Struggling with restless nights and constant fatigue? You’re not alone. Millions of people face sleep disturbances, but the good news is that total sleep management offers effective solutions. By combining sleep therapy, biofeedback for insomnia, and neurofeedback for sleep, you can regain control over your sleep patterns. Techniques such as breathing exercises for sleeplessness and CBT for sleep help to calm the mind and body, making it easier to fall and stay asleep. Whether you’re managing sleep difficulties or looking for natural ways to improve sleep quality, this guide will explore proven methods to say goodbye to insomnia for good.
Table of Contents
Toggle- Introduction: How Total Sleep Management Can End Sleepless Nights
- What is Total Sleep Management?
- The Science of Sleep Management: Why Managing Sleep Matters
- Biofeedback for Insomnia: A Natural Way to Improve Sleep
- Neurofeedback for Insomnia: Rewiring the Brain for Restful Sleep
- CBT for Sleep: How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Improves Sleep
- Breathing Exercises for Sleeplessness: A Simple Yet Effective Solution
- Best Biofeedback Devices for Sleep
- Integrating Sleep Therapy: A Comprehensive Approach to Total Sleep Management
- Tips for Better Sleep: Beyond Biofeedback
- FAQ -Total Sleep Management & Sleep Therapy for Insomnia
- Conclusion: Achieve Deep, Restorative Sleep with Total Sleep Management
Introduction: How Total Sleep Management Can End Sleepless Nights
Sleep is essential for physical health, mental clarity, and emotional balance. Yet, millions struggle with insomnia (as many as 35% of adults) —a condition that disrupts both the quantity and quality of rest. Insomnia can stem from stress, anxiety, or poor sleep habits, leaving individuals exhausted and frustrated. Fortunately, Total Sleep Management provides a holistic approach to overcoming these challenges.
By integrating Sleep Therapy methods like biofeedback and neurofeedback, you can train your body and mind to achieve more profound, restorative sleep. Whether you’re new to Biofeedback for Insomnia or looking for advanced techniques, this article will explore how these innovative tools can help you sleep better and wake up refreshed.
By understanding the root causes of sleep disturbances and implementing a structured sleep management plan, you can regain control over your nights and wake up energized. Let’s begin by exploring the role of sleep therapy in overcoming insomnia.
What is Total Sleep Management?
What is Sleep Therapy? A Key to Better Sleep Management
Sleep therapy is a structured approach to help individuals overcome sleep disturbances and develop healthier sleep patterns. It includes techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy, relaxation exercises, biofeedback, and lifestyle adjustments to improve overall sleep management. Unlike sleep medications that provide temporary relief, sleep therapy addresses the root causes of insomnia and promotes long-term solutions.
Types of Sleep Therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) – A scientifically proven method that helps individuals identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to sleeplessness.
- Biofeedback for Sleep – A technique that uses real-time monitoring of physiological functions, like heart rate and muscle tension, to train the body for more profound relaxation and better sleep.
- Neurofeedback for Insomnia – A brainwave-based therapy that helps regulate sleep patterns by improving the brain’s ability to transition into a restful state.
- Breathing Exercises for Sleeplessness – Controlled breathing techniques activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing stress and making it easier to fall asleep.
- Sleep Hygiene and Lifestyle Changes: Adjusting screen time, diet, and bedtime routines to create an optimal sleep environment.
Total Sleep Management
Total Sleep Management is a comprehensive approach designed to improve sleep quality by addressing the physical, mental, and environmental factors contributing to insomnia and other sleep disorders. Unlike traditional methods, which focus on a single aspect of sleep, Total Sleep Management combines evidence-based techniques such as biofeedback, neurofeedback, and sleep hygiene to create a personalized plan for better rest.
By using biofeedback, individuals can learn to regulate physiological functions like heart rate and breathing, which are often disrupted by stress or anxiety. Neurofeedback takes this further by training the brain to produce optimal brainwave patterns for relaxation and deep sleep. Additionally, incorporating sleep hygiene practices—such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a calming bedtime routine—ensures the body is primed for restful sleep.
These methods collectively establish the foundation of Total Sleep Management, providing a comprehensive approach to sleep optimization and enhancement solutions. Whether you’re struggling with occasional sleeplessness or chronic insomnia, this approach empowers you to take control of your sleep and wake up refreshed.
