Neurofeedback Article Category
Our Neurofeedback Article Categories take you inside the world of brainwave monitoring and mental optimization. We show you how neurofeedback works and why it matters. Moreover, we explain how this science-backed method can strengthen both your mental health and your cognitive performance.
You will learn how neurofeedback helps manage ADHD, anxiety, depression, PTSD, and other stress-related conditions. Each article breaks complex ideas into simple steps. As a result, you understand precisely how neurofeedback trains your brain and supports long-term improvement.
We also explore different neurofeedback techniques and highlight the unique benefits of each method. In addition, we guide you in selecting the right neurofeedback system to achieve your goals. Whether you want better focus, calmer emotions, or stronger cognitive flexibility, you’ll find clear and practical advice.
Furthermore, we provide tips on how to use these systems safely and effectively at home. So, you discover what to expect, how to track progress, and how to adjust your training for maximum results.
By following the insights in our Neurofeedback Article Categories, you can unlock the full potential of neurofeedback. Thus, you gain greater clarity, balance, and control over your mental well-being.
FAQ: Neurofeedback Article Category
Neurofeedback is a type of brain training that uses real-time brainwave monitoring to teach your brain how to self-regulate. It helps improve focus, emotional balance, and cognitive performance.
Neurofeedback works by measuring your brainwave activity and presenting that information to you through visual or auditory feedback. When your brain produces healthier patterns, the system rewards you. Over time, your brain learns to repeat those patterns on its own.
Neurofeedback can help with ADHD, anxiety, depression, PTSD, sleep problems, and stress-related disorders. It also supports cognitive enhancement for focus, memory, and mental clarity.
Yes. Neurofeedback is a non-invasive and drug-free method. It trains your brain through feedback alone and does not stimulate it directly.
Most people notice changes within 5–10 sessions. However, long-term improvement usually requires 20–40 sessions, depending on the condition and individual goals.
Yes. Many FDA-cleared and research-based home neurofeedback systems are available. They offer guided training, easy setup, and progress tracking.
You need a neurofeedback headset or sensors, a compatible app or software, and a device such as a smartphone, tablet, or computer to run the training sessions.
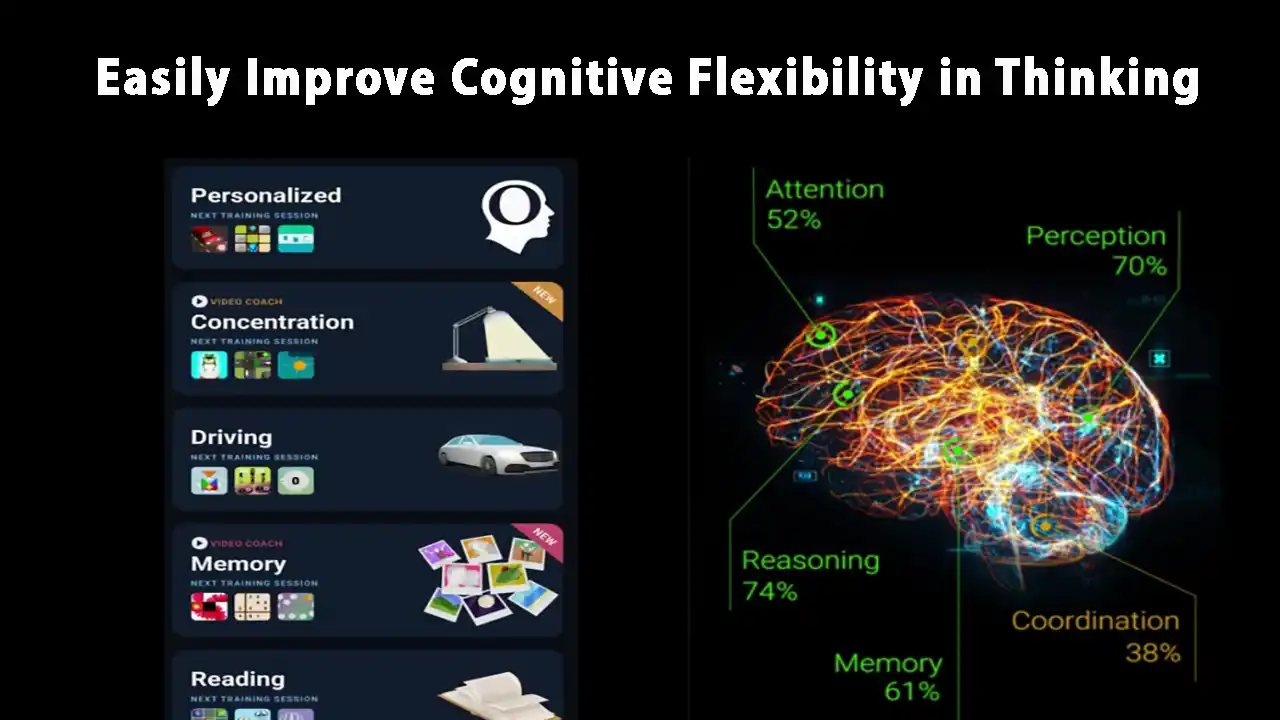
Boost Cognitive Flexibility in Thinking
Do you feel stuck thinking the same way, struggling to learn new skills, or forgetting important details? It’s not just frustration—it’s a sign your cognitive flexibility, cognitive learning, flexibility in thinking, and working memory could use a boost. Imagine being able to switch perspectives effortlessly, absorb new information faster, solve problems creatively, and remember key…
