high-frequency beta or gamma activity (hyperarousal) in the auditory cortex and other brain areas.
- Decreased alpha activity (which is associated with relaxation and calmness) in the temporal regions, leading to difficulties in relaxation.
- Imbalanced connectivity between auditory, limbic (emotional), and attentional brain circuits. These disruptions explain why tinnitus is not only heard as sound but also becomes an emotional and cognitive burden.
How Brainwaves Affect Tinnitus Perception
Moreover, research has shown that individuals with tinnitus display changes in brainwave patterns, including:
- Enhanced delta wave activity (1–4 Hz), especially in the temporal regions, which is associated with increased sensory processing.
- Increased gamma frequency coupling (above 30 Hz) between distant brain regions, linking auditory processing with cognitive and emotional control areas.
- Altered cortical network patterns, indicating the involvement of both the auditory and prefrontal brain regions in tinnitus perception and emotional response.
The Power of Neurofeedback for Tinnitus Relief
With neurofeedback tinnitus training, you can learn to reshape these abnormal brain patterns. Through non-invasive neurofeedback devices, you receive real-time information about your brainwaves. The system rewards healthier brainwave activity, such as increasing alpha waves (promoting relaxation) and reducing overactive beta or gamma waves (which are associated with hyperarousal).
As you train your brain to modulate these patterns, you may experience several benefits, including:
- Reduced tinnitus loudness perception as the brain learns to filter out the sound.
- Better emotional detachment from the sound, reducing distress and anxiety associated with tinnitus.
- Lower reactivity and distress, leading to less emotional burden from the tinnitus.
- Increased mental calmness, as the brain regains a more balanced state.
Some individuals report that their brain begins to “filter out” the tinnitus sound, making it much less noticeable over time.
By combining biofeedback for tinnitus and neurofeedback tinnitus techniques, you are addressing both the body and brain, providing a holistic approach. While biofeedback helps with regulating bodily responses, neurofeedback works to re-adapt the brain’s activity patterns, offering a powerful, drug-free method for long-term relief.
Tinnitus Biofeedback Training Techniques
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Biofeedback
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) biofeedback is a highly effective technique for managing the physiological responses linked to tinnitus. HRV measures the variation in time between each heartbeat, reflecting the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. A higher HRV indicates a healthier, more flexible autonomic nervous system, which is essential for regulating stress and emotional responses to tinnitus.
HeartMath Inner Balance for Focus & Calm is an excellent tool for those seeking to practice HRV training. By using this device, individuals can monitor their heart rate in real-time and receive feedback on how to adjust their breathing to optimize HRV. This training helps to balance the nervous system, reduce the intensity of tinnitus symptoms, and enhance overall well-being.
Through regular HRV biofeedback tinnitus training, individuals can expect:
- Reduced stress responses that often worsen tinnitus
- Better regulation of the autonomic nervous system function
- A sense of control over tinnitus intensity and related anxiety
To learn more about how to perform HRV training and to get started with your own HeartMath Inner Balance for Focus & Calm HRV Biofeedback Device, visit our HRV biofeedback training page at [insert link here]. This device provides real-time feedback, allowing you to easily monitor and improve your HRV levels from the comfort of your home.
Muscle Tension (EMG) Biofeedback
Muscle tension is a significant factor in the perception and exacerbation of tinnitus. Many individuals with tinnitus unknowingly clench their jaw or tighten the muscles in their neck and shoulders, which can contribute to stress and increase the intensity of their tinnitus. EMG biofeedback for tinnitus helps individuals become more aware of muscle tension and learn how to relax those areas to alleviate discomfort consciously.
NeuroTrac EMG Biofeedback Equipment is an ideal tool for monitoring muscle tension. It provides real-time feedback on muscle activity, guiding you to relax the muscles in the jaw, neck, or scalp areas often associated with tinnitus. By reducing muscle tension, you can decrease the physical stress that triggers or worsens tinnitus symptoms.
Benefits of EMG biofeedback for tinnitus include:
- Reduced muscle tension in the head, neck, and shoulders
- Lowered stress responses and reduced tinnitus perception
- Improved relaxation and mental clarity
To start practicing EMG biofeedback for tinnitus, consider the NeuroTrac EMG Biofeedback Equipment. This device helps you target specific muscle groups, offering immediate feedback to ensure you’re relaxing your muscles correctly. For more information and to get your NeuroTrac EMG Biofeedback Equipment, visit our product page.