The Science of Sleep Management: Why Managing Sleep Matters
Sleep is not just about rest—it’s a complex biological process essential for physical and mental well-being. Managing sleep effectively ensures proper cognitive function, emotional balance, immune system support, and overall health. Poor sleep, on the other hand, can lead to a weakened immune system, reduced focus, mood disorders, and an increased risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
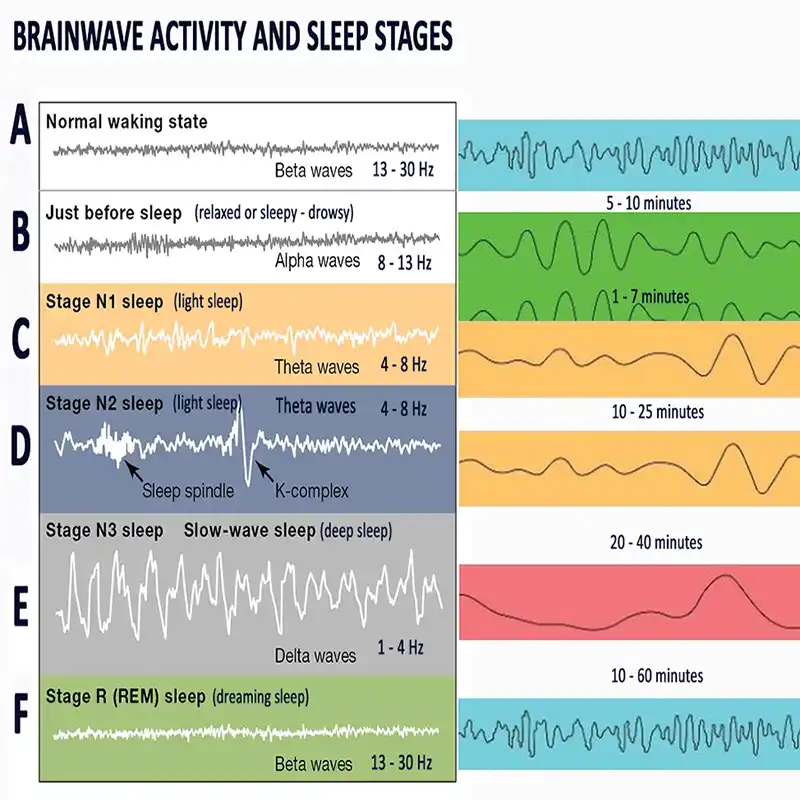
How Sleep Works: The Sleep Cycle Explained
Sleep consists of several stages that repeat in cycles throughout the night:
- Stage 1 (Light Sleep): The transition between wakefulness and sleep.
- Stage 2 (Light Sleep): The heart rate slows, body temperature drops, and brain activity decreases.
- Stage 3 (Deep Sleep): The most restorative stage, where the body repairs tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system.
- REM Sleep (Rapid Eye Movement): Essential for cognitive function, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation.

Managing sleep becomes crucial when sleep cycles are disrupted—whether due to stress, poor habits, or underlying conditions. Implementing structured sleep management techniques can help restore these cycles and improve overall sleep quality.
Key Factors Affecting Sleep Management
Insomnia is more than just difficulty falling asleep—it’s a complex condition that can disrupt every aspect of your life. Characterized by trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early, insomnia often stems from a combination of physical, psychological, and environmental factors. Common causes include stress, anxiety, poor sleep habits, irregular sleep schedules, and even underlying health conditions like sleep apnea or chronic pain.
- Circadian Rhythm Disruptions: Irregular sleep schedules, exposure to blue light at night, and shift work can throw off your body’s internal clock.
- Stress and Anxiety: Mental tension prevents the body from transitioning smoothly into deep sleep stages.
- Poor Sleep Hygiene: Inconsistent bedtimes, excessive caffeine intake, and an uncomfortable sleep environment can negatively impact sleep quality.
- Neurological Imbalances: Conditions such as insomnia can be linked to irregular brainwave activity, which therapies like biofeedback for insomnia and neurofeedback for insomnia can help regulate.
- Mental Health disorders: depression, schizophrenia, PTSD, bipolar disorder, Alzheimer’s disease. There is a close link between insomnia and many mental health conditions. Many people with a mental health condition also experience insomnia. Insomnia may also increase the risk for mental health conditions.
- Health conditions: sleep apnea, gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic pain, restless legs syndrome.
By understanding the science behind sleep and applying total sleep management strategies, you can optimize your rest and wake up feeling truly refreshed. In the next section, we will explore how biofeedback for insomnia can help naturally improve sleep quality.
What are the effects of insomnia?
The effects of insomnia extend far beyond feeling tired during the day. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to impaired cognitive function, mood disorders like depression, and a weakened immune system. Over time, it can also increase the risk of serious health issues such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. For many, the search for The Cure for Insomnia becomes a top priority, as the condition can significantly impact the quality of life.
The Wide-Ranging Impact of Insomnia
Insomnia may play a role in the development of:
- Cognitive Impairment – Memory problems, difficulty concentrating
- Weakened Immune System – Higher susceptibility to infections
- Mood Disorders – Increased risk of anxiety, depression, and irritability
- Heart Disease – Higher blood pressure and increased risk of heart attack
- Weight Gain – Hormonal imbalances leading to overeating
- Diabetes Risk – Increased insulin resistance and blood sugar imbalance
- Digestive Issues – Stomach pain, bloating, acid reflux
- Reduced Performance – Low energy, poor productivity, slow reaction time
- Increased Risk of Accidents – Higher likelihood of car and workplace accidents
- Premature Aging – Faster skin aging, dark circles, and fine lines
It can also undermine school and work performance and limit a person’s ability to do daily activities.
Cognitive and Neurological Effects of Insomnia
People with insomnia have changes in cognitive performance and brain structure, especially in the white matter and some regions that are affected in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
On the one hand, researchers analyzed the cognitive performance of people with insomnia and compared it with those with normal sleep. The results show that insomnia is associated with worse cognitive test results. In particular, they have described a reduction in some executive functions, such as working memory.
