Dyslexia is a complex learning disorder that affects individuals’ ability to read, write, and process language effectively. While traditional methods like speech therapy have provided support for years, innovative approaches are now transforming how we approach therapy for dyslexia. Cutting-edge technologies like biofeedback and neurofeedback offer non-invasive solutions directly targeting the brain’s functioning to enhance learning abilities. These methods are especially promising in advancing dyslexia therapy for children and adults alike. For those seeking dyslexia therapy for adults, combining modern techniques with established strategies offers a comprehensive and personalized solution. This article explores these emerging tools’ science, benefits, and effectiveness, highlighting their role in improving dyslexia treatment and expanding access to innovative dyslexia treatment for adults.
Table of Contents
Toggle- What Is Dyslexia and Why Does It Happen?
- Why Dyslexia Therapy Matters
- What Are the Brain Regions Involved in Dyslexia?
- What Are the Brainwave Changes in Dyslexia?
- How Does Biofeedback Work for Dyslexia Therapy?
- How Does Neurofeedback Help Dyslexia Therapy?
- How Does Dyslexia Speech Therapy Work?
- What Is Flashing Light Therapy and How Can It Help Dyslexia?
- Why Is Dyslexia Therapy for Adults Different?
- What Are the Benefits of Biofeedback and Neurofeedback for Dyslexia?
- FAQ – What Is Dyslexia and Why Does It Happen?
What Is Dyslexia and Why Does It Happen?
Dyslexia is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects an individual’s ability to read, write, and process language efficiently. Often misunderstood as a sign of low intelligence or lack of effort, dyslexia is rooted in brain function and structure differences. This condition can manifest in both children and adults, impacting academic performance, self-esteem, and daily life. Fortunately, advancements in therapy for dyslexia, including biofeedback and neurofeedback, offer promising avenues for improving outcomes.
Understanding Dyslexia: Causes and Symptoms
Dyslexia arises from a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors. Research shows that dyslexic individuals exhibit structural and functional differences in key brain regions, including the left temporal lobe, parietal lobe, and occipital lobe—areas critical for language processing and visual-auditory integration.
Causes of Dyslexia
- Genetic Factors:
Dyslexia often runs in families, suggesting a strong genetic component. Variations in certain genes associated with brain development have been linked to the condition.
- Neurological Differences:
Differences in brain activity, particularly in the phonological and orthographic systems, are central to dyslexia. These systems are responsible for decoding sounds and matching them to written symbols.
- Environmental Influences:
Early exposure to language, literacy, and quality education plays a role. While dyslexia is not caused by poor teaching, early intervention through dyslexia therapy can mitigate its impact.
Symptoms of Dyslexia
Dyslexia presents a range of symptoms that vary depending on age and severity. Common signs include:
- Difficulty recognizing words and decoding sounds.
- Problems with spelling and writing.
- Slow reading speed and poor comprehension.
- Challenges in organizing thoughts and expressing ideas in writing.
In adults, dyslexia symptoms may persist as challenges in spelling, reading aloud, or understanding complex written material, underscoring the importance of tailored adult dyslexia treatment.
Who Is Affected by Dyslexia?
Children and Dyslexia
Dyslexia is most often diagnosed during childhood when children begin learning to read. It affects approximately 5-10% of school-aged children, making early intervention crucial. Children with dyslexia often benefit from specialized dyslexia treatment programs, including phonics-based approaches and dyslexia speech therapy to address language deficits.
Challenges for Children:
- Struggling with academic tasks like reading and writing.
- Lower self-confidence due to perceived underachievement.
- Risk of falling behind without adequate support.
Adults and Dyslexia
While dyslexia is often identified in childhood, many individuals reach adulthood without a formal diagnosis. Dyslexia therapy for adults addresses persistent challenges that affect professional and personal life. Adult dyslexia treatment often incorporates advanced tools like qEEG-based neurofeedback, biofeedback, and adaptive learning strategies to improve reading and cognitive skills.
Challenges for Adults:
- Difficulty with tasks requiring strong reading and writing skills, such as email communication or report writing.
- Frustration in learning new skills or adapting to workplace demands.
- Emotional challenges, including anxiety or low self-esteem, stemming from years of unrecognized struggles.
Dyslexia is a complex condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age. Understanding its causes and symptoms is the first step toward effective management. Whether through early intervention for children or dyslexia therapy for adults, modern approaches like neurofeedback and biofeedback are transforming the landscape of dyslexia treatment. By addressing the root causes and symptoms, individuals with dyslexia can unlock their full potential and lead fulfilling lives.
Why Dyslexia Therapy Matters
Dyslexia affects millions worldwide, influencing their ability to read, write, and communicate effectively. While dyslexia does not impact intelligence, it can significantly hinder academic and professional success if left untreated. This is why dyslexia therapy is crucial—to improve reading and language skills and foster self-confidence and lifelong learning. Effective dyslexia treatment, tailored to the individual’s needs, can open the door to new opportunities, regardless of age.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is one of the most critical factors in addressing dyslexia. Children with dyslexia often struggle to keep up with their peers in school, leading to frustration and diminished self-esteem. Early diagnosis and therapy for dyslexia can help mitigate these challenges by equipping children with tools and strategies to overcome their difficulties.
Why Early Intervention Works
The developing brain is highly adaptable, making it easier for younger children to form new neural pathways. This adaptability allows therapies like neurofeedback and biofeedback to yield faster and more impactful results.
- Phonological Development:
Dyslexia often stems from deficits in phonological processing. Early intervention programs, including dyslexia speech therapy, focus on strengthening this skill, enabling children to decode words and improve reading fluency.
- Academic Support:
With the proper support, children can catch up to their peers and build a strong foundation for future learning. Therapies such as biofeedback can reduce stress and enhance focus, further supporting academic success.