Neurofeedback Tinnitus Protocols
Retraining the Brain: Neurofeedback for Tinnitus
Neurofeedback for tinnitus aims to retrain brain activity, particularly in the auditory cortex, to reduce the perception of tinnitus. Research has shown that abnormal brainwave patterns—particularly in the higher frequency ranges (beta, gamma)—are commonly associated with tinnitus. Neurofeedback helps regulate these patterns by providing real-time feedback on brain activity, enabling individuals to learn how to modify their brainwave states.
For neurofeedback tinnitus, a standard protocol typically involves placing electrodes on the scalp to measure brainwave activity. According to the 10-20 electrode placement system, the electrodes are positioned on the following regions:
- Cz (central area) for general brainwave activity,
- P3 and P4 (posterior regions) to target areas of the brain associated with auditory processing,
- F3 and F4 (frontal regions) to promote calmness and reduce anxiety.
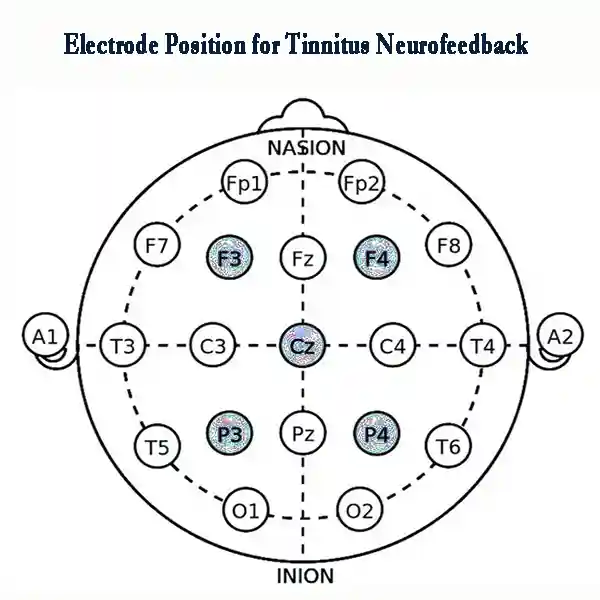
Neurofeedback tinnitus training sessions typically target enhancing low-frequency brainwave activity (alpha and theta waves) while reducing high-frequency activity. This helps the brain shift away from the hyperactivity often linked to tinnitus, leading to a reduction in symptom intensity.
Alternative Neurofeedback Solutions: Mendi Headband and NeuroVizr
An alternative to traditional EEG neurofeedback is the use of non-EEG neurofeedback devices, such as the Mendi Headband or the NeuroVizr.
These devices utilize different methods to influence brain activity:
- Mendi Headband: A non-invasive, user-friendly device that provides real-time feedback on brainwave activity. It utilizes a combination of audio-visual cues to guide the user into a relaxed, focused state, which may help modulate tinnitus perception. The Mendi Headband can be especially useful for those seeking a simple, at-home neurofeedback solution without the need for complex EEG setups.
- NeuroVizr: This innovative device combines neurofeedback with sensory stimulation to promote relaxation and cognitive enhancement. It uses a combination of light and sound to guide the brain into optimal states, helping reduce tinnitus symptoms and improve overall brain function.
Both devices offer accessible, at-home solutions for those seeking to benefit from neurofeedback without traditional equipment.
Relaxation, Breathing, and Mindfulness in Biofeedback Sessions
Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness into biofeedback sessions for tinnitus can significantly enhance the effectiveness of treatment. Stress is a major contributor to tinnitus, and managing it through relaxation techniques can help reduce the severity of symptoms. These techniques work by calming the nervous system, reducing tension, and promoting a sense of well-being.
The BioSignals 5 Biofeedback Sensors Device is an excellent tool for incorporating breathing exercises into your tinnitus management routine. This device monitors your breathing patterns and provides feedback on how to slow your breath and promote relaxation. Slow, deep breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress and helping mitigate tinnitus perception.
Benefits of breathing biofeedback tinnitus training include:
- Reduced anxiety and stress
- Improved relaxation and emotional regulation
- Enhanced ability to manage tinnitus-related discomfort
To start using breathing techniques to manage your tinnitus, visit our BioSignals 5 Biofeedback Sensors Device page and learn more about how it can help you manage your symptoms through controlled breathing techniques.