On the other hand, the study shows that participants with insomnia have a lower volume in some brain regions. Among them are the precuneus or the posterior cingulate cortex, which are affected in the early stages of the disease. The results suggest that people with insomnia are more vulnerable to Alzheimer’s disease.
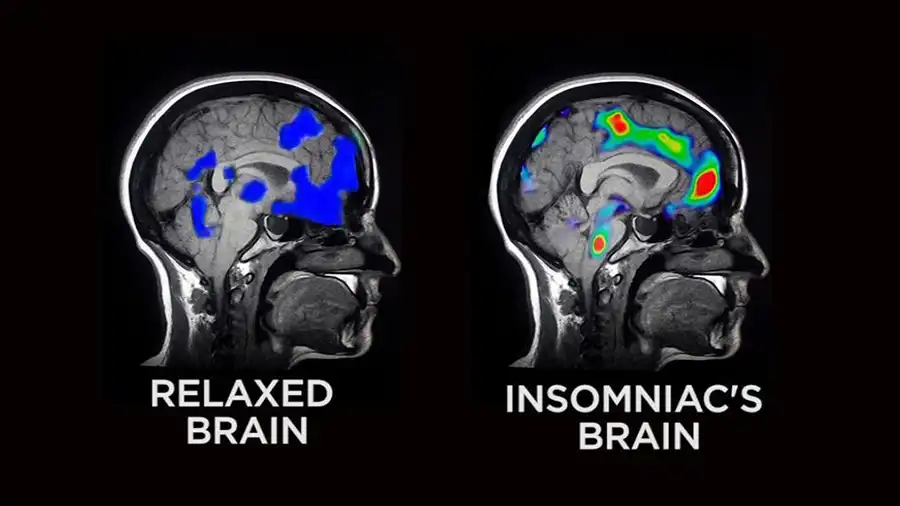
Understanding the root causes of insomnia is the first step toward effective treatment. By addressing these factors through Total Sleep Management and techniques like biofeedback and neurofeedback, individuals can break the cycle of sleeplessness and achieve lasting relief. In the following sections, we’ll explore how these innovative approaches can help you regain sleep control and improve your overall well-being.
Biofeedback for Insomnia: A Natural Way to Improve Sleep
Biofeedback for insomnia is a science-backed technique that helps individuals gain control over physiological processes that affect sleep. Using sensors to monitor bodily functions like muscle tension, heart rate, and skin temperature, biofeedback trains the body to enter a relaxed state conducive to sleep. Unlike medications, which only mask sleep problems, biofeedback addresses the underlying causes of sleeplessness and promotes long-term improvements.
How Biofeedback Works for Sleep Management
Biofeedback devices provide real-time data on your body’s responses, allowing you to learn how stress, anxiety, and tension impact your sleep. With guided practice, you can consciously regulate these responses to promote relaxation and deeper sleep.
Key biofeedback techniques for managing insomnia include:
- Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Biofeedback: Helps regulate the autonomic nervous system by promoting a balanced heart rate pattern, reducing stress and anxiety, and enhancing sleep quality.
- Muscle Tension Biofeedback: It detects excessive muscle activity, common in people with insomnia, and trains the body to release tension before bedtime.
- Skin Temperature Biofeedback: It teaches the body to increase peripheral circulation, a key signal for sleep readiness.
By incorporating biofeedback into a Total Sleep Management plan, individuals can address the underlying causes of insomnia and achieve long-term relief.
Benefits of Biofeedback for Insomnia
- Reduces stress and anxiety, leading to faster sleep onset
- Helps regulate the body’s relaxation response naturally
- Improves sleep duration and quality without medication
- Provides long-term sleep improvements through self-regulation
Many people struggling with sleep management have found relief through biofeedback, as it empowers them with the skills to naturally enhance their sleep patterns. In the next section, we will explore how neurofeedback for insomnia can further optimize brain activity for better sleep.
Neurofeedback for Insomnia: Rewiring the Brain for Restful Sleep
While biofeedback focuses on regulating physiological functions, neurofeedback takes sleep improvement a step further by targeting brain activity. By providing real-time feedback on brain function, neurofeedback trains the brain to transition smoothly between wakefulness and deep sleep. This method is particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle with managing sleep due to chronic insomnia, stress, or anxiety-related sleep disturbances.
How Neurofeedback Works for Sleep Management
Neurofeedback uses EEG (electroencephalogram) sensors to monitor brainwave activity while the individual engages in a neurofeedback training session. When the brain produces the desired sleep-promoting patterns, the system provides positive reinforcement, gradually teaching the brain to maintain these patterns naturally.
The key brainwave types involved in sleep therapy include:
- Delta Waves (Deep Sleep): Essential for deep, restorative sleep.
- Theta Waves (Light Sleep & Relaxation): Helps transition into sleep and maintain REM cycles.
- Beta Waves (Alertness): Often too high in people with insomnia, making it difficult to relax.
- Alpha Waves (Calm Wakefulness): Helps quiet an overactive mind before sleep.
By using neurofeedback for sleep, individuals can train their brains to produce more delta and theta waves, while reducing excessive beta activity that contributes to overthinking and sleep disruptions.
Neurofeedback Protocol for Sleep Management
EEG Biofeedback can help individuals regulate their sleep-wake cycles by targeting specific brainwave activity and reinforcing desirable neural states.