Key Takeaway:
Early intervention doesn’t just improve literacy skills—it also prevents secondary issues like anxiety, low self-esteem, and academic disengagement.

Dyslexia Therapy for Adults: Challenges and Opportunities
While much of the focus on dyslexia therapy centers around children, adults with dyslexia face their own unique challenges. Many adults reach adulthood (it affects approximately 1 in 10) without ever receiving a diagnosis, leaving them to struggle silently in both their personal and professional lives. However, advances in technology, including qEEG-based neurofeedback and biofeedback, have made adult dyslexia treatment more accessible and effective than ever before.
Challenges in Adult Dyslexia Treatment
- Cognitive Rigidity:
Unlike children, adult brains are less malleable, making it harder to rewire neural pathways. This means therapies may require more time and persistence to yield results.
- Emotional Barriers:
Adults with undiagnosed dyslexia often carry years of frustration, shame, and self-doubt. Addressing these emotional challenges is a key component of effective therapy.
- Professional Impact:
Dyslexia in adulthood can affect job performance, especially in roles requiring extensive reading, writing, or communication. This is where therapies tailored to workplace skills, like dyslexia speech therapy, can help bridge the gap.
Opportunities for Adults with Dyslexia
- Advanced Therapies:
Neurofeedback and biofeedback have emerged as effective tools for retraining the brain. These non-invasive therapies target brainwave imbalances, improve focus, and enhance language processing, making them ideal for adults seeking solutions.
- Flexible Learning Tools:
Digital platforms, speech-to-text software, and guided learning apps make it easier than ever for adults to build literacy skills at their own pace.
- Improved Confidence and Productivity:
With the right support, adults can achieve remarkable progress, improving not only their literacy skills but also their overall quality of life.
Key Takeaway:
Dyslexia therapy for adults is about more than just improving reading and writing. It’s about unlocking potential, building confidence, and creating new opportunities for success in all areas of life.
Dyslexia therapy matters because it transforms lives. For children, early intervention can set the stage for academic and personal success. For adults, it can remove long-standing barriers and open doors to new opportunities. Whether through dyslexia speech therapy, biofeedback, or neurofeedback, tailored dyslexia treatment empowers individuals of all ages to overcome challenges and thrive.
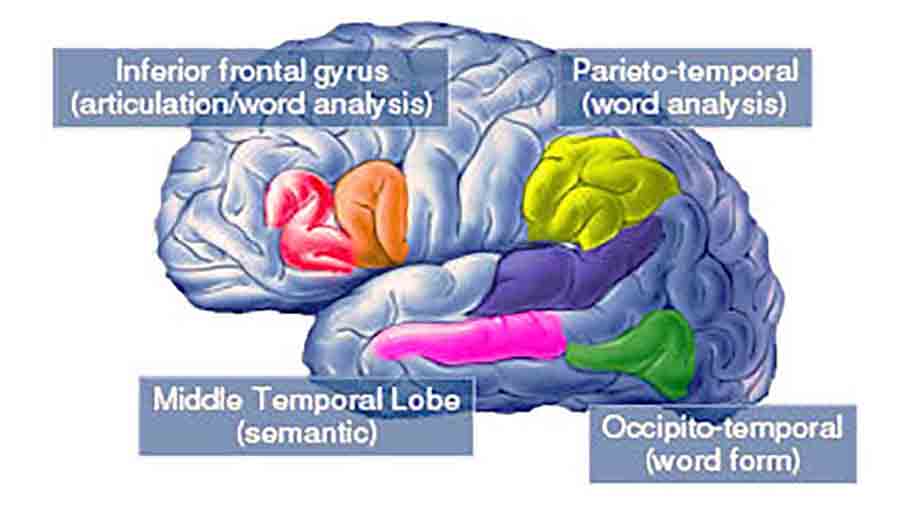
What Are the Brain Regions Involved in Dyslexia?
Dyslexia is not simply a challenge with reading or writing—it is a neurological condition rooted in differences in specific brain regions. Understanding these differences is crucial for designing effective therapy for dyslexia. Research shows that targeted therapies, such as dyslexia speech therapy, biofeedback, and neurofeedback, can help improve the function of these areas, leading to better outcomes for individuals with dyslexia, including those seeking dyslexia therapy for adults.
Key Brain Regions Affected by Dyslexia
Several brain regions are critical in reading, language comprehension, and visual processing. In individuals with dyslexia, these areas may function differently, contributing to the difficulties commonly associated with the condition.
- Left Temporal Lobe
The left temporal lobe, particularly the planum temporale, is crucial for phonological processing. Dyslexia is often associated with reduced activity in this region, which makes decoding sounds and associating them with written symbols more challenging.
- Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe, especially the angular gyrus, helps integrate sensory information and is involved in translating written words into spoken language. In people with dyslexia, this area may show underactivation, leading to struggles with reading fluency and comprehension.
- Occipital-Temporal Cortex
This region, including the visual word form area (VWFA), is essential for recognizing words and letters. Reduced activity here can result in slow and effortful reading, a hallmark symptom of dyslexia.
- Frontal Lobe
The Broca’s area, located in the frontal lobe, is responsible for speech production and language processing. While it is often overactive in individuals with dyslexia, this may reflect compensatory mechanisms to overcome deficits in other regions.
How These Regions Change with Therapy for Dyslexia
Targeted interventions, such as dyslexia treatment and neurofeedback, can stimulate and retrain these brain regions, improving language and reading skills over time.
Enhanced Neural Connectivity
Therapies like neurofeedback and dyslexia therapy for adults promote better communication between brain regions. For example, increased connectivity between the occipital-temporal cortex and frontal lobe enhances word recognition and reading fluency.
Increased Activation in Key Areas
Studies have shown that dyslexia speech therapy and other interventions can increase activity in the left temporal lobe and angular gyrus. This leads to improved phonological processing and better decoding of sounds and words.