COVID and Mental Health: A Full Guide
The COVID-19 pandemic has permanently linked the issues of COVID and mental health in our collective consciousness. Many are now grappling with the lingering effects of COVID 19 stress, a confusing battle with COVID and brain fog, and persistent feelings of COVID and anxiety. Understanding the profound impact of COVID 19 and mental health is…
Overwhelmed at Work? Find Balance
Feeling overwhelmed at work can leave you drained, anxious, and struggling to keep up with daily demands. When tasks pile up, deadlines loom, or emotional pressure mounts, it’s easy to spiral into overwhelming stress or even overwhelming depression. But there’s a way to break free: learning how to stop getting overwhelmed and how to stop…
Stop Overthinking: Retrain Your Brain
Do you constantly feel trapped in a cycle of racing thoughts and mental fatigue? Understanding what causes overthinking is the first step toward regaining control of your mind. Many people struggle daily without realizing that effective overthinking treatment exists. From stress and decision paralysis to sleepless nights, the consequences are real—but they are not inevitable.…
MS and Depression: What You Can Do
Living with multiple sclerosis (MS) is challenging enough, but when depression in MS adds another layer of struggle, it can feel overwhelming. Studies show that nearly 50% of people with MS experience depression at some point—a rate much higher than the general population. The connection between MS and depression isn’t just emotional; it’s neurological, with…
How QEEG Brain Mapping Therapy Works
Ever wondered why traditional treatments don’t always work for ADHD, anxiety, or brain fog? QEEG Brain Mapping offers a revolutionary approach—using advanced neuroscience to decode your unique brainwave patterns. Unlike guesswork-based methods, Brain Mapping Therapy pinpoints the exact areas of dysregulation, transforming how mental health and cognitive performance are optimized. Whether you’re seeking answers for…
Fear Therapy: Cure Phobias Fast
Do you feel paralyzed by irrational fears or phobias that control your life? Fear therapy offers a revolutionary, science-backed solution that goes beyond temporary fixes—rewiring your brain’s fear response for lasting freedom. Unlike traditional approaches, modern fear therapy combines proven techniques like exposure therapy with cutting-edge biofeedback and neurofeedback, giving you real-time control over anxiety…
Therapy for Burnout: Prevent & Recharge
Burnout is more than just feeling tired or stressed — it’s a state of emotional, mental, and physical exhaustion caused by prolonged stress and overwork. In this guide, we explore therapy for burnout, offering practical solutions for both prevention and recovery. Understanding the right strategies can make a big difference if you’re already feeling overwhelmed…
Biofeedback for Tinnitus: Does it work?