Neurofeedback training for sleep management can be performed using both simple wearable devices and professional neurofeedback systems.
Wearable headbands and headsets with frontal (FP1, FP2, Fz) or occipital (O1, O2) electrodes provide a convenient, user-friendly way to train brainwave activity at home. These devices use dry electrodes and built-in software to monitor and modulate brain activity in real-time, making neurofeedback accessible for daily use.
Professional neurofeedback systems utilize 10-20 system electrode caps with multiple channels and specialized software for a more advanced and customized approach. These systems allow for precise training at key locations such as C3, C4, Cz, Pz, and O1/O2, enabling tailored protocols for optimizing sleep architecture. Whether using a wearable headset for self-guided training or a clinical-grade system for professional supervision, neurofeedback provides an effective method to retrain brainwave patterns and improve sleep quality.
Below are the key neurofeedback protocols used for sleep management and their corresponding application sites based on the 10-20 system.
Neurofeedback protocols and application sites
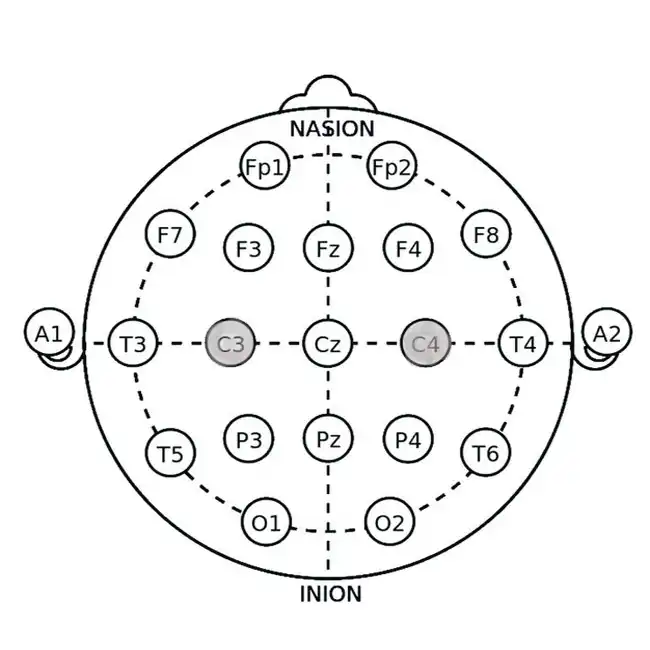
SMR (Sensorimotor Rhythm) Training
Application Site: C4 (right central region) or C3 (left central region)
Mechanism: SMR (12-15 Hz) is associated with calm, wakeful states and physical relaxation. Training SMR at C4 helps improve sleep onset and continuity by reducing nighttime arousal.
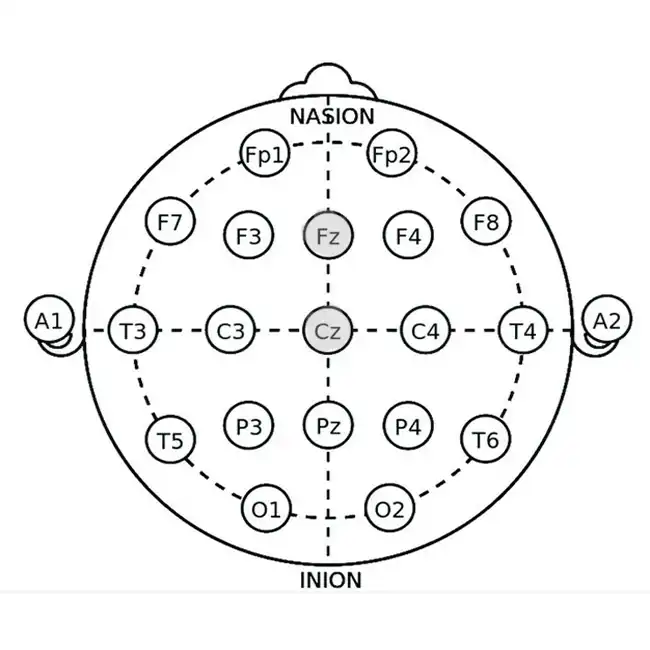
Theta-Beta Ratio Training
Application Site: Cz (central midline) or Fz (frontal midline)
Mechanism: A high theta (4-7 Hz) to beta (15-20 Hz) ratio is linked to difficulty maintaining sleep. Training involves reducing excessive theta and increasing beta to promote cognitive stability and improve sleep efficiency.