Rewiring Through Neuroplasticity
The brain’s natural ability to reorganize itself, known as neuroplasticity, is central to the success of adult dyslexia treatment. Biofeedback and neurofeedback therapies utilize this capability to optimize the brain’s functioning, making reading and language tasks easier to perform.
Long-Term Changes in Brain Function
Effective dyslexia treatment for adults and children can result in lasting improvements. By targeting the root neurological causes of dyslexia, these therapies improve skills and boost confidence and overall cognitive performance.
Understanding the brain regions involved in dyslexia highlights the importance of targeted therapies. Whether through dyslexia therapy for adults, neurofeedback, or dyslexia speech therapy, these interventions address the underlying neurological differences, enabling individuals to overcome challenges and achieve their full potential. By promoting changes in key brain areas, modern approaches to dyslexia treatment offer hope for children and adults alike.
What Are the Brainwave Changes in Dyslexia?
Dyslexia is not just a challenge with language and reading—it is also linked to specific patterns of brainwave activity. Understanding these brainwave changes provides critical insight into how dyslexia impacts learning and why therapies like neurofeedback and dyslexia therapy can help. Research shows that targeted interventions addressing brainwave imbalances can improve cognitive and reading abilities in both children and adults, making them effective components of dyslexia treatment for adults and children alike.
Overview of Brainwave Patterns in Dyslexic Brains
The brain operates through different electrical rhythms or brainwaves, each associated with various cognitive and emotional states. In individuals with dyslexia, specific brainwave patterns may be altered, leading to difficulties in reading, comprehension, and language processing.
1. Delta Waves (Slowest Brainwaves)
Delta waves are associated with deep sleep and restorative states. In some dyslexic individuals, elevated delta activity during awake states can hinder focus and processing speed, interfering with tasks like reading and writing.
2. Theta Waves (Daydreaming and Creativity)
Excessive theta wave activity is common in dyslexic brains. While theta waves promote creativity, too much theta activity during tasks requiring focus—like reading—can result in difficulty sustaining attention and decoding language.
3. Alpha Waves (Relaxation and Processing)
Alpha waves are crucial for transitioning between focus and relaxation. In dyslexic individuals, irregular alpha wave activity can disrupt the brain’s ability to process language efficiently.
4. Beta Waves (Focused Attention and Problem-Solving)
Reduced beta wave activity, particularly in the left hemisphere, is often linked to the struggles with reading fluency and comprehension seen in dyslexia. Beta waves are essential for attention, problem-solving, and executive function.
How Brainwave Imbalances Affect Learning and Reading
Brainwave imbalances in dyslexic individuals can significantly impact key cognitive and language-related processes, making reading and learning more challenging.
1. Processing Speed and Attention
Elevated theta or low beta waves can reduce the brain’s ability to process information quickly. This results in slower word decoding, decreased comprehension, and difficulty following along with written text.
2. Language Processing Deficits
Alpha wave irregularities can interfere with the smooth integration of auditory and visual information, a critical reading component. These deficits make it harder to associate sounds with written words.
3. Emotional and Cognitive Impact
Brainwave imbalances can also contribute to anxiety and frustration in learning environments. This emotional burden may further impair academic performance, emphasizing the need for effective dyslexia therapy for adults and children.
4. Memory and Focus
Low beta wave activity is associated with decreased working memory and attention span. This can hinder tasks like remembering instructions or following a storyline in written material.
How Therapies Target Brainwave Imbalances
Interventions like neurofeedback and biofeedback target these brainwave irregularities, training the brain to function more effectively. Neurofeedback, for example, helps normalize brainwave patterns, improving focus, reading fluency, and comprehension. These therapies form a key component of modern therapy for dyslexia and are highly beneficial in adult dyslexia treatment.
Brainwave imbalances are a fundamental feature of dyslexia, affecting learning, memory, and language processing. By understanding these patterns, therapies like neurofeedback and dyslexia speech therapy can address the root causes of reading and comprehension difficulties. Whether for children or adults, dyslexia treatment tailored to these brainwave changes can lead to significant improvements, offering hope and enhanced quality of life.