When practiced regularly, these biofeedback techniques can provide individuals with significant relief from tinnitus. If you’re interested in exploring these methods further, be sure to check out the recommended devices, which can be a valuable addition to your tinnitus management plan. For more detailed information on each technique and device, visit our product pages and begin your journey toward tinnitus relief today.
Benefits of Biofeedback for Tinnitus
Tinnitus Loudness and Distress Reduction
One of the most immediate and significant benefits of biofeedback for tinnitus is the reduction in both the loudness and emotional distress caused by the condition. Many individuals with tinnitus experience an amplification of their symptoms when they are stressed, anxious, or fatigued. Biofeedback training helps break this cycle by providing individuals with real-time feedback on their physiological responses, enabling them to gain control over their body’s reactions to tinnitus.
HRV biofeedback, EMG biofeedback, and neurofeedback can significantly impact tinnitus perception. By learning to regulate stress responses and muscle tension, you can lower the intensity of tinnitus sounds. For example:
- HRV biofeedback can help improve autonomic balance, leading to reduced sensitivity to tinnitus.
- EMG biofeedback trains you to relax tense muscles that may contribute to a heightened perception of tinnitus.
- Neurofeedback focuses on modulating brainwave activity, which directly influences auditory processing and emotional regulation related to tinnitus.
By consistently practicing biofeedback techniques, individuals report a noticeable reduction in both the loudness of tinnitus and the distress associated with the condition. Over time, this can help restore a sense of control and reduce the impact that tinnitus has on daily life.
If you’re ready to begin your journey toward reducing tinnitus loudness and distress, the HeartMath Inner Balance for Focus & Calm HRV Biofeedback Device, NeuroTrac EMG Biofeedback Equipment, or Mendi Headband (for neurofeedback) are excellent tools to consider. Visit our product pages to learn more.
Emotional and Physical Stress Management
Stress is a significant trigger and exacerbator of tinnitus symptoms. Whether it’s emotional stress, physical tension, or both, individuals with tinnitus often experience an intensification of their symptoms when under stress. Biofeedback offers an effective, non-invasive approach to managing both the emotional and physical aspects of stress.
Through biofeedback training, individuals can learn to activate their parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and counteracting the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. Techniques such as HRV biofeedback and EMG biofeedback focus on:
- Reducing muscle tension (especially in areas such as the jaw and neck) that may exacerbate tinnitus.
- Managing stress responses that increase tinnitus intensity.
- Calming the mind, which reduces the emotional distress and anxiety commonly associated with tinnitus.
By practicing biofeedback techniques regularly, people with tinnitus can significantly reduce the impact of stress on their symptoms, leading to both emotional and physical stress management. This, in turn, helps create a more balanced and peaceful state of being.
To begin managing your stress and tinnitus symptoms, consider using devices such as the HeartMath Inner Balance for Focus & Calm HRV Biofeedback Device, the Neurotrac Simplex EMG biofeedback device, or the NeuroVizr neurofeedback system. These tools will help you gain control over your body’s response to stress and improve your emotional and physical well-being.
Sleep and Cognitive Function Improvements
Biofeedback for Better Sleep: Alleviating Tinnitus Disruptions
Tinnitus can significantly disrupt sleep, with individuals often reporting difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep due to the constant ringing or buzzing in their ears. Additionally, the anxiety, stress, and cognitive overload caused by tinnitus can impair focus and concentration. Fortunately, biofeedback can help alleviate these issues by promoting relaxation, improving sleep quality, and enhancing cognitive function.
- Improved Sleep Quality: The relaxation achieved through HRV biofeedback, neurofeedback, and muscle relaxation training (EMG biofeedback) can help reduce the physiological arousal that keeps individuals awake at night. By training the body to enter a more relaxed state, biofeedback enables individuals to fall asleep more easily and enjoy deeper, restorative sleep.
Enhancing Cognitive Function and Reducing Stress with Biofeedback
- Enhanced Cognitive Function: Neurofeedback has been shown to improve attention, memory, and cognitive performance by training the brain to function more efficiently. For tinnitus sufferers, this is particularly helpful in combating cognitive fog or distraction caused by the constant noise. By modulating brain activity, neurofeedback helps restore cognitive clarity, improving concentration and focus.