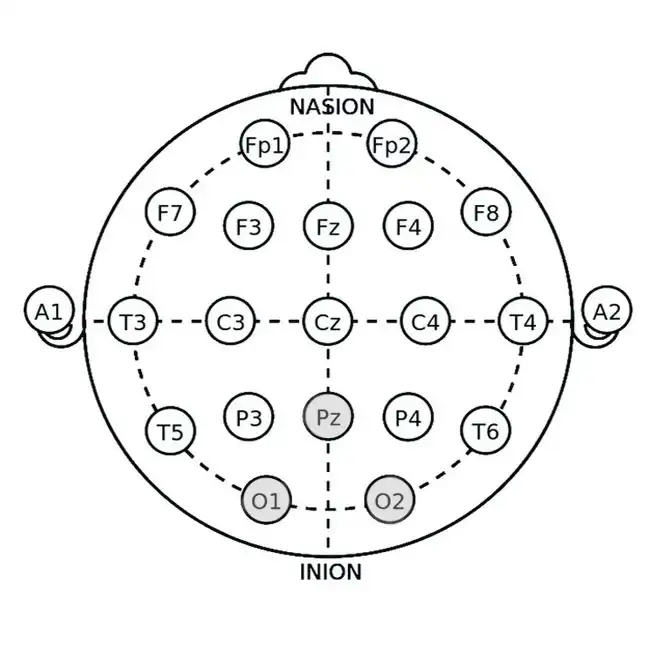
Delta Enhancement
Application Site: Pz (parietal midline) or O1/O2 (occipital regions)
Mechanism: Delta waves (0.5-4 Hz) dominate deep sleep. Enhancing delta activity improves slow-wave sleep, which is essential for physical and cognitive restoration.
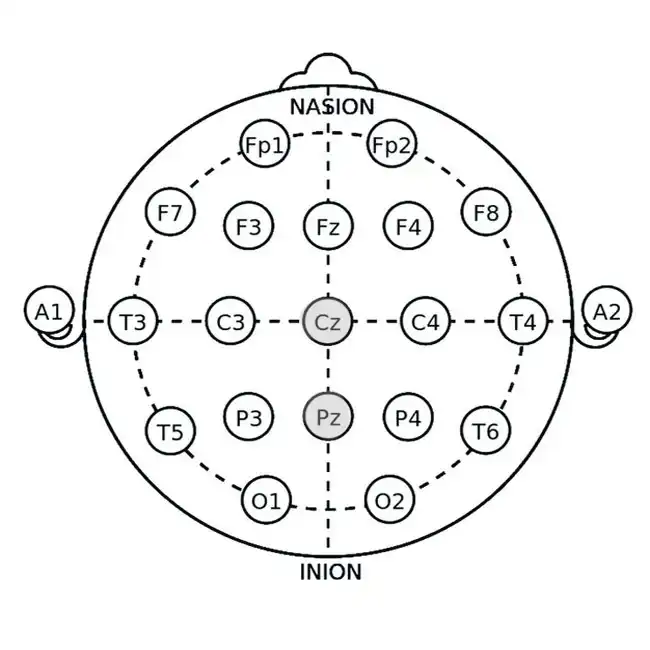
Alpha-Theta Training
Application Site: Pz (parietal midline) or Cz (central midline)
Mechanism: Alpha-theta training involves increasing theta (4-7 Hz) while maintaining stable alpha (8-12 Hz). This induces a hypnagogic state, easing sleep onset and reducing hyperarousal.
Frontal Inhibitory Training
Application Site: Fz (frontal midline) or FP1/FP2 (prefrontal cortex)
Mechanism: Excessive high beta (20-30 Hz) in the frontal cortex is linked to racing thoughts and anxiety, which interfere with sleep. Training reduces high beta and increases low-frequency activity, promoting relaxation.
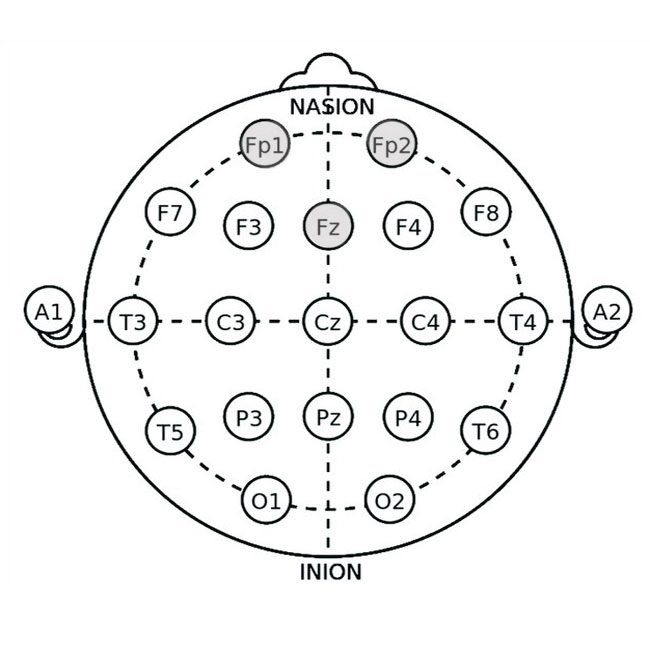
Neurofeedback provides
- Brainwave Monitoring:
Sensors placed on the scalp measure electrical activity in the brain, displaying it on a screen in real time. This allows individuals to see how their brainwaves change in response to different states, such as stress, focus, or relaxation. - Training for Relaxation:
Neurofeedback helps individuals learn to produce brainwave patterns linked to calmness and sleep, such as alpha and theta waves. By practicing techniques to increase these waves, you can train your brain to enter a relaxed state more easily, both at bedtime and during the night. - Addressing Hyperarousal: Many people with insomnia experience hyperarousal, where the brain remains overly active even at rest. Neurofeedback helps reduce this overactivity, allowing the brain to transition smoothly into sleep.