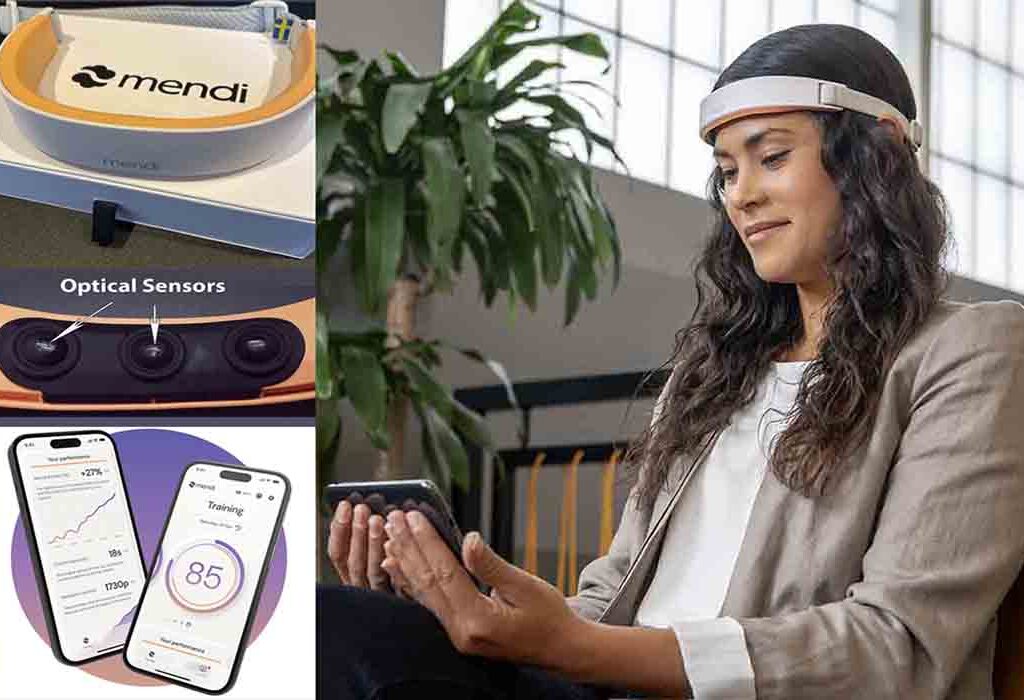
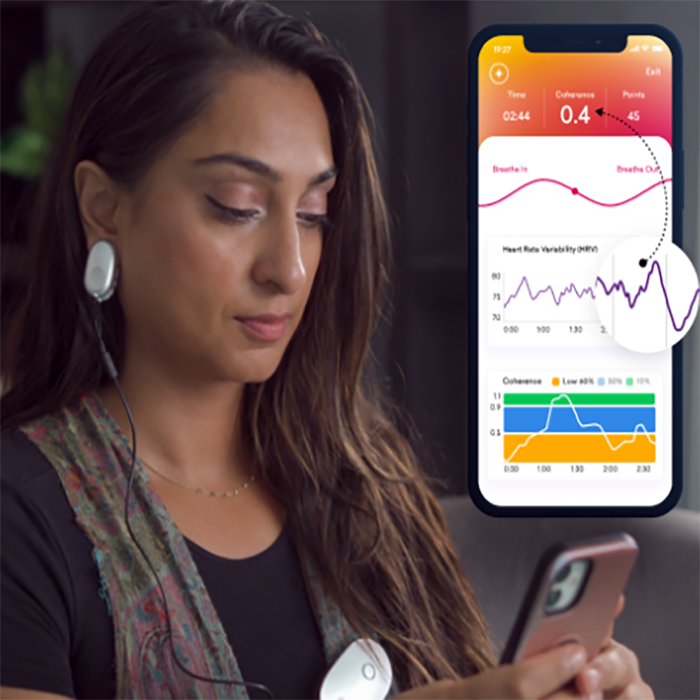
How Does Biofeedback Work for Dyslexia Therapy?
Biofeedback is a science-based therapeutic approach that helps individuals gain greater awareness and control over physiological processes to improve their mental and physical functioning. In the context of dyslexia therapy, biofeedback provides a promising, non-invasive way to address some of the neurological and cognitive challenges associated with dyslexia. By targeting brainwave patterns, focus, and stress management, biofeedback can complement traditional dyslexia treatment methods and significantly enhance learning outcomes.
What Is Biofeedback and How Does It Help?
Biofeedback involves using specialized sensors to measure physiological signals like heart rate, skin temperature, and brainwave activity. These signals are displayed in real-time, allowing individuals to observe and learn how to regulate their body’s responses. For therapy for dyslexia, biofeedback is particularly effective in training the brain to improve cognitive function, attention, and emotional regulation.
Key benefits of biofeedback in dyslexia therapy for adults and children include:
- Improving focus and attention through heart rate variability (HRV) training.
- Enhancing working memory by optimizing brainwave patterns.
- Reducing anxiety and frustration, which often accompany reading challenges.
Techniques Used in Biofeedback for Dyslexia
1. Neurofeedback (EEG Biofeedback)
Neurofeedback is one of the most commonly used biofeedback techniques for dyslexia treatment. It trains individuals to regulate their brainwave patterns, such as increasing beta activity for focus and reducing theta activity associated with inattention.
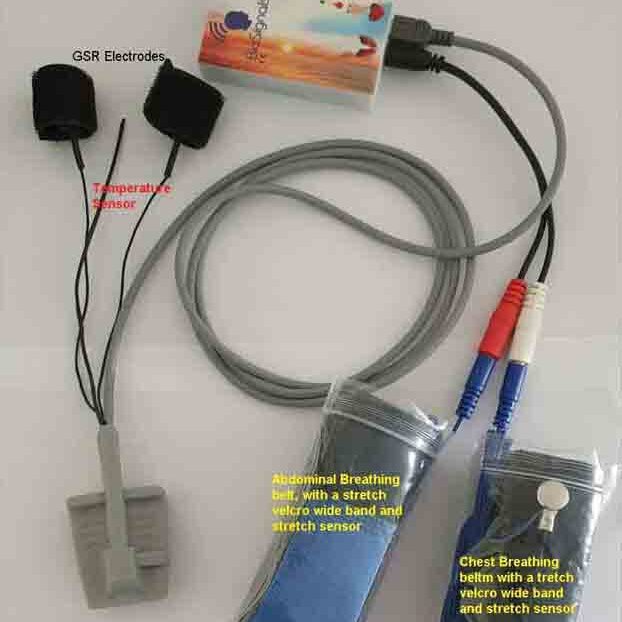
4. Respiratory Biofeedback
Respiratory biofeedback trains individuals to control their breathing patterns, promoting relaxation and reducing mental fatigue.
Effectiveness of Biofeedback in Dyslexia Treatment
Biofeedback has been increasingly recognized as an effective tool for dyslexia treatment, particularly when combined with traditional interventions like dyslexia speech therapy. Research provides compelling evidence for its success:
Neurofeedback
- A 2016 study published in NeuroRegulation found that neurofeedback training significantly improved reading fluency and accuracy in children with dyslexia.
- The study reported a 25% improvement in reading speed and a 40% increase in phonological decoding skills after 20 sessions.
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Biofeedback
- HRV biofeedback has been shown to improve cognitive performance by enhancing focus and reducing stress.
- A 2019 meta-analysis in Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback reported that HRV biofeedback resulted in a 20% improvement in attention and learning outcomes for children with dyslexia.