- Stress Reduction: The BioSignals 5 Biofeedback Sensors Device helps regulate breathing patterns, which is vital for controlling the body’s stress response and achieving better sleep. Deep breathing exercises reduce cortisol levels and promote a more relaxed state, preparing the body for rest.
With biofeedback tinnitus training, individuals report improved sleep quality, sharper cognitive function, and an overall sense of well-being. These benefits help alleviate the burden that tinnitus places on daily life, enabling better mental and physical health.
If you’re looking to enhance your sleep and cognitive function while managing your tinnitus, consider the HeartMath Inner Balance for Focus & Calm HRV Biofeedback Device, the NeuroTrac EMG Biofeedback Equipment, or the NeuroVizr neurofeedback device. These tools are designed to support your efforts to improve your quality of life and get a better night’s sleep.
Biofeedback offers a comprehensive solution for those struggling with tinnitus. Whether you’re looking to reduce loudness, manage stress, improve sleep, or enhance cognitive function, these techniques can significantly improve your quality of life. To explore the best biofeedback device for your needs, visit our product pages for detailed information on the HeartMath Inner Balance for Focus & Calm HRV Biofeedback Device, the NeuroTrac EMG Biofeedback Equipment, the Mendi Headband, and the NeuroVizr.
Evidence-Based Review
What Research Says About Biofeedback and Neurofeedback for Tinnitus
When it comes to managing tinnitus, many people seek effective, non-invasive treatments that don’t involve medication. Biofeedback and neurofeedback have gained attention as promising options for individuals with tinnitus. Research suggests that these therapies can help reduce the intensity and distress of tinnitus, providing individuals with a better quality of life.
Numerous studies have shown that biofeedback and neurofeedback can lead to improvements in the way the brain processes tinnitus. For example, neurofeedback helps retrain brainwaves and may enhance the brain’s ability to handle tinnitus-related signals. Individuals who have utilized neurofeedback for tinnitus have reported a decrease in the loudness of their tinnitus, as well as a reduction in anxiety and stress associated with the condition.
Additionally, studies involving biofeedback for tinnitus, particularly HRV biofeedback and EMG biofeedback, have demonstrated positive effects in reducing stress and calming the nervous system. Since stress is often a major trigger for tinnitus flare-ups, learning how to manage it can significantly reduce the perception of tinnitus sounds.
Overall, research suggests that both biofeedback and neurofeedback can play a significant role in tinnitus management, providing relief to many individuals by targeting the physiological and psychological factors that exacerbate tinnitus symptoms.
Success Stories and Clinical Case Examples
Numerous success stories and real-life case examples demonstrate the effectiveness of biofeedback and neurofeedback in managing tinnitus. Many people who have struggled with persistent tinnitus have found relief through these treatments, often reporting remarkable improvements in both the loudness and distress caused by the condition.
A typical success story involves individuals who have utilized HRV biofeedback to mitigate the severity of their tinnitus. By practicing breathing exercises and learning how to control their heart rate variability, they’ve been able to manage their body’s stress response and reduce the volume of tinnitus sounds. In some cases, patients have experienced relief after just a few sessions.
For neurofeedback tinnitus protocols, there are reports of individuals who have undergone brainwave training to retrain their brain’s response to tinnitus. These patients report improvements in their ability to tolerate tinnitus and a reduction in the anxiety and distress associated with it. Some have even shared that they no longer experience the constant ringing in their ears or have learned to “ignore” it over time, leading to a more peaceful daily life.
In clinical settings, these therapies have also shown positive outcomes. Doctors and audiologists often recommend biofeedback and neurofeedback to their patients with tinnitus as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Many individuals have benefited from combining these therapies with other methods, such as counseling and sound therapy.
These success stories highlight the potential of biofeedback and neurofeedback in providing relief for individuals with tinnitus, demonstrating that consistent practice can lead to significant improvements.
Limitations and Ongoing Research
While biofeedback and neurofeedback offer promising results for tinnitus sufferers, it’s essential to acknowledge that they are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Not every individual will experience the same level of improvement, and some may find limited relief or require ongoing treatment. Results can vary depending on the severity of tinnitus, the individual’s overall health, and the commitment to regular training.