Benefits of Neurofeedback for Insomnia
- Improves sleep onset and reduces nighttime awakenings: by training the brain to relax, neurofeedback makes it easier to fall asleep.
- Helps individuals fall asleep naturally without medication: increased alpha and theta waves promote deeper sleep stages, enhancing overall sleep quality.
- Trains the brain to develop long-term healthy sleep patterns: unlike medications, neurofeedback offers lasting benefits by teaching the brain to self-regulate.
- Reduces overactive mental activity that causes sleep disturbances.
When combined with biofeedback, neurofeedback creates a powerful synergy for Total Sleep Management. Together, these techniques address both the physical and mental barriers to sleep, offering a comprehensive solution for insomnia relief.
In the next section, we will explore how CBT for sleep can further enhance sleep quality by addressing negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Using Binaural Beats for Brainwave Entrainment in Insomnia
Using binaural beats is a non-invasive and effective method to help regulate brainwave activity and improve sleep quality for individuals with insomnia. Binaural beats work by playing two slightly different frequencies in each ear, which the brain perceives as a third frequency corresponding to the difference between them. This process, known as brainwave entrainment, encourages the brain to synchronize with the target frequency, promoting relaxation and better sleep. For sleep induction, delta (0.5-4 Hz) and theta (4-7 Hz) binaural beats are commonly used, as they mimic the brain’s natural sleep rhythms, helping to facilitate deep, restorative rest.
Additionally, alpha (8-12 Hz) binaural beats can help calm an overactive mind before bedtime, reducing stress and anxiety that often contribute to insomnia. Listening to binaural beats through headphones for 15-30 minutes before sleep can help ease the transition into sleep and improve overall sleep quality.
CBT for Sleep: How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Improves Sleep
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT for sleep) is a highly effective, evidence-based approach that helps individuals change negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to managing insomnia. Unlike sleep medications, which offer only temporary relief, CBT for sleep provides long-term solutions by addressing the root causes of sleep disturbances.
How CBT for Sleep Works
CBT for sleep focuses on identifying and replacing unhelpful sleep-related thoughts and habits with healthier alternatives. The therapy consists of several key components:
- Cognitive Restructuring: This technique identifies negative thoughts about sleep (e.g., “I’ll never fall asleep”) and replaces them with positive, realistic beliefs.
- Sleep Restriction Therapy: Limits the time spent in bed to strengthen the brain’s association between the bed and sleep.
- Stimulus Control Therapy: Encourages habits like using the bed only for sleep and going to bed only when sleepy.
- Relaxation Training: Includes techniques like breathing exercises for sleeplessness, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided meditation.
- Sleep Hygiene Optimization: This approach focuses on improving bedtime routines, reducing blue light exposure, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.
Benefits of CBT for Sleep Management
- Helps retrain the brain for healthy sleep habits
- Reduces anxiety and stress linked to sleep difficulties
- Provides long-term relief from insomnia without medication
- Improves overall sleep management and daily energy levels
Incorporating CBT for sleep into your total sleep management plan allows you to develop sustainable habits for restful and refreshing sleep. In the next section, we will explore breathing exercises for sleeplessness, an easy yet powerful way to naturally promote relaxation before bedtime.
Breathing Exercises for Sleeplessness: A Simple Yet Effective Solution
Breathing exercises are a powerful, natural way to calm the mind and body, making falling and staying asleep easier. Many people struggling with managing sleep experience stress, anxiety, or an overactive mind at night. By practicing controlled breathing, you can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation and prepares the body for rest.sum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
How Breathing Affects Sleep Management
When we are stressed or anxious, our breathing tends to become shallow and rapid, signaling to the body that we are in a heightened state of alertness. Breathing exercises for sleeplessness help slow the heart rate, reduce muscle tension, and encourage the body to shift into a sleep-ready state.
Best Breathing Techniques for Sleep
- 4-7-8 Breathing Method
- Inhale deeply through your nose for 4 seconds.
- Hold your breath for 7 seconds.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for 8 seconds.
- Repeat this cycle 4-6 times.
- Benefit: Slows the heart rate and induces a deep relaxation response.

- Diaphragmatic (Belly) Breathing
- Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly.
- Inhale deeply through your nose, allowing your belly to expand.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth, feeling your belly deflate.
- Repeat for several minutes.
- Benefit: Reduces stress and promotes deep, restful breathing.
- Box Breathing (4-4-4-4 Method)
- Inhale for 4 seconds.
- Hold your breath for 4 seconds.
- Exhale for 4 seconds.
- Hold again for 4 seconds.
- Repeat for several cycles.
- Benefit: Balances oxygen levels and reduces anxiety before sleep.
- Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana)
- Close your right nostril with your thumb and inhale through the left nostril.
- Close your left nostril with your finger and exhale through the right nostril.
- Inhale through the right nostril, then switch and exhale through the left.
- Repeat for several cycles.
- Benefit: Clears the mind, balances energy, and promotes relaxation.
Benefits of Breathing Exercises for Sleep Management
- Reduces stress, anxiety, and overactive thinking at bedtime
- Lowers heart rate and blood pressure, preparing the body for sleep
- Enhances oxygen flow, promoting more profound, more restful sleep
- Complements other total sleep management techniques like biofeedback for sleep.