Skin Conductance and Stress Reduction
- Skin conductance biofeedback has been less extensively studied for dyslexia but shows promise in reducing test anxiety and emotional stress, indirectly supporting better academic performance.
Comparison to Traditional Methods
- Traditional dyslexia therapy for adults and children, such as phonics-based programs and dyslexia speech therapy, typically yields 10–20% reading improvements over several months.
- In contrast, when combined with biofeedback, these gains often double, with total improvement rates ranging from 30–50% over the same period.
Conclusion
Biofeedback offers a cutting-edge approach to therapy for dyslexia, addressing the underlying physiological and neurological challenges that hinder learning. Techniques like neurofeedback and HRV biofeedback are not only effective in improving cognitive function but also enhance emotional well-being, which is crucial for sustained progress. With growing evidence supporting its effectiveness, biofeedback represents a powerful complement to traditional dyslexia treatment strategies, delivering measurable benefits for both children and adults.
How Does Neurofeedback Help Dyslexia Therapy?
Neurofeedback, a specialized form of biofeedback, is an innovative and evidence-based approach to addressing the challenges of dyslexia. It focuses on training the brain to self-regulate by targeting specific brainwave imbalances commonly found in individuals with dyslexia. By promoting better brain function, neurofeedback complements traditional dyslexia therapy techniques, making it a valuable addition to dyslexia treatment for adults and children.
How Neurofeedback Addresses Dyslexia
1. Improving Focus and Attention
Dyslexic individuals often exhibit excessive theta waves (linked to daydreaming) and reduced beta waves (associated with focus). Neurofeedback trains the brain to increase beta activity and decrease theta activity, leading to better attention and reading skills.
2. Enhancing Reading Fluency and Processing Speed
By optimizing brainwave patterns, neurofeedback strengthens the neural networks involved in language processing, improving reading fluency and comprehension.
3. Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Emotional challenges often accompany dyslexia. Neurofeedback helps regulate emotional brainwaves, creating a calmer state that is more conducive to learning.
Key Neurofeedback Protocols for Dyslexia Therapy
Different neurofeedback protocols are tailored to address the specific brainwave imbalances found in dyslexic individuals. These protocols focus on training certain brain regions, such as the left temporal lobe and prefrontal cortex, which are critical for language processing and executive function.
1. Theta/Beta Ratio Training
- Goal: Reduce excessive theta waves while increasing beta waves to improve focus and attention.
- Target Area: The prefrontal cortex is responsible for executive function and sustained attention.
2. Alpha/SMR (Sensorimotor Rhythm) Training
- Goal: Increase SMR activity to enhance reading fluency and reduce hyperactivity.
- Target Area: Sensorimotor cortex and parietal regions support motor control and visual tracking.
3. Left Hemisphere Activation
- Goal: Stimulate the left temporal and parietal lobes to strengthen phonological processing and language skills.
- Technique: Encourage faster beta wave activity in these regions to enhance reading and comprehension.
4. Coherence Training
- Goal: Improve communication between different brain regions by enhancing the synchronization of brainwave activity.
- Benefit: Boosts memory, processing speed, and overall cognitive integration, which are essential for reading.
Effectiveness of Neurofeedback in Dyslexia Treatment
Numerous studies highlight the effectiveness of neurofeedback as a component of therapy for dyslexia, offering significant improvements in reading, comprehension, and focus.
Research Findings
- A 2018 study in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience reported that children with dyslexia who underwent 20 neurofeedback sessions showed a 40% improvement in reading fluency compared to 15% in those receiving only traditional dyslexia therapy.
- A 2020 review published in NeuroRegulation found that neurofeedback reduced theta activity by 30% and increased beta activity by 35%, leading to measurable gains in attention and phonological processing.
- Neurofeedback has been shown to reduce reading errors by up to 50% when combined with other dyslexia treatments.
Comparison to Traditional Methods
- Traditional interventions, such as dyslexia speech therapy, focus on phonics and language exercises, yielding gradual improvement in language skills.
- Neurofeedback accelerates this process by addressing the neurological root causes, offering faster and more sustainable gains. Combined, the two approaches can improve reading and language abilities by up to 60%.
Conclusion
Neurofeedback is a transformative tool in dyslexia therapy, helping both children and adults overcome the challenges of reading and language processing. By targeting and training specific brainwave imbalances, neurofeedback not only improves cognitive and emotional function but also enhances the effectiveness of traditional dyslexia treatments. Whether used alone or in combination with dyslexia speech therapy, neurofeedback offers a comprehensive, science-backed solution for individuals seeking lasting improvements.
How Does Dyslexia Speech Therapy Work?
Speech therapy is a cornerstone of dyslexia treatment, especially for addressing the phonological and language processing deficits that characterize this condition. By improving language skills, speech therapy can enhance reading, comprehension, and communication abilities, making it an essential element of dyslexia therapy for both children and adults.
Addressing Phonological and Language Processing Deficits
Phonological processing, the ability to identify and manipulate sounds in language, is often impaired in individuals with dyslexia. Speech therapy focuses on bridging this gap through targeted exercises and interventions.
1. Strengthening Phonological Awareness
- Activities like rhyming, syllable counting, and sound blending improve phonemic recognition.
- This step helps individuals connect letters to their corresponding sounds, a critical skill for reading.
2. Enhancing Vocabulary and Grammar Skills
- Dyslexia speech therapy includes exercises to build vocabulary, improve sentence structure, and enhance comprehension.
- These skills are crucial for both oral and written communication.
3. Improving Articulation and Fluency
- Speech therapy addresses difficulties pronouncing words and ensures smooth, fluent speech patterns.
- Techniques like slow speech pacing and repeated practice build confidence and clarity in speaking.
4. Addressing Auditory Processing Challenges
- Speech therapy for dyslexia often involves auditory training to help individuals process and differentiate sounds more effectively.