Ongoing research continues to investigate how these therapies work and identify which individuals benefit the most. For example, while neurofeedback has been shown to help regulate brainwave activity, further studies are needed to understand its long-term effects and how best to tailor neurofeedback protocols to different types of tinnitus. Similarly, HRV biofeedback and EMG biofeedback have been shown to be helpful in managing stress and muscle tension; however, further research is needed to identify the specific mechanisms that reduce tinnitus symptoms.
Moreover, because biofeedback and neurofeedback are relatively new treatments for tinnitus, they may not yet be universally accepted or understood by all healthcare professionals. However, the growing body of research and positive patient outcomes suggest that these therapies will continue to gain popularity and may become a standard part of tinnitus management in the future.
As research progresses, we can expect to see even more refined and targeted approaches to using biofeedback and neurofeedback for tinnitus. For now, the evidence suggests that these therapies are a valuable tool in managing tinnitus and improving the lives of those affected by it.
How to Start Tinnitus Biofeedback Training
Embarking on tinnitus biofeedback training can seem like a big step, but it’s a valuable approach for managing and reducing the distress caused by tinnitus. Whether you’re considering professional sessions, home-based training, or a combination of both, there are a variety of options available to help you get started.
Options: Professional, Home-Based, or Hybrid Approaches
When it comes to tinnitus biofeedback training, you can choose between professional, home-based, or hybrid approaches. Each option offers different levels of guidance, support, and flexibility.
- Professional Biofeedback Training: This option involves working with a trained biofeedback therapist in a clinical setting. The therapist will guide you through the training process, adjusting parameters to suit your specific needs. This approach ensures that you receive expert feedback and personalized advice tailored to your tinnitus symptoms. It’s especially beneficial for those who need additional support or have complex tinnitus cases.
- Home-Based Biofeedback Training: With home-based training, you can practice biofeedback techniques at your convenience, using biofeedback devices specifically designed for at-home use. These devices provide real-time feedback on your body’s responses and allow you to train in a comfortable environment. Many people find this option to be more affordable and flexible, offering the convenience of practicing at their own pace.
- Hybrid Approach: The hybrid model combines both professional and home-based training. Typically, you’ll start with professional sessions to get guidance and feedback from an expert. Afterward, you can continue practicing at home with biofeedback devices, maintaining progress and receiving ongoing support as needed. This option offers the benefits of both worlds, with the flexibility of home training and the expertise of professional guidance.
Available Devices and Tools
Several biofeedback devices are available for tinnitus management, each targeting different bodily systems or brainwave activity.
- HeartMath Inner Balance for Focus & Calm: This device focuses on Heart Rate Variability (HRV) biofeedback, helping you regulate your autonomic nervous system and manage stress levels. HRV training is particularly useful for tinnitus sufferers who experience anxiety or stress, as it helps enhance relaxation and emotional regulation. The Heartmath device provides real-time feedback on your heart rate, allowing you to improve your body’s response to tinnitus-related stress.
- NeuroTrac EMG Biofeedback Equipment Muscle tension (EMG) biofeedback can help reduce the physical tension that often accompanies tinnitus, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and jaw. Using the Neurotrac Simplex Biofeedback Device, you can monitor muscle activity and learn to relax areas where tension may be exacerbating tinnitus symptoms. This device can be especially beneficial for those who experience physical discomfort in addition to the auditory symptoms of tinnitus.
- BioSignals 5 Biofeedback Sensors Device: Breathing plays a key role in regulating stress and tension. The BioSignals Biofeedback Device helps you monitor and optimize your breathing patterns, teaching you how to breathe slowly and deeply, which can reduce the impact of tinnitus. Proper breathing techniques help calm the body and mind, reducing the physiological reactions to tinnitus and improving overall well-being.
- Neurofeedback Devices (e.g., Mendi Headband, NeuroVizr): For neurofeedback tinnitus training, devices such as the Mendi Headband and NeuroVizr are designed to modulate brainwave activity. The Mendi Headband uses non-EEG neurofeedback to train your brain’s activity and help with emotional regulation, relaxation, and mental clarity. The NeuroVizr is another neurofeedback device that can track and influence brainwave patterns related to tinnitus perception, offering a comprehensive tool for self-regulation.
Recommendations for Effective Tinnitus Biofeedback Training
To maximize the benefits of tinnitus biofeedback training, it’s essential to follow these key recommendations:
- Consistency is Key: Just like any skill, biofeedback training requires consistent practice. Set aside time each day to use your biofeedback device, whether you’re using it at home or working with a professional. Over time, you’ll train your body and brain to respond more effectively to tinnitus.