Tinnitus is not just an annoying ringing or buzzing in the ears — for many people, it reflects deeper issues involving stress, brain activity, and nervous system imbalances. This is precisely where biofeedback for tinnitus becomes a valuable tool. Unlike conventional therapies, biofeedback for tinnitus focuses on helping individuals regain control over the body’s stress…
Total Sleep Management for Insomnia
Struggling with restless nights and constant fatigue? You’re not alone. Millions of people face sleep disturbances, but the good news is that total sleep management offers effective solutions. By combining sleep therapy, biofeedback for insomnia, and neurofeedback for sleep, you can regain control over your sleep patterns. Techniques such as breathing exercises for sleeplessness and…
Emotional Balance vs Emotional Imbalance
Achieving emotional balance is essential for overall well-being, yet many people struggle with emotional imbalance due to stress, lifestyle, and daily challenges. When emotions spiral out of control, they can negatively impact decision-making, relationships, and mental health. However, mastering self-management emotional intelligence allows individuals to regulate their emotional responses, build resilience, and maintain inner stability.…
Women’s Wellness Retreat At Home: Tricks
Women’s Wellness Retreat At Home: Tricks Transform your home into a women’s wellness retreat and experience relaxation, stress relief, and improved well-being. A women’s mental health retreat doesn’t have to involve expensive travel—you can create a peaceful and restorative space right at home. Many wellness retreats for women focus on mindfulness, relaxation, and self-care, and…
Best Biofeedback for Pain Relief
Biofeedback and pain management are gaining recognition as a highly effective natural approach to treating various types of pain. Unlike traditional pain relief methods that often rely on medication, biofeedback pain management empowers individuals to take control of their physiological responses, helping to reduce pain and improve overall well-being. By using biofeedback for pain management,…
Therapy for Dyslexia-Innovative Approach
Dyslexia is a complex learning disorder that affects individuals’ ability to read, write, and process language effectively. While traditional methods like speech therapy have provided support for years, innovative approaches are now transforming how we approach therapy for dyslexia. Cutting-edge technologies like biofeedback and neurofeedback offer non-invasive solutions directly targeting the brain’s functioning to enhance…
Mental Performance Training: NeuroVizr
Maintaining mental clarity, focus, and emotional balance is more important in today’s fast-paced world. Mental performance training offers a cutting-edge approach to improving brain function, and the NeuroVIZR device takes this concept to the next level. NeuroVIZR stimulates brain activity, promotes neuroplasticity, and enhances cognitive flexibility by combining light and sound therapy with innovative blinking…
Mendi Headset for Peak Performance
Achieving peak mental performance is essential for success in today’s fast-paced world, and the Mendi Headset offers a cutting-edge solution. This innovative brain-training device uses neurofeedback to help improve focus, enhance mental clarity, and reduce stress. Whether you’re an athlete, professional, or student, the Mendi Headset empowers you to unlock your full potential and reach…
Neurofeedback autism management
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. As the prevalence of autism continues to rise, with recent estimates suggesting that 1 in 54 children in the United States is diagnosed with ASD, there is an increasing need for effective management strategies. Traditional treatment…
Neurofeedback for PTSD. How Does It Help
In the realm of mental health care, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) stands as a formidable challenge, affecting millions worldwide with its enduring symptoms and complex neurobiological underpinnings. In recent years, a promising avenue for addressing this condition has emerged in the form of Neurofeedback for PTSD treatment. By harnessing the brain’s electrical activity, EEG Biofeedback…
Mini Stroke Recovery and Biofeedback
Mini strokes, also known as transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), are brief episodes of neurological dysfunction caused by a temporary interruption of blood flow to the brain. While they may not cause permanent damage themselves, TIAs are often warning signs of a potential future stroke. Therefore, understanding the process of mini stroke recovery is crucial for…
Neurofeedback for OCD is the Best Option
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) presents a complex interplay of intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors, often disrupting daily life and causing significant distress. Traditional treatments, such as medication and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), are usually effective. However, some individuals experience only limited relief or face unwanted side effects. In recent years, a promising alternative has emerged: neurofeedback for…
Nomophobia treatment. Biofeedback.