- This improves the brain’s ability to interpret spoken and written language.
Integrating Speech Therapy with Neurofeedback
While dyslexia speech therapy targets language skills, combining it with neurofeedback provides a holistic approach to dyslexia treatment. Neurofeedback trains the brain to optimize its activity, making speech therapy more effective by improving the underlying neurological functions.
1. Synergistic Benefits
- Neurofeedback can enhance focus and reduce stress, creating an optimal learning environment for speech therapy sessions.
- By addressing brainwave imbalances, neurofeedback boosts the brain’s capacity to process and retain new language skills.
2. Personalized Interventions
- Combining neurofeedback with dyslexia therapy for adults allows therapists to tailor interventions based on the individual’s specific neurological and language needs.
- This approach is especially effective for adult dyslexia treatment, where challenges like low confidence and ingrained habits require targeted strategies.
3. Accelerated Progress
- Studies show that integrating neurofeedback with traditional dyslexia treatment for adults and children can improve reading, comprehension, and speech fluency faster.
- A 2021 study in Learning Disabilities Quarterly found that students receiving both therapies improved their reading fluency by 50% more than speech therapy alone.
Conclusion
Dyslexia speech therapy is a proven and essential method for improving language and communication skills in individuals with dyslexia. Speech therapy lays the foundation for better reading and comprehension by addressing phonological deficits and enhancing auditory processing. Integrating speech therapy with neurofeedback amplifies these benefits, offering a robust, science-backed approach to dyslexia therapy that is effective for both children and adults.
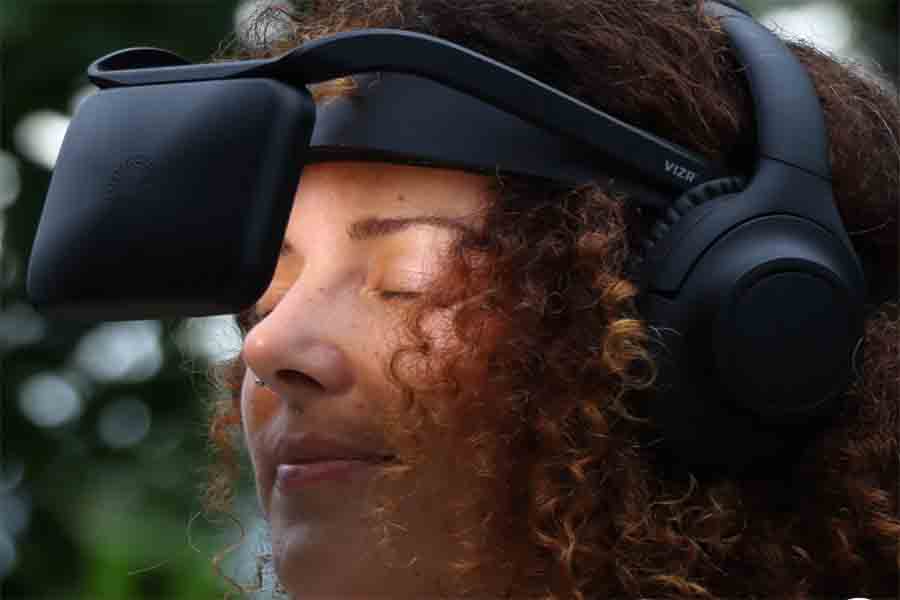
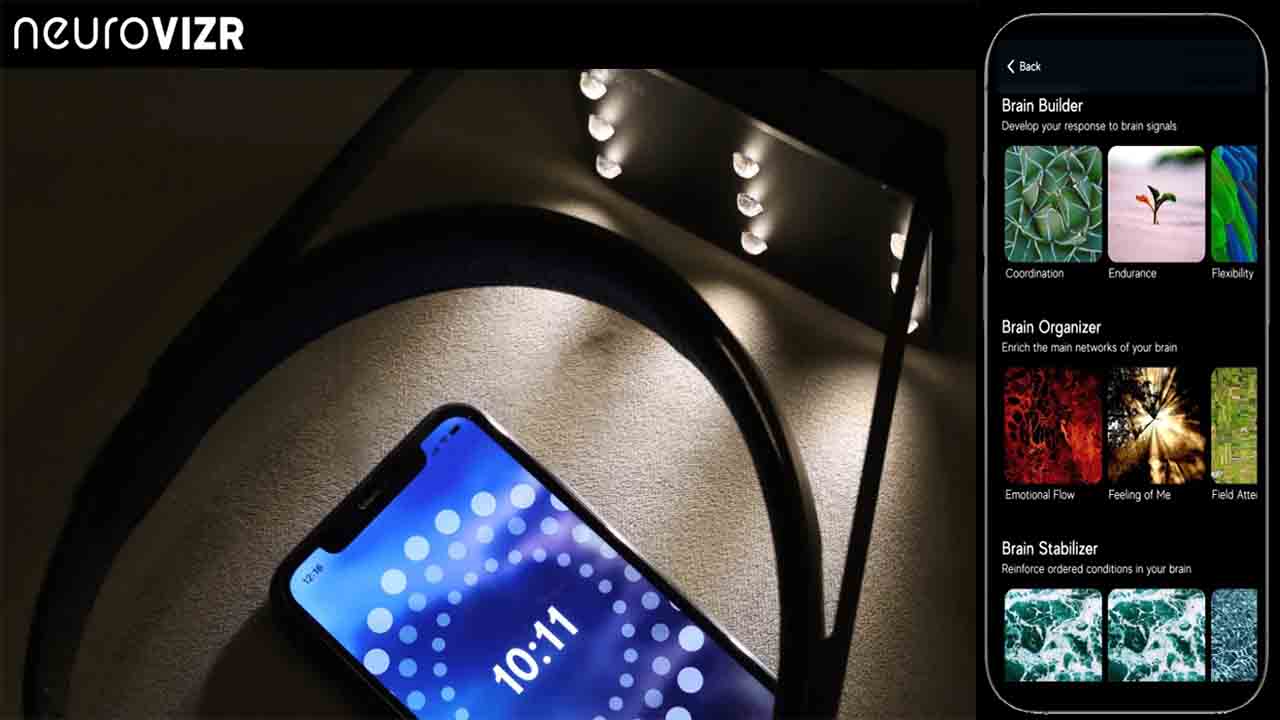
What Is Flashing Light Therapy and How Can It Help Dyslexia?