Incorporating these breathing exercises for sleeplessness into your bedtime routine can naturally improve your sleep quality.
The following section will explore some of the Best Biofeedback Devices for Sleep to help you start your journey to better rest.
Best Biofeedback Devices for Sleep
If you’re ready to take control of your sleep using biofeedback and neurofeedback, choosing the right device is a crucial first step. Here are some of the best biofeedback devices for sleep that can help you achieve Total Sleep Management and improve your sleep quality:
1. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Biofeedback Device
- Example Devices: HeartMath HRV Biofeedback Device for use at home
- How It Helps: The HRV biofeedback device tracks your heart rate variability, a key indicator of stress and relaxation. By practicing breathing exercises with real-time feedback, you can activate your body’s relaxation response and prepare for sleep.
2. EEG Neurofeedback Headsets
- Example Devices: Mendy Headband
- How It Helps: The Mendi Headband is an easy-to-use neurofeedback device, making it ideal for individuals unfamiliar with brainwave training. Unlike traditional EEG-based systems, Mendi uses functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) to measure blood flow and oxygenation in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), which plays a key role in stress regulation and cognitive control. By engaging in regular Mendi training, users can enhance self-regulation of brain activity, reduce stress, and improve relaxation—factors crucial for better sleep. Over time, this training helps balance brainwave activity, promoting a shift from high beta waves (linked to stress and overthinking) to more alpha and theta waves associated with calmness and sleep readiness.
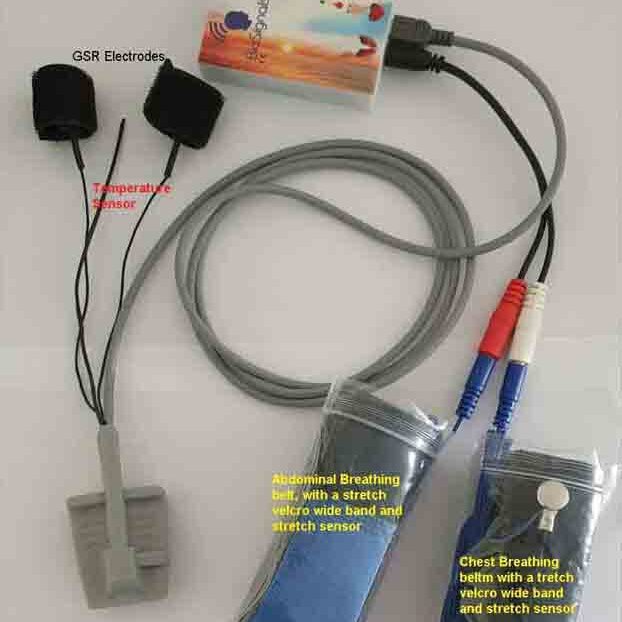
3. Respiration Biofeedback Devices
- Example Devices: BioSignals 5 sensor, Respiration Biofeedback Device for use at home.
- How It Helps: These devices focus on breathing patterns, guiding you to slow and deepen your breath. This can reduce stress and improve sleep onset.
4. Comprehensive Biofeedback Systems
- Example Devices: BioSignals Biofeedback 5 sensors Device
- How It Helps: These advanced systems combine multiple biofeedback modalities (e.g., HRV, breathing, muscle tension) to provide a holistic approach to sleep improvement.
Choosing the Right Device
When selecting a biofeedback device, consider the following:
- Ease of Use: Look for user-friendly devices with clear instructions.
- Features: Choose a device that targets your specific sleep issues (e.g., stress, brainwave regulation).
- Budget: Prices vary widely, so find a device that fits your budget while meeting your needs.
By incorporating one of these best biofeedback devices for sleep into your routine, you can take a proactive step toward Total Sleep Management and enjoy the benefits of improved sleep quality. In the next section, we’ll explore how to combine biofeedback with other Sleep Therapy techniques for even greater results.
Integrating Sleep Therapy: A Comprehensive Approach to Total Sleep Management
Now that we’ve explored breathing exercises for sleeplessness, it’s time to look at how various techniques, including biofeedback for sleep, neurofeedback for insomnia, and CBT for sleep, can be combined into a structured sleep therapy plan. By integrating multiple approaches, you can create a highly effective total sleep management strategy tailored to your specific sleep challenges.
The Key Components of an Effective Sleep Therapy Plan
A well-rounded approach to sleep management should focus on four key areas:
- Mind-Body Relaxation Techniques
- Breathing exercises for sleeplessness to calm the nervous system before bed.
- Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) to release physical tension.
- Guided meditation or mindfulness to quiet an overactive mind.
- Behavioral Sleep Training
- CBT for sleep to address negative thought patterns related to insomnia.
- Stimulus control techniques (e.g., using the bed only for sleep, maintaining a consistent bedtime routine).
- Sleep restriction therapy to increase sleep efficiency.
- Technology-Assisted Sleep Optimization
- Biofeedback for insomnia to improve self-regulation of stress and muscle tension.
- Neurofeedback for sleep to train the brain to enter restful sleep states more easily.
- Wearable sleep trackers to monitor and optimize sleep cycles.
- Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Sleep Health
- Optimizing your sleep environment (dark, cool, and quiet room).
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.
- Avoid caffeine and screens before bedtime.