- Focus on Relaxation: Many people with tinnitus experience increased stress, which can exacerbate the perception of the sound. Make relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, muscle relaxation, and mindfulness, a core part of your training. This can significantly reduce the emotional burden of tinnitus.
- Start Slowly and Build Gradually: Begin with short sessions and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable. Biofeedback training is about gradual improvement, so it’s essential to listen to your body and give yourself time to learn.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a journal or log of your tinnitus symptoms and the effects of your training. This will help you track improvements and see patterns in how your biofeedback training is influencing your tinnitus. Additionally, some devices offer built-in progress tracking to help guide your training.
- Consult a Professional if Needed: While home-based devices are effective for many people, seeking professional guidance can provide additional support if you’re struggling with your training or if you have specific concerns. A trained biofeedback therapist can tailor your training and provide expert advice specifically designed to meet your needs.
By selecting the appropriate approach and device for your needs, you can initiate your tinnitus biofeedback training journey and gain control over your symptoms. Remember that this is a gradual process, and with consistency, you can experience relief and regain a sense of calm in your life.
Who Should Consider Biofeedback for Tinnitus?
Biofeedback for tinnitus can be a highly effective method for managing symptoms, but not everyone may be a suitable candidate. In this chapter, we’ll explore who could benefit most from biofeedback training and discuss the limitations and potential contraindications for its use.
Suitable Candidates
Biofeedback Benefits for Tinnitus-Related Stress and Sleep Issues
Biofeedback can benefit a wide range of individuals, particularly those who experience tinnitus-related distress or struggle with managing the emotional and physical impacts of the condition. The following groups of people may find biofeedback especially helpful:
- Individuals with Tinnitus-Induced Stress and Anxiety: If tinnitus causes high levels of stress, anxiety, or emotional distress, biofeedback can help regulate the body’s stress responses. By training to control heart rate, muscle tension, and respiration, individuals can reduce their emotional reactions to the sound of tinnitus, which can help decrease its perceived intensity.
- People with Difficulty Sleeping Due to Tinnitus: Sleep disturbances are common among tinnitus sufferers. Biofeedback techniques, such as HRV and muscle relaxation, can improve sleep by promoting relaxation and reducing the physiological arousal associated with tinnitus. For those who struggle with falling or staying asleep, biofeedback can help restore more peaceful and restorative sleep.
Biofeedback for Musculoskeletal Tension, Long-Term Relief, and Emotional Support
- Tinnitus Sufferers with Coexisting Musculoskeletal Tension: Tinnitus can often lead to muscle tension in the neck, jaw, and shoulders, which may worsen the perception of tinnitus. Biofeedback techniques targeting muscle relaxation, such as EMG (muscle tension) biofeedback, can help alleviate physical discomfort, making tinnitus less intrusive.
- Individuals Seeking Non-Invasive, Drug-Free Treatments: Many tinnitus sufferers are looking for natural or drug-free ways to manage their symptoms. Biofeedback offers a non-invasive, drug-free approach that can be done at home or with a professional. For individuals looking to avoid medications or additional therapies, biofeedback provides an alternative that focuses on self-regulation.
- Those Interested in Long-Term Relief: Biofeedback provides a long-term solution by teaching individuals how to regulate their physiological and mental responses to tinnitus. Unlike temporary relief from medications or sound therapy, biofeedback trains the body and brain to reduce sensitivity to tinnitus over time, promoting lasting changes.
- Individuals with Coexisting Emotional or Psychological Issues: If tinnitus is accompanied by depression, anxiety, or other emotional disorders, biofeedback can help regulate the body’s response to these issues, potentially providing relief from both emotional and auditory distress. This is particularly helpful for individuals who experience a vicious cycle where anxiety worsens tinnitus, and tinnitus worsens anxiety.
Contraindications and Warnings
Contraindications and Warnings for Biofeedback in Tinnitus Management
While biofeedback is generally safe for most individuals, there are certain conditions where it may not be appropriate or where caution should be exercised. It’s essential to be aware of the following contraindications and warnings before starting biofeedback for tinnitus:
- Severe Psychological Disorders: While biofeedback can be effective in managing stress and anxiety, individuals with severe psychological disorders, such as schizophrenia or psychosis, should consult a healthcare professional before starting biofeedback. In some cases, professional therapy may be more appropriate to address underlying psychological issues.