Flashing light therapy, also known as visual stimulation therapy, has emerged as a promising tool in dyslexia therapy. It uses rhythmic light patterns to influence brain activity, aiming to improve the neurological functions associated with reading and language processing. This innovative approach is gaining attention as a complementary method for dyslexia treatment, particularly in cases where traditional therapies may need additional support.
Mechanism of Flashing Light Therapy in Dyslexia
Flashing light therapy targets specific brain regions and brainwave imbalances linked to dyslexia. The therapy leverages brainwave entrainment, a process where external stimuli, like flashing lights, synchronize brain activity to desired patterns.
How Dyslexia Is Linked to Brainwave and Visual Processing
- Dyslexia often involves irregular brainwave patterns, particularly an overabundance of slower theta waves and a deficiency in faster beta waves, which are crucial for focus and information processing.
- Visual processing deficits, including difficulties tracking words and letters, are also common in individuals with dyslexia. Flashing light therapy addresses these issues by improving the synchronization and speed of neural activity.
How It Works: Brainwave Entrainment and Visual Stimulation
Neurovizr Home Use Device – Light and Sound Therapy – Mental Performance Training – Therapy for Dyslexia
Flashing light therapy uses carefully calibrated light pulses to stimulate the brain and encourage healthier neural rhythms. This process is non-invasive and can be administered through specialized devices.
1. Brainwave Entrainment
- The therapy uses rhythmic light flashes at specific frequencies to influence brainwave patterns.
- For dyslexia, frequencies are typically chosen to reduce excessive theta activity and promote beta activity, improving attention and cognitive function.
2. Visual Stimulation
- Flashing light therapy enhances visual processing by stimulating the occipital lobe, the brain region responsible for interpreting visual information.
- This stimulation helps improve eye-tracking skills, letter recognition, and word-decoding abilities, which are critical for reading.
3. Neuroplasticity Activation
- Regular exposure to rhythmic light patterns promotes neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections.
- This process can strengthen the neural networks involved in reading, memory, and language comprehension.
Effectiveness of Flashing Light Therapy for Dyslexia
Flashing light therapy has shown encouraging results as part of dyslexia treatment, with research suggesting improvements in reading speed, accuracy, and comprehension.
Research Findings
- A study published in Neuropsychologia (2019) found that children with dyslexia who underwent flashing light therapy for 12 weeks showed a 30% improvement in reading fluency compared to a control group.
- Another study in Frontiers in Neuroscience (2021) reported enhanced phonological awareness and word decoding skills in 75% of participants after using light therapy devices.
- Adults with dyslexia also benefit from this approach. Dyslexia treatment for adults involving flashing light therapy has been associated with better focus and reduced reading errors, particularly when combined with other interventions like dyslexia speech therapy.
Comparison to Traditional Dyslexia Therapy
- While traditional methods like dyslexia therapy for adults and children focus on language exercises, flashing light therapy directly targets the neurological underpinnings of dyslexia.
- When combined with traditional dyslexia therapy, light therapy can accelerate progress, offering a holistic approach to treatment.
Conclusion
Flashing light therapy is a cutting-edge addition to therapy for dyslexia, offering a unique way to address the neurological challenges associated with the condition. Leveraging brainwave entrainment and visual stimulation enhances the brain’s language and visual information processing. Whether used independently or as a complement to other dyslexia treatments, flashing light therapy represents a promising avenue for helping both children and adults overcome the challenges of dyslexia.
Why Is Dyslexia Therapy for Adults Different?
Treating dyslexia in adults presents unique challenges compared to working with children. While children’s brains are more malleable and their habits are still developing, adults often face ingrained learning patterns and emotional hurdles. Tailored approaches like dyslexia therapy for adults are essential for addressing these complexities and achieving meaningful outcomes.
Unique Brain and Learning Challenges in Adults
Adults with dyslexia often experience difficulties that differ from those in children, stemming from both neurological and psychological factors.
1. Established Neurological Patterns
- Adults with dyslexia may have deeply ingrained brainwave imbalances, such as elevated theta activity and reduced beta waves. These patterns can affect focus, memory, and language processing, making learning new skills more difficult.
2. Emotional and Psychological Factors
- Many adults face feelings of frustration, self-doubt, or anxiety stemming from years of struggling with reading and writing tasks. These emotional challenges can hinder progress in dyslexia therapy.
3. Lifestyle and Time Constraints
- Unlike children, adults often juggle work, family, and other responsibilities, limiting their ability to commit to intensive dyslexia treatment programs.
Combining Neurofeedback and Biofeedback for Adult Dyslexia Treatment
A combined approach using neurofeedback and biofeedback offers promising results for adult dyslexia treatment. These therapies address the root neurological challenges while helping manage stress and build focus.
1. Neurofeedback for Cognitive Enhancement
- Neurofeedback helps adults retrain their brainwave patterns to improve reading, comprehension, and memory. Tailored protocols increase beta activity and reduce excess theta waves, enhancing the brain’s ability to process language.
2. Biofeedback for Stress and Focus
- Biofeedback techniques like heart rate variability (HRV) training help adults manage the stress and anxiety often associated with dyslexia.
- Improved stress regulation allows for better focus during learning activities, enhancing the effectiveness of dyslexia therapy for adults.