In the digital era, the pervasive phenomenon of Nomophobia, or the fear of being without one’s mobile phone, has given rise to a pressing need for effective interventions. Among the innovative approaches, Nomophobia treatment through biofeedback emerges as a promising solution. Leveraging advanced technology, Biofeedback offers a tailored and dynamic method to address the escalating…
Biofeedback speech therapy for stuttering
Stuttering is an action-induced speech disorder with involuntary, audible, or silent repetitions or prolongations in the utterance of short speech elements (sounds, syllables) and words. Stuttering typically begins in childhood and may persist into adulthood. It can vary in severity, with some individuals experiencing only mild stuttering while others may have more pronounced difficulties speaking…
Neurofeedback for Tourette Syndrome
Tourette Syndrome and other tics disorders affect millions of people worldwide, often presenting significant challenges in daily life. While traditional treatments for Tourette’s focus on managing symptoms with medication or behavioral therapy, a growing body of research highlights the potential of neurofeedback for Tourette Syndrome as a non-invasive and effective alternative. This innovative approach targets…
COVID 19 – How to Cope with Stress, Anxiety and Fears
The outbreak of diseases, such as the coronavirus disease 2019 – COVID 19, may be stressful for all of us. Fear and anxiety about a COVID 19 disease and quarantine stress can be overwhelming and cause strong emotions in adults and children. Stress is a natural response that can be both useful and harmful. A…
COVID 19 –“Stay At Home”. How to Stay Mentally Healthy In COVID 19 Quarantine
A recent review of research, published in The Lancet, found that COVID 19 quarantine is linked with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms, confusion, and anger, with some research suggesting these effects are long-lasting. Given that the coronavirus crisis is likely to be with us for some time, the mental health implications can’t be dismissed. Don’t…
Neurofeedback for depression. Protocols
Depression is one of the most common mental disorders and the number one cause of disability worldwide. Traditionally, depression has been treated with therapy and medication, both of which have limitations. Even with medication, countless depression sufferers continue to struggle. Medication doesn’t teach the brain how to get out of the unhealthy brain pattern of…
Neurofeedback for Migraines. Neurofeedback Protocols.
Migraine is a debilitating illness with long-term consequences for the brain. Research has explored the origins of migraine and suggests that it is an electrical phenomenon initiated in the occipital cortex. Assessments of the brain using the EEG have found abnormal electrical activity supporting this idea. Neurofeedback for migraines is a treatment targeting electrical firing…
Neurofeedback for ADHD Management
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) has become one of the most common neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders of childhood (3% to 7% of school-age children) that persists into adolescence and adulthood in 40-60% of cases. ADHD treatment’s main strategies are the use of pharmacological therapy, omega-3, multivitamins, and multi-minerals. Neurofeedback for ADHD management is a non-pharmacological intervention…
Neurofeedback for Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are some of the most prevalent mental health challenges, often severely impacting a person’s ability to live a fulfilling life. Neurofeedback for anxiety offers a natural and effective approach to managing these disorders by reshaping and rewiring brain activity rather than simply masking symptoms. As one of the best treatment methods, neurofeedback therapy…
Dyscalculia Treatment – Neurofeedback
While there are a few general learning difficulties/disabilities that can impact mathematical performance, there is only one identified math-specific learning disability. This disability is known as dyscalculia, which refers to problems with specific mathematical concepts and calculations. However, today, there is considerable scientific evidence on the effectiveness of Neurofeedback in treating dyscalculia. Dyscalculia learning disability…