- Pregnancy: Some biofeedback devices, particularly those that use electrical signals (such as muscle biofeedback), may not be suitable for pregnant individuals. It’s essential to consult with a doctor before starting any biofeedback training during pregnancy to ensure the safety of both mother and child.
- Heart Conditions: Biofeedback devices that monitor heart rate, such as the HRV biofeedback device, should be used with caution in individuals with severe heart conditions. Although HRV training can be beneficial for regulating stress, those with certain heart conditions (e.g., arrhythmias or severe hypertension) should consult their doctor before beginning HRV biofeedback.
- Epilepsy or Seizure Disorders: Neurofeedback training involves modulating brainwaves, and for individuals with a history of seizures or epilepsy, this may not always be recommended without medical supervision. Neurofeedback training can potentially alter brainwave activity, which could trigger seizures in sensitive individuals. It is essential to consult with a neurologist before considering neurofeedback.
Biofeedback and Tinnitus: Special Considerations for Specific Populations
- Severe Physical Disabilities: While biofeedback is generally safe, individuals with severe physical disabilities or those with limited mobility may have difficulty using specific biofeedback devices that require manual interaction, such as electromyography (EMG) or heart rate variability (HRV) devices. In such cases, adjustments to the training method or device may be necessary, and consulting a therapist is recommended.
- Children and Adolescents: While biofeedback can be beneficial for managing tinnitus in children, it may require modifications to make the training appropriate for younger individuals. Children and adolescents should undergo biofeedback training under the guidance of a trained therapist who can ensure the process is engaging and effective. Additionally, some devices may not be suitable for younger users.
- Severe Hearing Loss: In cases of profound or complete hearing loss, biofeedback for tinnitus may not be as effective, as tinnitus perception may be closely tied to auditory processing. If an individual has severe hearing loss along with tinnitus, they should seek professional advice to determine if biofeedback is the right approach.
Before starting any biofeedback program, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider. This is particularly important if you have any underlying health conditions or concerns. A medical professional can help assess whether biofeedback is appropriate for your specific situation. They can also advise you on the best course of action.
FAQ – Biofeedback for Tinnitus
Does biofeedback for tinnitus work?
Yes, many people find biofeedback for tinnitus helpful, particularly in reducing stress and the emotional burden associated with tinnitus. While biofeedback may not eliminate the sound itself, it often reduces its perceived intensity and the adverse reactions to it.
Is biofeedback or neurofeedback better for tinnitus?
Both biofeedback and neurofeedback can be effective for tinnitus, but they target different mechanisms. Biofeedback focuses on stress reduction, heart rate variability, and muscle relaxation, whereas neurofeedback aims to correct abnormal brainwave patterns associated with tinnitus. Combining both may bring the best results.
How long does tinnitus biofeedback training take to show results?
Most people need several weeks to a few months of regular biofeedback or neurofeedback training to notice improvement. However, some report positive changes even after the first few sessions, especially regarding relaxation and reduced distress.
Can I do biofeedback tinnitus training at home?
Yes, home-based biofeedback for tinnitus is possible using specialized devices. However, for neurofeedback tinnitus training, professional guidance is often recommended to ensure proper protocols and safety.
Who benefits most from biofeedback for tinnitus?
People who experience tinnitus worsened by stress, anxiety, or muscle tension often benefit the most. Those looking for a non-invasive, side-effect-free approach may also find biofeedback or neurofeedback helpful.
10. Conclusion: Biofeedback for Tinnitus – A Complementary Solution
Final Thoughts
Tinnitus can be a persistent and often debilitating condition, affecting both physical and emotional well-being. While there is no universal cure, biofeedback offers a promising approach to managing tinnitus symptoms. It provides individuals with tools to regulate their body’s responses to the condition. In many cases, it can even reduce the severity of the tinnitus sound itself. Biofeedback focuses on modulating physiological reactions, including heart rate, muscle tension, and brainwave activity. This approach enables individuals to manage tinnitus naturally and non-invasively.
Through biofeedback and neurofeedback, you can address the auditory perception of tinnitus. You can also address the emotional and psychological components that often accompany it. Reducing stress, improving emotional regulation, and retraining the brain’s response to tinnitus can improve quality of life. Biofeedback can be used alone or with other therapies. It provides a holistic, complementary solution tailored to individual needs.