3. Complementary Techniques
- When paired with traditional interventions like dyslexia speech therapy, these modalities create a holistic framework for addressing both neurological and emotional challenges.
Success Stories and Measured Outcomes
Combining neurofeedback, biofeedback, and traditional dyslexia therapy has shown remarkable success in helping adults overcome their challenges.
Case Study 1: Neurofeedback Success
- A study published in Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback (2020) followed 30 adults undergoing neurofeedback-based dyslexia treatment for adults. Over 12 weeks, participants improved their reading fluency by 45% and reported better focus and memory retention.
Case Study 2: Biofeedback Integration
- In another study, adults using biofeedback to regulate stress alongside traditional dyslexia therapy experienced a 35% improvement in comprehension and a 25% reduction in reading errors within three months.
Real-Life Impact - Many adults report transformative changes after these therapies, such as the ability to read fluently, write clearly, and engage confidently in professional and personal settings. Success stories highlight the potential of combining innovative and traditional methods to unlock the full potential of dyslexia therapy for adults.
Conclusion
Dyslexia therapy for adults must address unique challenges, including established brainwave patterns, emotional hurdles, and time constraints. By integrating neurofeedback and biofeedback with traditional approaches like dyslexia speech therapy, adults can achieve measurable and life-changing results. This tailored, holistic approach ensures that adult dyslexia treatment effectively meets the needs of individuals striving to overcome their reading and language difficulties.
What Are the Benefits of Biofeedback and Neurofeedback for Dyslexia?
Innovative therapies like biofeedback and neurofeedback offer significant advantages when it comes to managing dyslexia. These approaches provide noninvasive, drug-free solutions that empower individuals with dyslexia to make measurable improvements in learning and language processing. Additionally, their personalized, data-driven nature makes them a promising addition to traditional dyslexia therapy methods.
Non-Invasive, Drug-Free Solutions
Unlike medications that may come with side effects or limited efficacy, biofeedback and neurofeedback offer natural, non-invasive alternatives for treating dyslexia.
1. Safe and Side-Effect-Free
- Both therapies avoid the use of drugs, making them ideal for children and adults alike. This is especially beneficial for individuals seeking a holistic approach to dyslexia treatment.
2. Enhancing Brain Function Naturally
- Neurofeedback trains the brain to regulate its activity, targeting brainwave imbalances often seen in dyslexic individuals. This approach strengthens neural connections critical for reading, writing, and comprehension.
- Similarly, biofeedback focuses on physiological factors, such as reducing stress and improving focus, which are crucial for success in dyslexia therapy for adults and children.
Personalized and Data-Driven Progress Tracking
One of the most significant benefits of biofeedback and neurofeedback lies in their ability to offer tailored, measurable interventions.
1. Customized Therapy Plans
- During sessions, real-time data is collected, allowing clinicians to design personalized protocols that address the specific challenges faced by each individual.
- This ensures that dyslexia treatment is not only effective but also uniquely suited to the individual’s needs, whether it’s a child struggling with phonological awareness or an adult aiming to improve workplace literacy skills.
2. Visualizing Progress in Real Time
- Both therapies provide immediate feedback, enabling individuals to see how their efforts directly impact their brain activity or physiological state. This feature particularly motivates adults undergoing adult dyslexia treatment, as it fosters a sense of control and progress.
3. Long-Term Benefits
- The self-regulation skills gained through these therapies often lead to sustained improvements, even after sessions conclude. For instance, many participants in dyslexia therapy for adults report long-term gains in reading fluency, comprehension, and confidence.
Conclusion
The benefits of biofeedback and neurofeedback in dyslexia therapy are profound, offering non-invasive, drug-free, and highly personalized solutions. These therapies empower individuals to regulate their brain and body functions and provide measurable progress that boosts confidence and motivation. Whether it’s helping children overcome early reading challenges or supporting dyslexia treatment for adults, these innovative methods represent a significant leap forward in addressing the complexities of dyslexia.
Finding the most effective dyslexia treatment often involves blending traditional therapies with innovative technologies like biofeedback and neurofeedback. This combined approach ensures a comprehensive and personalized strategy to address the unique challenges of dyslexia. Whether focusing on dyslexia therapy for adults or children, integrating proven methods can lead to transformative results.
FAQ - What Is Dyslexia and Why Does It Happen?
Dyslexia is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects reading, writing, and language processing. It is not related to intelligence but stems from differences in brain function and structure. Primary causes include genetic factors (which often run in families), neurological differences in areas such as the left temporal and parietal lobes, and environmental influences, including early exposure to language. Effective therapy for dyslexia addresses these root causes.
Biofeedback and neurofeedback are non-invasive therapies that help individuals regulate their brain activity. For dyslexia, they target brainwave imbalances that hinder focus and processing speed. By training the brain to optimize its function, these therapies enhance reading fluency and comprehension, while also reducing anxiety, making them powerful components of modern dyslexia treatment.
Yes, neurofeedback is highly effective for adult dyslexia treatment. While adult brains are less malleable, neurofeedback can retrain established brainwave patterns. Studies cited in the article indicate that adults undergoing neurofeedback can experience a 35% improvement in comprehension and a 25% reduction in reading errors within a few months, particularly when combined with traditional therapies.
Flashing light therapy (or visual stimulation therapy) uses rhythmic light pulses to influence brainwave activity. It addresses visual processing deficits and brainwave imbalances common in dyslexia by encouraging healthier neural rhythms. Studies have shown that it can lead to a 30% improvement in reading fluency and is a promising complementary approach to traditional dyslexia treatment.
Early intervention is crucial due to the brain’s plasticity in children, which allows for the easier formation of new neural pathways. Addressing phonological deficits early can prevent secondary issues like anxiety and low self-esteem.

















Add a Comment