- Engaging in regular physical activity to promote deeper sleep.
How to Personalize Your Sleep Therapy Plan
Everyone’s sleep struggles are different, so a personalized sleep therapy approach is key to success. Here’s how you can tailor your total sleep management strategy:
- For chronic insomnia: Focus on CBT for sleep, neurofeedback for insomnia, and structured relaxation techniques.
- For stress-related sleep issues: Prioritize breathing exercises for sleeplessness and biofeedback for insomnia to calm the nervous system.
- For difficulty falling asleep: Implement stimulus control therapy and breathing exercises to ease into sleep naturally.
- For frequent night awakenings: Use neurofeedback for sleep and optimize your sleep environment.
Combining these elements allows you to develop a total sleep management routine that promotes deep, restorative sleep every night.
Tips for Better Sleep: Beyond Biofeedback
While biofeedback and neurofeedback are powerful tools for improving sleep, incorporating simple yet effective habits into your daily routine can further enhance your Total Sleep Management plan. Here are some practical tips for better sleep that complement biofeedback techniques:
Establishing Healthy Sleep Habits
- Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule
- Go to bed and wake up simultaneously every day, even on weekends.
- This helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
- Wind down with calming activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing mindfulness meditation.
- Avoid stimulating activities before bed, such as working or watching intense TV shows.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment
- Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet.
- Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows to support restful sleep.
- Consider using blackout curtains, white noise machines, or earplugs if needed.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed
- The blue light emitted by phones, tablets, and computers can interfere with melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep.
- Try to avoid screens at least an hour before bedtime, or use blue light filters if necessary.
Supporting Sleep Through Lifestyle Choices
- Watch Your Diet and Hydration
- Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime, as they can disrupt sleep.
- If you’re hungry, choose a light snack, such as a banana or a small handful of nuts.
- Stay Active During the Day
- Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime.
- Activities like yoga or gentle stretching in the evening can help relax your body and mind.
- Manage Stress and Anxiety
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery.
- Use biofeedback tools to monitor and reduce stress levels throughout the day.
- Limit Naps
- If you need to nap, keep it short (20–30 minutes) and avoid napping late in the afternoon.
- Long or late naps can interfere with your ability to fall asleep at night.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed
- If insomnia persists despite your efforts, consider consulting a sleep specialist or therapist.
- They can help you explore additional treatments, such as CBT-I or advanced neurofeedback protocols.
By incorporating these tips for better sleep into your routine, you can amplify the benefits of biofeedback and neurofeedback, creating a well-rounded approach to Total Sleep Management. In the final section, we’ll summarize the key takeaways and encourage you to take the next step toward better sleep.
FAQ -Total Sleep Management & Sleep Therapy for Insomnia
Total Sleep Management is a comprehensive, holistic approach to overcoming insomnia by addressing the physical, mental, and environmental factors that disrupt sleep. It combines evidence-based techniques, such as sleep therapy, biofeedback, neurofeedback, and lifestyle changes, to create a personalized plan for achieving deep, restorative sleep.
Biofeedback for insomnia is a technique that utilizes sensors to provide real-time data on physiological functions, such as heart rate, muscle tension, and skin temperature. By learning to control these bodily responses, individuals can reduce stress and anxiety, activate the body’s relaxation response, and improve their ability to fall and stay asleep naturally, without the need for medication.
Chronic insomnia extends beyond fatigue and can lead to serious health issues, including impaired cognitive function (memory and concentration problems), an increased risk of heart disease, weight gain, diabetes, a weakened immune system, and even structural changes in the brain linked to conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Neurofeedback works by monitoring brainwave activity in real-time with EEG sensors. When the brain produces desirable sleep-promoting patterns (like alpha or SMR waves), the system provides positive feedback. Over time, this trains the brain to self-regulate and maintain these calm states, making it easier to fall asleep and reducing nighttime awakenings.
Binaural beats are an auditory illusion created when two slightly different frequencies are played in each ear. The brain perceives a third tone equal to the difference between them. This process, known as brainwave entrainment, can guide the brain into sleep-promoting states, such as theta and delta waves, thereby helping to calm an overactive mind and facilitate deeper sleep.
Conclusion: Achieve Deep, Restorative Sleep with Total Sleep Management
With the right tools and strategies, achieving restful, restorative sleep is within your reach. Total Sleep Management offers a comprehensive approach to overcoming insomnia by combining biofeedback, neurofeedback, and proven Sleep Therapy techniques. From learning to regulate your physiological responses with biofeedback to training your brain for relaxation through neurofeedback, these methods address both the physical and mental barriers to sleep.
By incorporating practical tips for better sleep, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, optimizing your sleep environment, and managing stress, you can create a holistic plan that works for you. Whether you’re exploring Biofeedback for Insomnia, seeking The Cure for Insomnia, or curious about the Best Biofeedback Devices for Sleep, the journey to better sleep starts with taking the first step.
Take control of your sleep today by integrating these strategies into your routine. Explore the best biofeedback devices for sleep, experiment with relaxation techniques, and commit to a Total Sleep Management plan that prioritizes your well-being. Remember, better sleep isn’t just a dream—it’s a skill you can learn and master.














Add a Comment