By taking a proactive approach, you can incorporate biofeedback into your tinnitus management plan. This can help you move toward more significant relief, mental clarity, and emotional balance. It’s essential to note that results may vary. Biofeedback is most effective when combined with other lifestyle adjustments and therapies. These adjustments support your overall well-being. As you embark on this journey, remember that gradual and consistent practice is key. These are essential to achieving long-term success.
Recommendations for Getting Started
Getting Started with Biofeedback for Tinnitus: Key Considerations
- Consult with a Healthcare Provider: Before starting biofeedback for tinnitus, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that it’s the right approach for you. They can help assess your specific symptoms. They will guide you on the best modalities for your individual needs. They can also advise you on integrating biofeedback into your overall treatment plan.
- Choose the Right Biofeedback Device: A variety of biofeedback devices are available, targeting different aspects of tinnitus. If you’re considering home-based training, start with devices that suit your symptoms. For example, if you’re dealing with anxiety or stress from tinnitus, HRV biofeedback may be a great starting point. Devices like the Heartmath HRV Biofeedback Device can help you begin. For those experiencing muscle tension, the Neurotrack Simplex Biofeedback Device can help alleviate physical discomfort. For neurofeedback, Mendi Headband and NeuroVizr offer non-invasive, user-friendly options that modulate brainwave patterns to reduce tinnitus-related distress.
- Start Slowly and Be Consistent: Biofeedback training is most effective when practiced consistently over time. Begin with shorter sessions and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable with the process. Patience and regular practice are essential for achieving significant improvements in your tinnitus symptoms.
Maximizing the Effectiveness of Biofeedback for Tinnitus Relief
- Track Your Progress: Keeping a journal or using an app to track your symptoms, progress, and any noticeable changes can help you stay motivated and identify patterns. Tracking your emotional and physical responses during and after each session provides valuable insights into your progress. It helps you fine-tune your approach.
- Combine Biofeedback with Other Therapies: Biofeedback is often most effective when used in combination with other tinnitus management strategies, such as sound therapy, counseling, and relaxation techniques. Consider working with a tinnitus specialist who can help you integrate biofeedback into a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Stay Patient and Positive: Tinnitus management is a journey, and results may take time. Stay committed to the process, remain open to adjusting your approach, and be patient with yourself. Many individuals experience gradual improvements, with some even reporting a significant reduction in tinnitus severity after consistent biofeedback training.
Biofeedback offers a promising, drug-free option for managing tinnitus. It empowers you to take control of your symptoms and enhance your quality of life. By incorporating biofeedback into your routine and combining it with a comprehensive treatment plan, you can alleviate the burden of tinnitus and work toward achieving lasting relief.
FAQ – Biofeedback for Tinnitus: Does It Work?
Tinnitus often worsens when the body is under stress. Many sufferers experience an overactive sympathetic nervous system. Biofeedback helps restore autonomic balance and activate the parasympathetic “rest and repair” state.
- HRV Biofeedback – Improves heart rate variability and stress resilience
- EMG Biofeedback – Releases muscle tension in the neck, jaw, and shoulders
- Respiration Biofeedback – Regulates breathing to calm the nervous system
- Neurofeedback – Retrains irregular brainwave patterns associated with tinnitus perception
Neurofeedback measures and trains your brainwaves in real time. It helps reduce overactive beta and gamma activity, while increasing calming alpha waves, making tinnitus less intrusive and emotionally disruptive.
Yes. It reduces anxiety, improves sleep, and promotes emotional resilience. Users report feeling more in control, less reactive, and less overwhelmed.
Tension in the jaw, neck, and shoulders can directly trigger or worsen tinnitus. EMG biofeedback teaches you to recognize and relax these muscle groups.
Stress, muscle tension, and irregular brain activity amplify tinnitus perception. Biofeedback addresses all three by training your body and brain to relax and regulate themselves more effectively.
With consistent biofeedback training, users typically notice:
- Reduced tinnitus intensity,
- Less stress and anxiety
- Better sleep,
- Improved focus and calm,
- Greater emotional control over the condition.
Many users report benefits within a few weeks. However, consistent training over 6–12 weeks yields the most reliable and lasting improvements.












Ηi there collеagues, how iѕ everything, and what you desire to say concerning this article, in my view its really awesome in favor of me.